Egress Private Service Connect Endpoint Setup: Elasticsearch on Google Cloud for Confluent Cloud
This topic presents the steps for configuring the Elasticsearch Sink V2 connector in Confluent Cloud using Egress Private Service Connect on Google Cloud.
Prerequisites
The following is a list of prerequisites for configuring the Elasticsearch Sink V2 connector with an Egress Private Service endpoint:
In Confluent Cloud, one of the following cluster types is set up with the specified network resource:
A Dedicated cluster with a Confluent Cloud network.
For the steps to create a Confluent Cloud network, see Create a Confluent Cloud network on Google Cloud. The Connection type of the network needs to be Private Service Connect Access.
A Enterprise cluster with a network gateway
For the steps to create a gateway, see Use Google Cloud Private Service Connect for Dedicated Clusters on Confluent Cloud.
An Elasticsearch Cloud deployment is running in Google Cloud within the same region and cloud as the Confluent Cloud network resource.
Confluent Cloud network (Dedicated or Serverless Egress Gateway) setup within same region and cloud as Elasticsearch.
Step 1. Obtain Service attachment URI and Private zone DNS name from Elasticsearch
Consult the Elastic documentation to capture the following values for your region:
Service attachment URI: Use this as the PrivateLink service name in Confluent Cloud.
Private zone DNS name: Use this as the Domain when creating the DNS record in Confluent Cloud.
Step 2. Create an Egress PrivateLink Endpoint
In the Network management page or tab of the desired Confluent Cloud environment, click the Confluent Cloud network you want to add the PrivateLink endpoint to. The Connection Type of the network should be PrivateLink Access.
Click Create endpoint in the Egress connections tab.
Click the service you want to connect to, specifically, Elasticsearch. Select Other if you do not see the specific service.
Follow the steps below to specify the following field values:
SERVICE: Name of service connecting to - Elasticsearch.
Endpoint Name: Name of the PrivateLink endpoint.
PrivateLink service name: The name of the PrivateLink service you retrieved Step 1. Obtain Service attachment URI and Private zone DNS name from Elasticsearch.
Create an endpoint with high availability: Select this checkbox to deploy an endpoint with high availability.
Click Create to create the PrivateLink endpoint.
If there are additional steps for the specific target service, follow the prompt to complete the tasks, and then click Finish.
In the Network management page or tab of the desired Confluent Cloud environment, click the For serverless products tab.
Click the gateway to which you want to add the PrivateLink endpoint.
In the Access points tab, click Add access point.
Click the service you want to connect to, specifically, Elasticsearch. Select Other if you do not see the specific service.
Follow the steps below to specify the following field values:
Access point name: Name of the PrivateLink endpoint.
Create an endpoint with high availability: Select this checkbox to deploy an endpoint with high availability.
PrivateLink service name: The name of the PrivateLink service you retrieved in Step 1. Obtain Service attachment URI and Private zone DNS name from Elasticsearch.
Click Create access point to create the PrivateLink endpoint.
If there are additional steps for the specific target service, follow the prompt to complete the tasks, and click Finish.
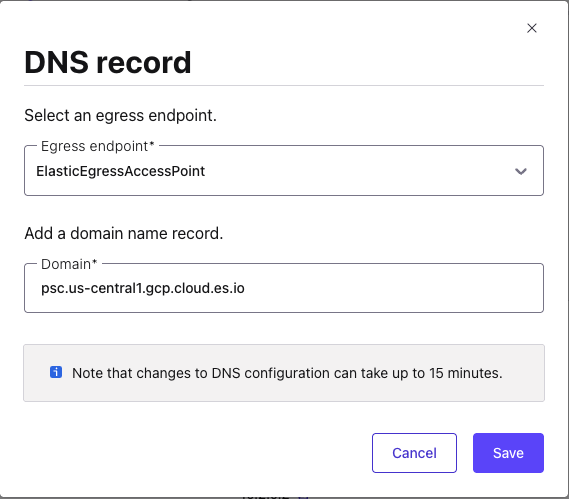
Step 3. Create a DNS record
When the PrivateLink endpoint status transitions to Ready, in the DNS tab, click Create record on the associated PrivateLink endpoint.
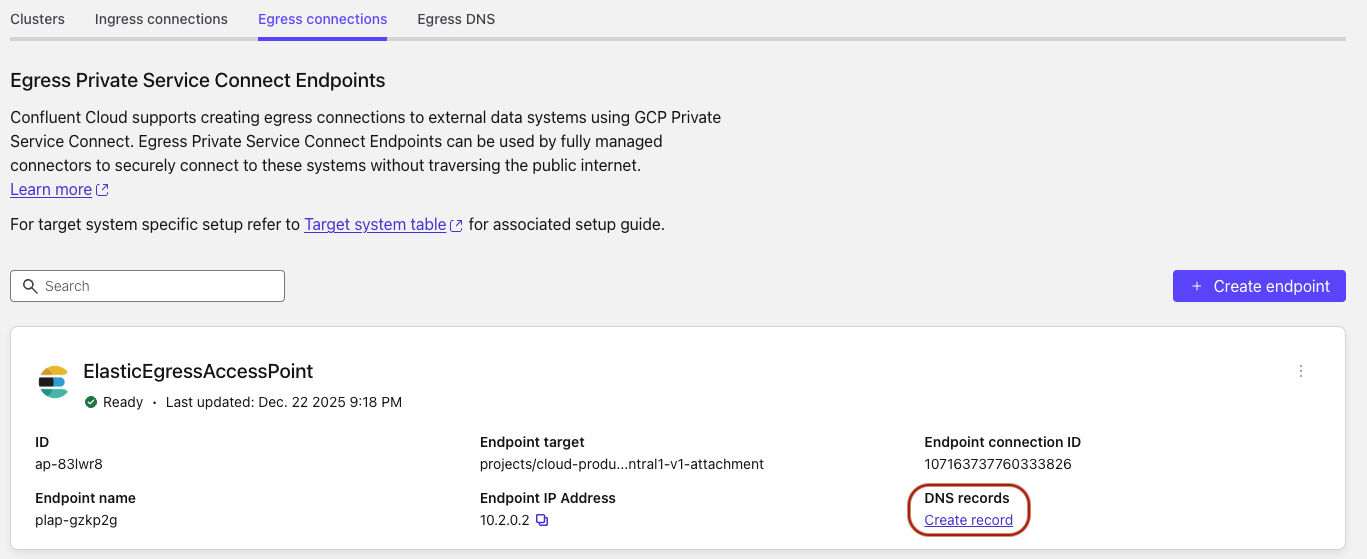
Specify the following, and click Save.
Access point: Select the PrivateLink endpoint you created in Step 2. Create an Egress PrivateLink Endpoint.
Domain: Enter the Private zone DNS name retrieved in Step 1. Obtain Service attachment URI and Private zone DNS name from Elasticsearch.
In the Network Management tab of your environment, click the For serverless products tab, and click the Confluent Cloud gateway.
In the DNS tab, click Create DNS record.
Specify the following field values:
Access point: Select the Private Service Connect endpoint you created in Step 2. Create an Egress PrivateLink Endpoint.
Domain: Enter the Private zone DNS name retrieved in Step 1. Obtain Service attachment URI and Private zone DNS name from Elasticsearch.
Click Save.
Step 4. Add Private Endpoint within Elasticsearch Deployment
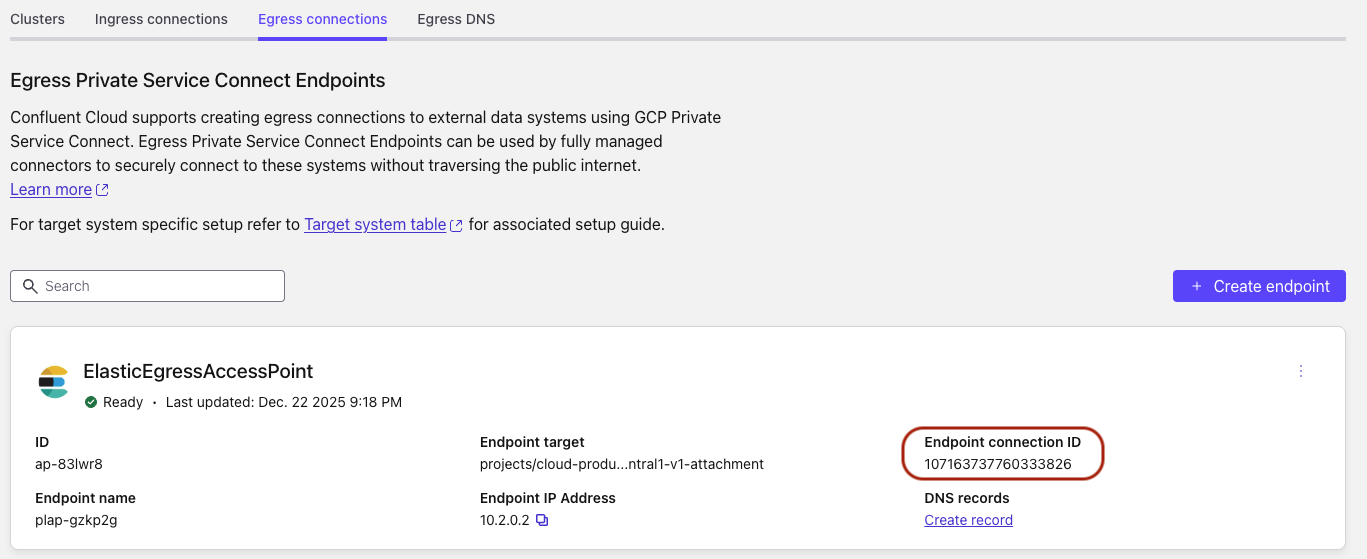
In the Confluent Cloud console, click the Egress connections tab and copy the Endpoint connection ID.
Log in to the Elastic Cloud Console.
From any deployment or project on the home page, select Manage.
From the left navigation menu, select Access and security > Network security.
Click the Create dropdown and select Private connection.
Specify the following field values to create the policy:
Resource Type: Select hosted deployments.
Cloud provider and region: Select the cloud provider and region for the private connection, matching your Confluent Cloud cluster and network region.
Connectivity: Select Privatelink.
VPC Filter: Enter the Endpoint connection ID retrieved in the previous step.
Apply to resources: Under Apply to resources, associate the new private connection policy to your deployment. If you specified a VPC filter, then after you associate the filter with a deployment, it starts filtering traffic.
Click Create.
To create a new private connection policy in the Elastic Cloud Console, you can also follow Elasticsearch documentation.
Step 5. Create the Elasticsearch Sink V2 connector
While creating the connector, use the following URL structure for the Connection URI on the authentication page. This URL uses the endpoint information from your Elastic deployment and your registered private hosted zone domain name. For more information, see the Elasticsearch GCP Private Service Connect documentation.
https://{{alias}}.{{product}}.{{private_hosted_zone_domain_name}}For example:
https://my-deployment-d53192.es.psc.asia-southeast1.gcp.elastic-cloud.com
Note
You can use either 443 or 9243 as a port.
You can also connect to the cluster using the Elasticsearch cluster ID, for example,
https://6b111580caaa4a9e84b18ec7c600155e.psc.asia-southeast1.gcp.elastic-cloud.com
See the Elasticsearch Sink V2 connector documentation for the steps to create the sink connector in Confluent Cloud.