MariaDB CDC Source (Debezium) Connector for Confluent Cloud
The fully-managed MariaDB Change Data Capture (CDC) Source (Debezium) connector for Confluent Cloud can obtain a snapshot of the existing data in a MariaDB database, then monitor and record all subsequent row-level changes. The connector supports AVRO, JSON Schema, and PROTOBUF output data formats. All events for each table are recorded in a separate Apache Kafka® topic in Confluent Cloud, capturing row-level changes (inserts, updates, and deletes) as event streams. These events can then be easily consumed by applications and services.
Note
If you require private networking for fully-managed connectors, make sure to set up the proper networking beforehand. For more information, see Manage Networking for Confluent Cloud Connectors.
Features
The MariaDB CDC Source (Debezium) connector provides the following features:
Topics created automatically: The connector automatically creates Kafka topics using the naming convention:
<topic.prefix>.<schemaName>.<tableName>. The tables are created with the properties:topic.creation.default.partitions=1andtopic.creation.default.replication.factor=3. For more information, see Maximum message size.Database authentication: Uses password authentication.
SSL support: Supports SSL encryption when configured to establish an encrypted connection to the MariaDB server.
Databases included and Databases excluded: Sets whether a database is or is not monitored for change captures. By default, the connector monitors every database on the server.
Tables included and Tables excluded: Sets whether a table is or is not monitored for changes. By default, the connector monitors every non-system table.
Tombstones on delete: Sets whether a tombstone event is generated after a delete event. Default is
true.Output formats: The connector supports AVRO, JSON_SR, or PROTOBUF output Kafka record value format. It supports AVRO, JSON_SR, STRING or PROTOBUF output record key format. Schema Registry must be enabled to use a Schema Registry-based format (for example, AVRO, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or PROTOBUF). See Schema Registry Enabled Environments for additional information.
Client-side encryption (CSFLE and CSPE) support: The connector supports CSFLE and CSPE for sensitive data. For more information about CSFLE or CSPE setup, see the Manage CSFLE or CSPE for connectors.
For more information and examples to use with the Confluent Cloud API for Connect, see the Confluent Cloud API for Connect Usage Examples section.
Supported database versions
The MariaDB CDC Source (Debezium) connector is compatible with the following MariaDB version: 11.4.x
Limitations
Be sure to review the following information.
For connector limitations, see MariaDB CDC Source (Debezium) Connector limitations.
If you plan to use one or more Single Message Transforms (SMTs), see SMT Limitations.
If you plan to use Confluent Cloud Schema Registry, see Schema Registry Enabled Environments.
Maximum message size
This connector creates topics automatically. When it creates topics, the internal connector configuration property max.message.bytes is set to the following:
Basic cluster:
8 MBStandard cluster:
8 MBEnterprise cluster:
8 MBDedicated cluster:
20 MB
For more information about Confluent Cloud clusters, see Kafka Cluster Types in Confluent Cloud.
Log retention during snapshot
When launched, the CDC connector creates a snapshot of the existing data in the database to capture the nominated tables. To do this, the connector executes a “SELECT *” statement. Completing the snapshot can take a while if one or more of the nominated tables is very large.
During the snapshot process, the database server must retain transaction logs so that when the snapshot is complete, the CDC connector can start processing database changes that have completed since the snapshot process began. These logs are retained in a binary log (binlog) on the database server.
If one or more of the tables are very large, the snapshot process could run longer than the binlog retention time set on the database server (that is, expire_logs_days = <number-of-days>). To capture very large tables, you should temporarily retain the binlog for longer than normal by increasing the expire_logs_days value.
Manage custom offsets
You can manage the offsets for this connector. Offsets provide information on the point in the system from which the connector is accessing data. For more information, see Manage Offsets for Fully-Managed Connectors in Confluent Cloud.
To manage offsets:
Manage offsets using Confluent Cloud APIs. For more information, see Confluent Cloud API reference.
To get the current offset, make a GET request that specifies the environment, Kafka cluster, and connector name.
GET /connect/v1/environments/{environment_id}/clusters/{kafka_cluster_id}/connectors/{connector_name}/offsets
Host: https://api.confluent.cloud
Response:
Successful calls return HTTP 200 with a JSON payload that describes the offset.
{
"id": "lcc-example123",
"name": "{connector_name}",
"offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"server": "offset.test"
},
"offset": {
"event": 2,
"file": "mysqld-bin.000006",
"gtids": "0-1-7903",
"pos": 5058223,
"row": 1,
"server_id": 1,
"ts_sec": 1750318086
}
}
],
"metadata": {
"observed_at": "2024-03-28T17:57:48.139635200Z"
}
}
Responses include the following information:
The position of latest offset.
The observed time of the offset in the metadata portion of the payload. The
observed_attime indicates a snapshot in time for when the API retrieved the offset. A running connector is always updating its offsets. Useobserved_atto get a sense for the gap between real time and the time at which the request was made. By default, offsets are observed every minute. Calling get repeatedly will fetch more recently observed offsets.The
gtids(global transaction identifier) of the latest offset.Information about the connector.
Ensure that the offsets provided in the POST request are valid. To find valid offsets, check the binlog files in your database.
Caution
Providing an arbitrary offset can stop the connector streaming with an exception: An exception occurredin the change event producer. This connector will be stopped.
POST /connect/v1/environments/{environment_id}/clusters/{kafka_cluster_id}/connectors/{connector_name}/offsets/request
Host: https://api.confluent.cloud
{
"type": "PATCH",
"offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"server": "server_01"
},
"offset": {
"event": 2,
"file": "mariadb-bin.000006",
"gtids": "0-1-7902",
"pos": 1423,
"row": 1
}
}
]
}
Considerations:
You can only make one offset change at a time for a given connector.
This is an asynchronous request. To check the status of this request, you must use the check offset status API. For more information, see Get the status of an offset request.
For source connectors, the connector attempts to read from the position defined by the requested offsets.
Response:
Successful calls return HTTP 202 Accepted with a JSON payload that describes the offset.
{
"id": "lcc-example123",
"name": "{connector_name}",
"offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"server": "server_01"
},
"offset": {
"event": 2,
"file": "mariadb-bin.000598",
"gtids": "0-1-7902",
"pos": 1423,
"row": 1
}
}
],
"requested_at": "2024-03-28T17:58:45.606796307Z",
"type": "PATCH"
}
Responses include the following information:
The requested position of the offsets in the source.
The time of the request to update the offset.
Information about the connector.
To delete the offset, make a POST request that specifies the environment, Kafka cluster, and connector name. Include a JSON payload that specifies the delete type.
POST /connect/v1/environments/{environment_id}/clusters/{kafka_cluster_id}/connectors/{connector_name}/offsets/request
Host: https://api.confluent.cloud
{
"type": "DELETE"
}
Considerations:
Delete requests delete the offset for the provided partition and reset to the base state. A delete request is as if you created a fresh new connector.
This is an asynchronous request. To check the status of this request, you must use the check offset status API. For more information, see Get the status of an offset request.
Do not issue delete and patch requests at the same time.
For source connectors, the connector attempts to read from the position defined in the base state.
Response:
Successful calls return HTTP 202 Accepted with a JSON payload that describes the result.
{
"id": "lcc-example123",
"name": "{connector_name}",
"offsets": [],
"requested_at": "2024-03-28T17:59:45.606796307Z",
"type": "DELETE"
}
Responses include the following information:
Empty offsets.
The time of the request to delete the offset.
Information about Kafka cluster and connector.
The type of request.
To get the status of a previous offset request, make a GET request that specifies the environment, Kafka cluster, and connector name.
GET /connect/v1/environments/{environment_id}/clusters/{kafka_cluster_id}/connectors/{connector_name}/offsets/request/status
Host: https://api.confluent.cloud
Considerations:
The status endpoint always shows the status of the most recent PATCH/DELETE operation.
Response:
Successful calls return HTTP 200 with a JSON payload that describes the result. The following is an example of an applied patch.
{
"request": {
"id": "lcc-example123",
"name": "{connector_name}",
"offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"server": "server_01"
},
"offset": {
"event": 2,
"file": "mariadb-bin.000598",
"gtids": "0-1-7902",
"pos": 1423,
"row": 1
}
}
],
"requested_at": "2024-03-28T17:58:45.606796307Z",
"type": "PATCH"
},
"status": {
"phase": "APPLIED",
"message": "The Connect framework-managed offsets for this connector have been altered successfully. However, if this connector manages offsets externally, they will need to be manually altered in the system that the connector uses."
},
"previous_offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"server": "server_01"
},
"offset": {
"event": 2,
"file": "mariadb-bin.000598",
"gtids": "0-1-7903",
"pos": 2326,
"row": 1
}
}
],
"applied_at": "2024-03-28T17:58:48.079141883Z"
}
Responses include the following information:
The original request, including the time it was made.
The status of the request: applied, pending, or failed.
The time you issued the status request.
The previous offsets. These are the offsets that the connector last updated prior to updating the offsets. Use these to try to restore the state of your connector if a patch update causes your connector to fail or to return a connector to its previous state after rolling back.
JSON payload
The table below offers a description of the unique fields in the JSON payload for managing offsets of the MariaDB Change Data Capture (CDC) Source connector.
Field | Definition | Required/Optional |
|---|---|---|
| The number of rows and events to skip while starting from this file and position. Use | Optional |
| The file from the last processed binlog. Use | Required |
| The position from the last processed binlog. Use | Required |
| The number of rows and events to skip while starting from this file and position. Use | Optional |
| The id of the server from which the event originated. For more information, see MariaDB documentation. | Optional |
| Mostly null, provided only when | Optional |
| The timestamp at which the event at this pos was executed in the database. | Optional |
Important
Do not reset the offset to an arbitrary number. Use only offsets found in the binlog file. To find offsets in a binlog file, use the MariaDB binlog utility. Offsets appear in this format: # at <offset>.
Quick Start
Use this quick start to get up and running with the MariaDB CDC Source (Debezium) connector. The quick start provides the basics of selecting the connector and configuring it to obtain a snapshot of the existing data in a MariaDB database and then monitoring and recording all subsequent row-level changes.
- Prerequisites
Authorized access to a Confluent Cloud cluster on Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure (Azure), or Google Cloud.
The Confluent CLI installed and configured for the cluster. See Install the Confluent CLI.
Schema Registry must be enabled to use a Schema Registry-based format (for example, Avro, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or Protobuf). See Schema Registry Enabled Environments for additional information.
Public access may be required for your database. See Manage Networking for Confluent Cloud Connectors for details. The example below shows the AWS Management Console when setting up a MariaDB database.
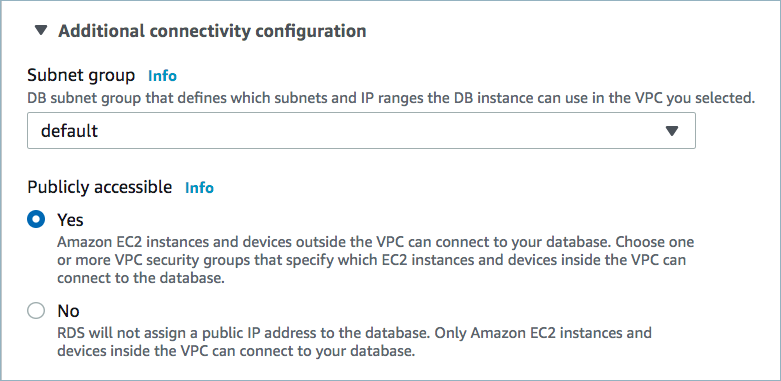
Public access enabled
For networking considerations, see Networking and DNS. To use a set of public egress IP addresses, see Public Egress IP Addresses for Confluent Cloud Connectors. The example below shows the AWS Management Console when setting up security group rules for the VPC.
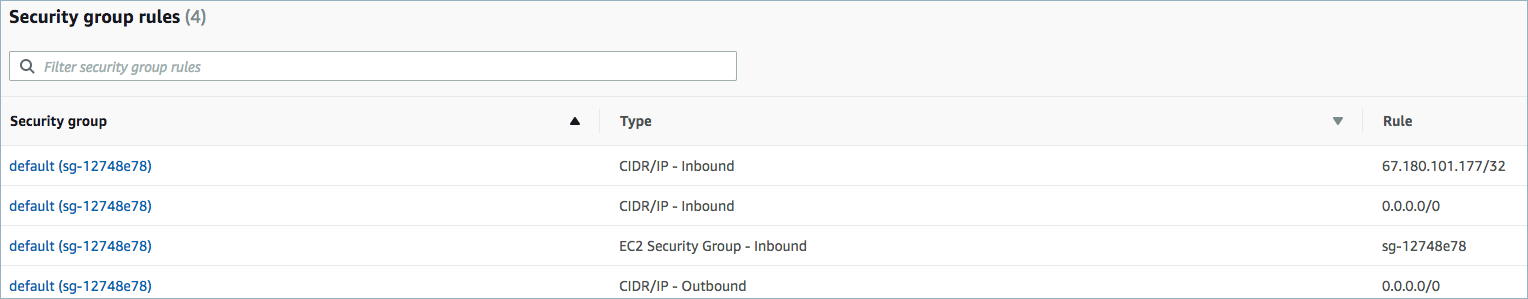
Open inbound traffic
Note
See your specific cloud platform documentation for how to configure security rules for your VPC.
Kafka cluster credentials. The following lists the different ways you can provide credentials.
Enter an existing service account resource ID.
Create a Confluent Cloud service account for the connector. Make sure to review the ACL entries required in the service account documentation. Some connectors have specific ACL requirements.
Create a Confluent Cloud API key and secret. To create a key and secret, you can use confluent api-key create or you can autogenerate the API key and secret directly in the Cloud Console when setting up the connector.
Update the following settings for the MariaDB database.
Turn on backup for the database.
Create a new parameter group and set the following parameters:
binlog_format=ROW binlog_row_image=full
Apply the new parameter group to the database.
Reboot the database.
The following example screens are from Amazon RDS:


Using the Confluent Cloud Console
Step 1: Launch your Confluent Cloud cluster
To create and launch a Kafka cluster in Confluent Cloud, see Create a kafka cluster in Confluent Cloud.
Step 2: Add a connector
In the left navigation menu, click Connectors. If you already have connectors in your cluster, click + Add connector.
Step 3: Select your connector
Click the MariaDB CDC Source connector card.

Step 4: Enter the connector details
Note
Make sure you have all your prerequisites completed.
At the MariaDB CDC Source (Debezium) Connector screen, complete the following:
Select the way you want to provide Kafka Cluster credentials. You can choose one of the following options:
My account: This setting allows your connector to globally access everything that you have access to. With a user account, the connector uses an API key and secret to access the Kafka cluster. This option is not recommended for production.
Service account: This setting limits the access for your connector by using a service account. This option is recommended for production.
Use an existing API key: This setting allows you to specify an API key and a secret pair. You can use an existing pair or create a new one. This method is not recommended for production environments.
Note
Freight clusters support only service accounts for Kafka authentication.
Click Continue.
Configure the authentication properties:
How should we connect to your database?
Database hostname: The IP address or hostname of the MariaDB database server.
Database port: The port number used to connect to the MariaDB database server.
Database username: The name of the MariaDB database user connecting to the MariaDB database.
Database password: Password for the MariaDB database user that has the required authorization.
SSL mode: Specify whether to use an encrypted connection to the MariaDB server. Possible settings are:
disableandtrust. Note that it does not perform certificate or hostname verification.disable(default): specifies the use of an unencrypted connection.trust: establishes an encrypted connection or fails if one cannot be made for any reason.
SSL Keystore: Path to the SSL keystore file for MariaDB connection. This property is only required when you enable SSL certificate verification (
verify-caorverify-fullmodes)SSL Keystore Password: Password for the SSL keystore file for MariaDB connection. This property is only required when you enable SSL certificate verification (
verify-caorverify-fullmodes)SSL Truststore: Path to the SSL truststore file for MariaDB connection. This property is only required when you enable SSL certificate verification (
verify-caorverify-fullmodes)SSL Truststore Password: Password for the SSL truststore file for MariaDB connection. This property is only required when you enable SSL certificate verification (
verify-caorverify-fullmodes)
Click Continue.
Output messages
Select output record value format: Sets the output Kafka record value format Valid entries are AVRO, JSON_SR, STRING or PROTOBUF. Note that you need to have Schema Registry configured to use a Schema Registry-based format (for example, AVRO, JSON_SR, or PROTOBUF). For more information, see Schema Registry Enabled Environments.
Output Kafka record key format: Sets the output Kafka record key format. Valid entries are AVRO, JSON_SR, PROTOBUF, STRING or JSON. Note that you need to have Confluent Cloud Schema Registry configured if using a schema-based message format like AVRO, JSON_SR, and PROTOBUF.
How should we name your topic(s)?
Topic prefix: Provides a namespace (logical server name) for the MariaDB database server or cluster in which Debezium is capturing changes. It must be unique and can include only alphanumeric characters, hyphens, dots, and underscores. This prefix
<topic.prefix>.<databaseName>.<tableName>is added to all Kafka topic names receiving events from this connector.
Database config
Databases included: An optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions used to match database names for change capture. The connector does not capture changes in any database whose name is not in this list. By default, the connector captures changes in all databases.
To match the name of a database, Debezium applies the regular expression that you specify as an anchored regular expression. This means the expression must match the entire name string of the database; it does not match substrings.
Databases excluded: An optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match the names of databases from which you do not want the connector to capture changes. The connector captures changes in any database that is not named in the
database.exclude.listproperty.GTID included: A comma-separated list of regular expressions that match source domain IDs in the GTID set. The connector uses these expressions to find the binlog position on the MariaDB server. When this property is set, the connector uses only GTID ranges whose source UUIDs match a specified include pattern.
GTID excluded: A comma-separated list of regular expressions that match source domain IDs in the GTID set. The connector uses these expressions to find the binlog position on the MariaDB server. When this property is set, the connector uses only GTID ranges whose source UUIDs do not match any specified exclude pattern.
Connector config
Snapshot mode: The criteria for running a snapshot when the connector starts. Select one of the following snapshot options:
initial(default): the connector runs a snapshot only when no offsets have been recorded for the logical server name.initial_only: the connector runs a snapshot only when no offsets have been recorded for the logical server name and then stops. That is, it does not read change events from the binlog.when_needed: the connector runs a snapshot upon startup whenever it deems it necessary. This occurs when no offsets are available, or when a previously recorded offset specifies a binlog location or global transaction identifier (GTID) that is not available on the server.never: the connector never uses snapshots. Upon first startup with a logical server name, the connector reads from the beginning of the binlog. Configure this behavior with caution. It is valid only when the binlog is guaranteed to contain the entire history of the database.schema_only(deprecated): useno_datainstead.no_data: the connector runs a snapshot of the schemas, but not the data. This setting is useful when you require topics to contain only changes since the connector started, rather than a consistent snapshot of the data.schema_only_recovery(deprecated): Userecoveryinstead.recovery: a recovery setting for connectors that have already been capturing changes. When you restart the connector, this setting enables recovery of a corrupted or lost database schema history topic. You might also set it periodically to clean up a database schema history topic that has been growing unexpectedly. Note that database schema history topics require infinite retention.
Tables included: A comma-separated list of regular expressions that match fully-qualified table identifiers for the tables whose changes you want to capture. The connector will only capture changes from tables that match these expressions. Each identifier is of the form
schemaName.tableName. By default, the connector captures changes from all non-system tables in each captured database.To match the name of a table, the connector applies the regular expression that you specify as an anchored regular expression. That is, the specified expression is matched against the entire identifier for the table; it does not match substrings that might be present in a table name.
Note
If you use this property, do not use the
table.exclude.listproperty.Tables excluded: An optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match fully-qualified table identifiers for tables whose changes you do not want to capture. Each identifier is of the form schemaName.tableName. When this property is set, the connector captures changes from every table that you do not specify. To match the name of a table, Debezium applies the regular expression that you specify as an anchored regular expression. That is, the specified expression is matched against the entire identifier for the table; it does not match substrings that might be present in a table name. If you include this property in the configuration, do not set the
table.include.listproperty.
Schema Config
Include schema changes: A boolean value that specifies whether the connector publishes database schema changes to a Kafka topic with the same name as the topic prefix. Each schema change is recorded with a key (the database name) and a value (a JSON structure describing the schema update). This mechanism for recording schema changes is independent of the connector’s internal recording of changes to the database schema history. Defaults to
false.
How should we handle data types?
Event converting failure handling mode: Specifies how the connector responds when it cannot convert a table record due to a mismatch between a column’s data type and the type specified by the Debezium internal schema. Defaults to
warn.
Data encryption
Enable Client-Side Field Level Encryption for data encryption. Specify a Service Account to access the Schema Registry and associated encryption rules or keys with that schema. For more information on CSFLE or CSPE setup, see Manage encryption for connectors.
Show advanced configurations
Additional configurations
To add an additional configuration, see Additional Connector Configuration Reference for Confluent Cloud.
Schema context: Select a schema context to use for this connector, if using a schema-based data format. This property defaults to the Default context, which configures the connector to use the default schema set up for Schema Registry in your Confluent Cloud environment. A schema context allows you to use separate schemas (like schema sub-registries) tied to topics in different Kafka clusters that share the same Schema Registry environment. For example, if you select a non-default context, a Source connector uses only that schema context to register a schema and a Sink connector uses only that schema context to read from. For more information about setting up a schema context, see What are schema contexts and when should you use them?.
Additional Configs
Value Converter Replace Null With Default: Whether to replace fields that have a default value and that are null to the default value. When set to true, the default value is used, otherwise null is used. Applicable for JSON Converter.
Value Converter Reference Subject Name Strategy: Set the subject reference name strategy for value. Valid entries are DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy or QualifiedReferenceSubjectNameStrategy. Note that the subject reference name strategy can be selected only for PROTOBUF format with the default strategy being DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy.
Value Converter Schemas Enable: Include schemas within each of the serialized values. Input messages must contain schema and payload fields and may not contain additional fields. For plain JSON data, set this to false. Applicable for JSON Converter.
Errors Tolerance: Use this property if you would like to configure the connector’s error handling behavior. WARNING: This property should be used with CAUTION for SOURCE CONNECTORS as it may lead to dataloss. If you set this property to ‘all’, the connector will not fail on errant records, but will instead log them (and send to DLQ for Sink Connectors) and continue processing. If you set this property to ‘none’, the connector task will fail on errant records.
Value Converter Ignore Default For Nullables: When set to true, this property ensures that the corresponding record in Kafka is NULL, instead of showing the default column value. Applicable for AVRO,PROTOBUF and JSON_SR Converters.
Value Converter Decimal Format: Specify the JSON/JSON_SR serialization format for Connect DECIMAL logical type values with two allowed literals: BASE64 to serialize DECIMAL logical types as base64 encoded binary data and NUMERIC to serialize Connect DECIMAL logical type values in JSON/JSON_SR as a number representing the decimal value.
Key Converter Schema ID Serializer: The class name of the schema ID serializer for keys. This is used to serialize schema IDs in the message headers.
Value Converter Connect Meta Data: Allow the Connect converter to add its metadata to the output schema. Applicable for Avro Converters.
Value Converter Value Subject Name Strategy: Determines how to construct the subject name under which the value schema is registered with Schema Registry.
Key Converter Key Subject Name Strategy: How to construct the subject name for key schema registration.
Value Converter Schema ID Serializer: The class name of the schema ID serializer for values. This is used to serialize schema IDs in the message headers.
Auto-restart policy
Enable Connector Auto-restart: Control the auto-restart behavior of the connector and its task in the event of user-actionable errors. Defaults to
true, enabling the connector to automatically restart in case of user-actionable errors. Set this property tofalseto disable auto-restart for failed connectors. In such cases, you would need to manually restart the connector.
Output messages
After-state only: Controls whether the generated Kafka record should contain only the state of the row after the event occurred. Defaults to
false.Tombstones on delete: Configure whether a tombstone event should be generated after a delete event. The default is
true.
Database config
Signal data collection: Fully-qualified name of the data collection that is used to send signals to the connector. Use the following format to specify the fully-qualified collection name:
databaseName.tableName. These signals can be used to perform incremental snapshotting.Ignore built-in system tables: A boolean value that specifies whether built-in system tables should be ignored. This applies regardless of any table include and exclude lists. By default, Debezium does not capture changes from system tables or generate events for them.
How should we name your topic(s)?
Database schema history topic name: The name of the topic for the database schema history. A new topic with the provided name is created if it doesn’t already exist. If the topic already exists, ensure that it has a single partition, infinite retention period and is not in use by any other connector. If no value is provided, the name defaults to
dbhistory.<topic-prefix>.<lcc-id>.
Connector config
Snapshot locking mode: Controls whether and how long the connector holds the global MariaDB read lock, which prevents any updates to the database, while the connector is performing a snapshot. Possible settings are:
minimal,minimal_percona,extended, andnone.minimal: the connector holds the global read lock for just the initial portion of the snapshot, while the database schemas and other metadata are being read. The remaining work in a snapshot involves selecting all rows from each table. This is accomplished using a REPEATABLE READ transaction, even when the lock is no longer held and other MariaDB clients are updating the database.minimal_percona: similar tominimalmode except the connector uses a (Percona-specific) backup lock. This mode does not flush tables to disk, is not blocked by long-running reads, and is available only in Percona Server.extended: blocks all writes for the duration of the snapshot. Use this setting if there are clients that are submitting operations that MariaDB excludes from REPEATABLE READ semantics.none: prevents the connector from acquiring any table locks during the snapshot. While this setting is allowed with all snapshot modes, it is safe to use if and only if no schema changes are happening while the snapshot is running. For tables defined with MyISAM engine, the tables would still be locked despite this property being set as MyISAM acquires a table lock. This behavior is unlike InnoDB engine, which acquires row level locks.
Allow schema changes during incremental snapshot: Specifies whether the connector allows schema changes during an incremental snapshot. When
true, the connector detects schema changes and re-selects the current chunk to avoid locking DDLs.Columns excluded: An optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match the fully-qualified names of columns to exclude from change event record values. Fully-qualified names for columns are of the form
databaseName.tableName.columnName.Event processing failure handling mode: Specifies how the connector should react to exceptions during processing of events. Possible settings are:
fail,skip, andwarn.fail(default): propagates the exception, indicates the offset of the problematic event, and causes the connector to stop.skip: skips the problematic event and continues processing.warn: logs the offset of the problematic event, skips that event, and continues processing.
Schema name adjustment mode: Specifies how schema names should be adjusted for compatibility with the message converter used by the connector. Possible settings are:
none,avro, andavro_unicode.none(default): does not apply any adjustment.avro: replaces the characters that cannot be used in the Avro type name with underscore.avro_unicode: replaces the underscore or characters that cannot be used in the Avro type name with corresponding unicode like _uxxxx. Note: _ is an escape sequence like backslash in Java.
Field name adjustment mode: Specifies how field names should be adjusted for compatibility with the message converter used by the connector. Possible settings are:
none,avro, andavro_unicode.none(default): does not apply any adjustment.avro: replaces the characters that cannot be used in the Avro type name with underscore.avro_unicode: replaces the underscore or characters that cannot be used in the Avro type name with corresponding unicode like _uxxxx. Note: _ is an escape sequence like backslash in Java.
Heartbeat interval (ms): Controls how frequently the connector sends heartbeat messages to a Kafka topic. The default value 0 means that the connector does not send heartbeat messages. Heartbeat messages are useful for monitoring whether the connector is receiving change events from the database. Heartbeat messages might help decrease the number of change events that need to be re-sent when a connector restarts. To send heartbeat messages, set this property to a positive integer that indicates the number of milliseconds between heartbeat messages.
Database connection timeout: A positive integer value that specifies the maximum time (in milliseconds) the connector waits to establish a connection to the MariaDB database server before the connection request times out.
Use non-graceful disconnect: A boolean value that specifies whether the binary log client’s keepalive thread sets the
SO_LINGERsocket option to 0 to immediately close stale TCP connections. Set the value totrueif the connector experiences deadlocks inSSLSocketImpl.close.
Schema Config
Key converter reference subject name strategy: Set the subject reference name strategy for key. Valid entries are DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy or QualifiedReferenceSubjectNameStrategy. Note that the subject reference name strategy can be selected only for PROTOBUF format with the default strategy being DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy.
Skip unparseable DDL: A Boolean value that specifies whether the connector should ignore malformed or unknown database statements (
true), or stop processing so a human can fix the issue (false). Defaults tofalse. Consider setting this totrueto ignore unparseable statements.Store only captured tables DDL: A Boolean value that specifies whether the connector records schema structures from all tables in a schema or database, or only from tables that are designated for capture.
false(default): During a database snapshot, the connector records the schema data for all non-system tables in the database, including tables that are not designated for capture. It’s best to retain the default setting. If you later decide to capture changes from tables that you did not originally designate for capture, the connector can easily begin to capture data from those tables, because their schema structure is already stored in the schema history topic.true: During a database snapshot, the connector records the table schemas only for the tables from which Debezium captures change events. If you change the default value, and you later configure the connector to capture data from other tables in the database, the connector lacks the schema information that it requires to capture change events from the tables.
Kafka recovery poll interval: An integer value that specifies the maximum number of milliseconds the connector waits during startup/recovery while polling for persisted data.
Kafka query timeout: An integer value that specifies the maximum number of milliseconds the connector waits while fetching cluster information using Kafka admin client.
Kafka create topic timeout: An integer value that specifies the maximum number of milliseconds the connector waits while creating the Kafka history topic using Kafka admin client.
Store only captured databases DDL: A boolean value that specifies whether the connector records schema structures from all logical databases in the database instance. Specify one of the following values:
true: The connector records schema structures only for tables within the logical database and schema from which Debezium captures change events.false: The connector records schema structures for all logical databases.
How should we handle data types?
Decimal handling mode: Specifies how the connector should handle values for
DECIMALandNUMERICcolumns. Possible settings are:precise,double, andstring.precise(default): represents values by usingjava.math.BigDecimalto represent values in binary form in change events.double: represents values by using double values, which might result in a loss of precision but which is easier to use.string: encodes values as formatted strings, which are easy to consume but semantic information about the real type is lost.
Enable time adjuster: A boolean value that indicates whether the connector converts a 2-digit year specification to 4 digits. Set the value to
falsewhen conversion is fully delegated to the database.Note
MariaDB users can insert year values with either 2 or 4 digits. Two-digit values are mapped to a year in the range 1970-2069.
Time precision mode: Time, date, and timestamps can be represented with different kinds of precisions:
adaptive_time_microseconds(default): captures the date, datetime and timestamp values exactly as in the database using either millisecond, microsecond, or nanosecond precision values based on the database column’s type. An exception isTIMEtype fields, which are always captured as microseconds.connect: always represents time and timestamp values by using Kafka Connect’s built-in representations for Time, Date, and Timestamp, which use millisecond precision regardless of the database columns’ precision.
BigInt unsigned handling mode: Specifies how the connector represents
BIGINT UNSIGNEDcolumns in change events. Set one of the following options:longprecise(BigDecimal)
Inconsistent schema handling mode: Specifies how the connector should react to binlog events that belong to a table missing from internal schema representation. Possible settings are:
fail,skip, andwarn.fail(default): throws an exception that indicates the problematic event and its binlog offset, and causes the connector to stop.skip: passes over the problematic event and does not log anything.warn: logs the problematic event and its binlog offset and skips the event.
Transforms
Single Message Transforms: To add a new SMT, see Add transforms. For more information about unsupported SMTs, see Unsupported transformations.
Processing position
Set offsets: Click Set offsets to define a specific offset for this connector to begin procession data from. For more information on managing offsets, see Manage offsets.
For additional information about the Debezium SMTs ExtractNewRecordState and EventRouter (Debezium), see Debezium transformations.
For all property values and definitions, see Configuration Properties.
Click Continue.
Based on the number of topic partitions you select, you will be provided with a recommended number of tasks.
To change the number of tasks, use the Range Slider to select the desired number of tasks.
Click Continue.
Verify the connection details by previewing the running configuration.
After you’ve validated that the properties are configured to your satisfaction, click Launch.
The status for the connector should go from Provisioning to Running.
Step 5: Check the Kafka topic
After the connector is running, verify that messages are populating your Kafka topic.
Note
A topic named dbhistory.<topic.prefix>.<connect-id> is automatically created for schema.history.internal.kafka.topic with one partition.
For more information and examples to use with the Confluent Cloud API for Connect, see the Confluent Cloud API for Connect Usage Examples section.
Using the Confluent CLI
Complete the following steps to set up and run the connector using the Confluent CLI.
Note
Make sure you have all your prerequisites completed.
Step 1: List the available connectors
Enter the following command to list available connectors:
confluent connect plugin list
Step 2: List the connector configuration properties
Enter the following command to show the connector configuration properties:
confluent connect plugin describe <connector-plugin-name>
The command output shows the required and optional configuration properties.
Step 3: Create the connector configuration file
Create a JSON file that contains the connector configuration properties. The following examples show the required connector properties for both password and IAM role-based authentication.
Using password authentication:
{
"connector.class": "MariaDbCdcSource",
"name": "MariaDBCdcSourceConnector_0",
"kafka.auth.mode": "KAFKA_API_KEY",
"kafka.api.key": "****************",
"kafka.api.secret": "****************************************************************",
"database.hostname": "database-hostname",
"database.port": "3306",
"database.user": "database-username",
"database.password": "database-password",
"topic.prefix": "mariadb",
"table.include.list":"employees.departments,
"output.data.format": "JSON",
"tasks.max": "1"
}
Note the following property definitions:
"connector.class": Identifies the connector plugin name."name": Sets a name for your new connector.
"kafka.auth.mode": Identifies the connector authentication mode you want to use. There are two options:SERVICE_ACCOUNTorKAFKA_API_KEY(the default). To use an API key and secret, specify the configuration propertieskafka.api.keyandkafka.api.secret, as shown in the example configuration (above). To use a service account, specify the Resource ID in the propertykafka.service.account.id=<service-account-resource-ID>. To list the available service account resource IDs, use the following command:confluent iam service-account list
For example:
confluent iam service-account list Id | Resource ID | Name | Description +---------+-------------+-------------------+------------------- 123456 | sa-l1r23m | sa-1 | Service account 1 789101 | sa-l4d56p | sa-2 | Service account 2
"database.hostname": IP address or hostname of the MariaDB database server."database.port": Port number of the MariaDB database server."database.user": The name of the MariaDB database user that has the required authorization."database.password": Password of the MariaDB database user that has the required authorization. Only applicable when using password-based authentication."topic.prefix": Provides a namespace for the particular database server/cluster that the connector is capturing changes from."table.include.list": An optional, comma-separated list of fully-qualified table identifiers for the connector to monitor. By default, the connector monitors all non-system tables. A fully-qualified table name is in the formdatabaseName.tableName. This property cannot be used with the propertytable.exclude.list."output.data.format": Sets the output Kafka record value format (data coming from the connector). Valid entries are AVRO, JSON_SR, or PROTOBUF. You must have Confluent Cloud Schema Registry configured if using a schema-based record format (for example, AVRO, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or PROTOBUF)."tasks.max": Enter the number of tasks in use by the connector. Organizations can run multiple connectors with a limit of one task per connector (that is,"tasks.max": "1").
Note
To enable CSFLE or CSPE for data encryption, specify the following properties:
csfle.enabled: Flag to indicate whether the connector honors CSFLE or CSPE rules.sr.service.account.id: A Service Account to access the Schema Registry and associated encryption rules or keys with that schema.
For more information on CSFLE or CSPE setup, see Manage encryption for connectors.
Single Message Transforms: See the Single Message Transforms (SMT) documentation for details about adding SMTs using the CLI. For additional information about the Debezium SMTs ExtractNewRecordState and EventRouter (Debezium), see Debezium transformations.
See Configuration Properties for all properties and definitions.
Step 4: Load the properties file and create the connector
Enter the following command to load the configuration and start the connector:
confluent connect cluster create --config-file <file-name>.json
For example:
confluent connect cluster create --config-file mariadb-cdc-source.json
Example output:
Created connector MariaDbCdcSourceConnector_1 lcc-ix4dl
Step 5: Check the connector status
Enter the following command to check the connector status:
confluent connect cluster list
Example output:
ID | Name | Status | Type
+-----------+-------------------------------+---------+-------+
lcc-ix4dl | MariaDbCdcSourceConnector_1 | RUNNING | source
Step 6: Check the Kafka topic.
After the connector is running, verify that messages are populating your Kafka topic.
Note
A topic named dbhistory.<topic.prefix>.<connect-id> is automatically created for schema.history.internal.kafka.topic with one partition.
For more information and examples to use with the Confluent Cloud API for Connect, see the Confluent Cloud API for Connect Usage Examples section.
Configuration Properties
Use the following configuration properties with the fully-managed connector.
How should we connect to your data?
nameSets a name for your connector.
Type: string
Valid Values: A string at most 64 characters long
Importance: high
Kafka Cluster credentials
kafka.auth.modeKafka Authentication mode. It can be one of KAFKA_API_KEY or SERVICE_ACCOUNT. It defaults to KAFKA_API_KEY mode, whenever possible.
Type: string
Valid Values: SERVICE_ACCOUNT, KAFKA_API_KEY
Importance: high
kafka.api.keyKafka API Key. Required when kafka.auth.mode==KAFKA_API_KEY.
Type: password
Importance: high
kafka.service.account.idThe Service Account that will be used to generate the API keys to communicate with Kafka Cluster.
Type: string
Importance: high
kafka.api.secretSecret associated with Kafka API key. Required when kafka.auth.mode==KAFKA_API_KEY.
Type: password
Importance: high
How should we connect to your database?
database.hostnameIP address or hostname of the MariaDB database server.
Type: string
Importance: high
database.portPort number of the MariaDB database server.
Type: int
Valid Values: [0,…,65535]
Importance: high
database.userThe name of the MariaDB database user that has the required authorization.
Type: string
Importance: high
database.passwordPassword for the MariaDB database user that has the required authorization.
Type: password
Importance: high
database.ssl.modeWhether to use an encrypted connection to the MariaDB server. Possible settings are
disable,trust,verify-ca, andverify-full.disable: Does not use SSL/TLS.trust: Uses SSL/TLS for encryption. It does not perform certificate or hostname verification.verify-ca: Uses SSL/TLS for encryption and performs certificate verification, but does not perform hostname verification.verify-full: Uses SSL/TLS for encryption, certificate verification, and hostname verification.Type: string
Default: disable
Importance: high
database.ssl.keystorePath to the SSL keystore file for MariaDB connection. This property is only required when you enable SSL certificate verification (
verify-caorverify-fullmodes)Type: password
Importance: medium
database.ssl.keystore.passwordPassword for the SSL keystore file for MariaDB connection. This property is only required when you enable SSL certificate verification (
verify-caorverify-fullmodes)Type: password
Importance: medium
database.ssl.truststorePath to the SSL truststore file for MariaDB connection. This property is only required when you enable SSL certificate verification (
verify-caorverify-fullmodes)Type: password
Importance: medium
database.ssl.truststore.passwordPassword for the SSL truststore file for MariaDB connection. This property is only required when you enable SSL certificate verification (
verify-caorverify-fullmodes)Type: password
Importance: medium
Output messages
output.data.formatSets the output Kafka record value format. Valid entries are AVRO, JSON_SR, PROTOBUF. Note that you need to have Confluent Cloud Schema Registry configured if using a schema-based message format like AVRO, JSON_SR, and PROTOBUF.
Type: string
Default: AVRO
Importance: high
output.key.formatSets the output Kafka record key format. Valid entries are AVRO, JSON_SR, PROTOBUF, STRING or JSON. Note that you need to have Confluent Cloud Schema Registry configured if using a schema-based message format like AVRO, JSON_SR, and PROTOBUF
Type: string
Default: JSON
Valid Values: AVRO, JSON, JSON_SR, PROTOBUF, STRING
Importance: high
after.state.onlyControls whether the generated Kafka record should contain only the state of the row after the event occurred.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
tombstones.on.deleteControls whether a tombstone event should be generated after a delete event.
true - a delete operation is represented by a delete event and a subsequent tombstone event.
false - only a delete event is emitted.
After a source record is deleted, emitting the tombstone event (the default behavior) allows Kafka to completely delete all events that pertain to the key of the deleted row in case log compaction is enabled for the topic.
Type: boolean
Default: true
Importance: medium
How should we name your topic(s)?
topic.prefixTopic prefix that provides a namespace (logical server name) for the particular MariaDB database server or cluster in which Debezium is capturing changes. The prefix should be unique across all other connectors, since it is used as a topic name prefix for all Kafka topics that receive records from this connector. Only alphanumeric characters, hyphens, dots and underscores must be used. The connector automatically creates Kafka topics using the naming convention: <topic.prefix>.<databaseName>.<tableName>.
Type: string
Importance: high
schema.history.internal.kafka.topicThe name of the topic for the database schema history. A new topic with provided name is created, if it doesn’t already exist. If the topic already exists, ensure that it has a single partition, infinite retention period and is not in use by any other connector. If no value is provided, the name defaults to
dbhistory.<topic-prefix>.<lcc-id>.Type: string
Default: dbhistory.${topic.prefix}.{{.logicalClusterId}}
Importance: high
Database config
signal.data.collectionFully-qualified name of the data collection that needs to be used to send signals to the connector. Use the following format to specify the fully-qualified collection name: databaseName.tableName
Type: string
Importance: medium
database.include.listAn optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match the names of the databases for which to capture changes. The connector does not capture changes in any database whose name is not in this list. By default, the connector captures changes in all databases.
To match the name of a database, Debezium applies the regular expression that you specify as an anchored regular expression. That is, the specified expression is matched against the entire name string of the database; it does not match substrings that might be present in a database name.
Type: list
Importance: medium
database.exclude.listAn optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match the names of databases from which you do not want the connector to capture changes. The connector captures changes in any database that is not named in the database.exclude.list.
Type: list
Importance: medium
gtid.source.includesA comma-separated list of regular expressions that match source domain IDs in the GTID set used that the connector uses to find the binlog position on the MariaDB server. When this property is set, the connector uses only the GTID ranges that have source UUIDs that match one of the specified include patterns.
Type: list
Importance: medium
gtid.source.excludesA comma-separated list of regular expressions that match source domain IDs in the GTID set that the connector uses to find the binlog position on the MariaDB server. When this property is set, the connector uses only the GTID ranges that have source UUIDs that do not match any of the specified exclude patterns.
Type: list
Importance: medium
table.ignore.builtinA Boolean value that specifies whether built-in system tables should be ignored. This applies regardless of the table include and exclude lists. By default, changes that occur to the values in system tables are excluded from capture, and Debezium does not generate events for system table changes.
Type: boolean
Default: true
Importance: medium
Connector config
snapshot.modeSpecifies the criteria for running a snapshot when the connector starts. Possible settings are: initial, initial_only, when_needed, no_data, and recovery.
initial - the connector runs a snapshot only when no offsets have been recorded for the logical server name.
initial_only - the connector runs a snapshot only when no offsets have been recorded for the logical server name and then stops; i.e. it will not read change events from the binlog.
when_needed - the connector runs a snapshot upon startup whenever it deems it necessary. That is, when no offsets are available, or when a previously recorded offset specifies a binlog location or GTID that is not available in the server.
no_data - the connector runs a snapshot of the schemas and not the data. This setting is useful when you do not need the topics to contain a consistent snapshot of the data but need them to have only the changes since the connector was started.
recovery - this is a recovery setting for a connector that has already been capturing changes. When you restart the connector, this setting enables recovery of a corrupted or lost database schema history topic. You might set it periodically to “clean up” a database schema history topic that has been growing unexpectedly.
Type: string
Default: initial
Valid Values: initial, initial_only, no_data, recovery, when_needed
Importance: medium
snapshot.locking.modeControls whether and how long the connector holds the global MariaDB read lock, which prevents any updates to the database, while the connector is performing a snapshot. Possible settings are: minimal, extended, and none.
minimal - the connector holds the global read lock for just the initial portion of the snapshot, while the database schemas and other metadata are being read. The remaining work in a snapshot involves selecting all rows from each table. This is accomplished using a REPEATABLE READ transaction, even when the lock is no longer held and other MariaDB clients are updating the database.
extended - blocks all writes for the duration of the snapshot. Use this setting if there are clients that are submitting operations that MariaDB excludes from REPEATABLE READ semantics.
none - prevents the connector from acquiring any table locks during the snapshot. While this setting is allowed with all snapshot modes, it is safe to use if and only if no schema changes are happening while the snapshot is running. For tables defined with MyISAM engine, the tables would still be locked despite this property being set as MyISAM acquires a table lock. This behavior is unlike InnoDB engine, which acquires row level locks.
Type: string
Default: minimal
Valid Values: extended, minimal, none
Importance: low
incremental.snapshot.allow.schema.changesSpecifies whether the connector allows schema changes during an incremental snapshot. When the value is set to true, the connector detects schema change during an incremental snapshot, and re-select a current chunk to avoid locking DDLs.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: medium
table.include.listAn optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match fully-qualified table identifiers for tables whose changes you want to capture. When this property is set, the connector captures changes only from the specified tables. Each identifier is of the form schemaName.tableName. By default, the connector captures changes in every non-system table in each schema whose changes are being captured.
To match the name of a table, Debezium applies the regular expression that you specify as an anchored regular expression. That is, the specified expression is matched against the entire identifier for the table; it does not match substrings that might be present in a table name.
If you include this property in the configuration, do not also set the
table.exclude.listproperty.Type: list
Importance: medium
table.exclude.listAn optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match fully-qualified table identifiers for tables whose changes you do not want to capture. Each identifier is of the form schemaName.tableName. When this property is set, the connector captures changes from every table that you do not specify.
To match the name of a table, Debezium applies the regular expression that you specify as an anchored regular expression. That is, the specified expression is matched against the entire identifier for the table; it does not match substrings that might be present in a table name.
If you include this property in the configuration, do not set the
table.include.listproperty.Type: list
Importance: medium
column.exclude.listAn optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match the fully-qualified names of columns to exclude from change event record values. Fully-qualified names for columns are of the form databaseName.tableName.columnName.
To match the name of a column, Debezium applies the regular expression that you specify as an anchored regular expression. That is, the specified expression is matched against the entire name string of the column; it does not match substrings that might be present in a column name. Do not set
column.include.listif you set this property.Type: list
Importance: medium
event.processing.failure.handling.modeSpecifies how the connector should react to exceptions during processing of events. Possible settings are: fail, skip, and warn.
fail propagates the exception, indicates the offset of the problematic event, and causes the connector to stop.
warn logs the offset of the problematic event, skips that event, and continues processing.
skip skips the problematic event and continues processing.
Type: string
Default: fail
Valid Values: fail, skip, warn
Importance: low
schema.name.adjustment.modeSpecifies how schema names should be adjusted for compatibility with the message converter used by the connector. Possible settings are: none, avro, and avro_unicode.
none does not apply any adjustment.
avro replaces the characters that cannot be used in the Avro type name with underscore.
avro_unicode replaces the underscore or characters that cannot be used in the Avro type name with corresponding unicode like _uxxxx. Note: _ is an escape sequence like backslash in Java.
Type: string
Default: none
Valid Values: avro, avro_unicode, none
Importance: medium
field.name.adjustment.modeSpecifies how field names should be adjusted for compatibility with the message converter used by the connector. Possible settings are: none, avro, and avro_unicode.
none does not apply any adjustment.
avro replaces the characters that cannot be used in the Avro type name with underscore.
avro_unicode replaces the underscore or characters that cannot be used in the Avro type name with corresponding unicode like _uxxxx. Note: _ is an escape sequence like backslash in Java.
Type: string
Default: none
Valid Values: avro, avro_unicode, none
Importance: medium
heartbeat.interval.msControls how frequently the connector sends heartbeat messages to a Kafka topic. The behavior of default value 0 is that the connector does not send heartbeat messages. Heartbeat messages are useful for monitoring whether the connector is receiving change events from the database. Heartbeat messages might help decrease the number of change events that need to be re-sent when a connector restarts. To send heartbeat messages, set this property to a positive integer, which indicates the number of milliseconds between heartbeat messages.
Type: int
Default: 0
Valid Values: [0,…]
Importance: low
connect.timeout.msA positive integer value that specifies the maximum time in milliseconds that the connector waits to establish a connection to the MariaDB database server before the connection request times out.
Type: int
Default: 5000 (5 seconds)
Importance: medium
use.nongraceful.disconnectA Boolean value that specifies whether the binary log client’s keepalive thread sets the SO_LINGER socket option to 0 to immediately close stale TCP connections.
Set the value to true if the connector experiences deadlocks in SSLSocketImpl.close.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: medium
Schema Config
schema.context.nameAdd a schema context name. A schema context represents an independent scope in Schema Registry. It is a separate sub-schema tied to topics in different Kafka clusters that share the same Schema Registry instance. If not used, the connector uses the default schema configured for Schema Registry in your Confluent Cloud environment.
Type: string
Default: default
Importance: medium
key.converter.reference.subject.name.strategySet the subject reference name strategy for key. Valid entries are DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy or QualifiedReferenceSubjectNameStrategy. Note that the subject reference name strategy can be selected only for PROTOBUF format with the default strategy being DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy.
Type: string
Default: DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy
Importance: high
include.schema.changesBoolean value that specifies whether the connector publishes changes in the database schema to a Kafka topic with the same name as the topic prefix. The connector records each schema change with a key that contains the database name, and a value that is a JSON structure that describes the schema update. This mechanism for recording schema changes is independent of the connector’s internal recording of changes to the database schema history.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: medium
schema.history.internal.skip.unparseable.ddlA Boolean value that specifies whether the connector should ignore malformed or unknown database statements (true), or stop processing so a human can fix the issue (false). Defaults to false. Consider setting this to true to ignore unparseable statements.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
schema.history.internal.store.only.captured.tables.ddlA Boolean value that specifies whether the connector records schema structures from all tables in a schema or database, or only from tables that are designated for capture. Defaults to false.
false - During a database snapshot, the connector records the schema data for all non-system tables in the database, including tables that are not designated for capture. It’s best to retain the default setting. If you later decide to capture changes from tables that you did not originally designate for capture, the connector can easily begin to capture data from those tables, because their schema structure is already stored in the schema history topic.
true - During a database snapshot, the connector records the table schemas only for the tables from which Debezium captures change events. If you change the default value, and you later configure the connector to capture data from other tables in the database, the connector lacks the schema information that it requires to capture change events from the tables.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
schema.history.internal.kafka.recovery.poll.interval.msAn integer value that specifies the maximum number of milliseconds the connector should wait during startup/recovery while polling for persisted data.
Type: int
Default: 100
Valid Values: [100,…]
Importance: low
schema.history.internal.kafka.query.timeout.msAn integer value that specifies the maximum number of milliseconds the connector should wait while fetching cluster information using Kafka admin client.
Type: int
Default: 3000 (3 seconds)
Importance: low
schema.history.internal.kafka.create.timeout.msAn integer value that specifies the maximum number of milliseconds the connector should wait while create kafka history topic using Kafka admin client.
Type: int
Default: 30000 (30 seconds)
Importance: low
schema.history.internal.store.only.captured.databases.ddlA Boolean value that specifies whether the connector records schema structures from all logical databases in the database instance. Specify one of the following values:
true
The connector records schema structures only for tables in the logical database and schema from which Debezium captures change events.
false
The connector records schema structures for all logical databases.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
How should we handle data types?
decimal.handling.modeSpecifies how the connector should handle values for DECIMAL and NUMERIC columns. Possible settings are: precise, double, and string.
precise represents values by using java.math.BigDecimal to represent values in binary form in change events. double represents values by using double values, which might result in a loss of precision but which is easier to use. string encodes values as formatted strings, which are easy to consume but semantic information about the real type is lost.
Type: string
Default: precise
Valid Values: double, precise, string
Importance: medium
event.converting.failure.handling.modeSpecifies how the connector responds when it cannot convert a table record due to a mismatch between the data type of a column and the type specified by the Debezium internal schema.
Set one of the following options: fail, warn, skip
Type: string
Default: warn
Valid Values: fail, skip, warn
Importance: medium
enable.time.adjusterBoolean value that indicates whether the connector converts a 2-digit year specification to 4 digits. Set the value to false when conversion is fully delegated to the database.
MariaDB users can insert year values with either 2-digits or 4-digits. 2-digit values are mapped to a year in the range 1970 - 2069.
Type: boolean
Default: true
Importance: medium
time.precision.modeTime, date, and timestamps can be represented with different kinds of precisions:
adaptive_time_microseconds captures the date, datetime and timestamp values exactly as in the database using either millisecond, microsecond, or nanosecond precision values based on the database column’s type. An exception is TIME type fields, which are always captured as microseconds.
connect always represents time and timestamp values by using Kafka Connect’s built-in representations for Time, Date, and Timestamp, which use millisecond precision regardless of the database columns’ precision.
Type: string
Default: adaptive_time_microseconds
Valid Values: adaptive_time_microseconds, connect
Importance: low
bigint.unsigned.handling.modeSpecifies how the connector represents BIGINT UNSIGNED columns in change events. Set one of the following options: long, or precise (BigDecimal)
Type: string
Default: long
Valid Values: long, precise
Importance: medium
inconsistent.schema.handling.modeSpecifies how the connector should react to binlog events that belong to a table missing from internal schema representation. Possible settings are: fail, skip, and warn.
fail - throws an exception that indicates the problematic event and its binlog offset, and causes the connector to stop.
skip - passes over the problematic event and does not log anything.
warn - logs the problematic event and its binlog offset and skips the event.
Type: string
Default: fail
Valid Values: fail, skip, warn
Importance: medium
Number of tasks for this connector
tasks.maxMaximum number of tasks for the connector.
Type: int
Valid Values: [1,…,1]
Importance: high
Additional Configs
column.include.listA comma-separated list of regular expressions that match the fully-qualified names of columns that should be included in change event record values. Fully-qualified names for columns are of the form databaseName.tableName.columnName. Do not set
column.exclude.listif you set this property.Type: list
Importance: low
column.propagate.source.typeA comma-separated list of regular expressions matching fully-qualified names of columns that adds the column’s original type and original length as parameters to the corresponding field schemas in the emitted change records. When this property is set, the connector adds the following fields to the schema of event records with prefix
__debezium.source.column. These parameters propagate a column’s original type name and length (for variable-width types), respectively. Include ‘.*’ to match all column types.’Type: list
Importance: low
header.converterThe converter class for the headers. This is used to serialize and deserialize the headers of the messages.
Type: string
Importance: low
message.key.columnsA semicolon-separated list of expressions that match fully-qualified tables and column(s) to be used as message key. Each expression must match the pattern ‘<fully-qualified_tableName>:<keyColumn>,<keyColumn>’, where the fully qualified table name could be defined as <databaseName>.<tableName> and the key columns are a comma-separated list of columns representing the custom key. For any table without an explicit key configuration the table’s primary key column(s) will be used as message key. The config can include entries for multiple tables. Use a semicolon to separate table entries in the list. Example: inventory.customers:pk1,pk2;(.*).purchaseorders:pk3,pk4
Type: string
Importance: low
notification.enabled.channelsList of notification channels names that are enabled. The following channels are available:
logandsink. Whensinkis enabled, the connector sends notifications to a topic specified by thenotification.sink.topic.nameproperty.Type: list
Importance: low
notification.sink.topic.nameThe name of the topic for the notifications. This is required in case
sinkis in the list of enabled channels.Type: string
Importance: low
producer.override.compression.typeThe compression type for all data generated by the producer. Valid values are none, gzip, snappy, lz4, and zstd.
Type: string
Importance: low
producer.override.linger.msThe producer groups together any records that arrive in between request transmissions into a single batched request. More details can be found in the documentation: https://docs.confluent.io/platform/current/installation/configuration/producer-configs.html#linger-ms.
Type: long
Valid Values: [100,…,1000]
Importance: low
signal.enabled.channelsA comma-separated list of channel names that are enabled for the connector. If not set, the connector enables only the
sourcechannel by default. Supported values are:source(default): Signals are read from a signaling table in the source database.kafka: Signals are consumed from a Kafka topic.Type: list
Importance: low
signal.kafka.topicThe name of the Kafka topic that the connector monitors for ad hoc signals. Note that you can currently send signal messages to this topic via the Confluent CLI.
Type: string
Importance: low
snapshot.include.collection.listA comma-separated list of regular expressions that match the fully-qualified names (<databaseName>.<tableName>) of the tables to include in a snapshot. If not explicitly set, the connector defaults to snapshotting all tables listed in table.include.list. The specified items must be named in the connector’s table.include.list property. This property takes effect only if the connector’s snapshot.mode property is set to a value other than never.
Type: list
Importance: low
value.converter.allow.optional.map.keysAllow optional string map key when converting from Connect Schema to Avro Schema. Applicable for Avro Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.auto.register.schemasSpecify if the Serializer should attempt to register the Schema.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.connect.meta.dataAllow the Connect converter to add its metadata to the output schema. Applicable for Avro Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.enhanced.avro.schema.supportEnable enhanced schema support to preserve package information and Enums. Applicable for Avro Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.enhanced.protobuf.schema.supportEnable enhanced schema support to preserve package information. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.flatten.unionsWhether to flatten unions (oneofs). Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.generate.index.for.unionsWhether to generate an index suffix for unions. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.generate.struct.for.nullsWhether to generate a struct variable for null values. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.int.for.enumsWhether to represent enums as integers. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.latest.compatibility.strictVerify latest subject version is backward compatible when use.latest.version is true.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.object.additional.propertiesWhether to allow additional properties for object schemas. Applicable for JSON_SR Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.optional.for.nullablesWhether nullable fields should be specified with an optional label. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.optional.for.proto2Whether proto2 optionals are supported. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.scrub.invalid.namesWhether to scrub invalid names by replacing invalid characters with valid characters. Applicable for Avro and Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.use.latest.versionUse latest version of schema in subject for serialization when auto.register.schemas is false.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.use.optional.for.nonrequiredWhether to set non-required properties to be optional. Applicable for JSON_SR Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.wrapper.for.nullablesWhether nullable fields should use primitive wrapper messages. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.wrapper.for.raw.primitivesWhether a wrapper message should be interpreted as a raw primitive at root level. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
incremental.snapshot.chunk.sizeThe maximum number of rows that the connector fetches and reads into memory during an incremental snapshot chunk. Increasing the chunk size improves efficiency by running fewer, larger snapshot queries. However, larger chunk sizes also require more memory to buffer the snapshot data. Adjust the chunk size to a value that provides the best performance in your environment.
Type: int
Default: 1024
Valid Values: [1,…,1024]
Importance: medium
binary.handling.modeSpecify how binary (blob, binary, etc.) columns should be represented in change events, including: ‘bytes’ represents binary data as byte array (default); ‘base64’ represents binary data as base64-encoded string; ‘base64-url-safe’ represents binary data as base64-url-safe-encoded string; ‘hex’ represents binary data as hex-encoded (base16) string
Type: string
Default: bytes
Importance: low
errors.toleranceUse this property if you would like to configure the connector’s error handling behavior. WARNING: This property should be used with CAUTION for SOURCE CONNECTORS as it may lead to dataloss. If you set this property to ‘all’, the connector will not fail on errant records, but will instead log them (and send to DLQ for Sink Connectors) and continue processing. If you set this property to ‘none’, the connector task will fail on errant records.
Type: string
Default: none
Importance: low
incremental.snapshot.watermarking.strategySpecify the strategy used for watermarking during an incremental snapshot: ‘INSERT_INSERT’ both open and close signal is written into signal data collection (default); ‘INSERT_DELETE’ only open signal is written on signal data collection, the close will delete the relative open signal.
Type: string
Default: INSERT_INSERT
Importance: low
key.converter.key.schema.id.serializerThe class name of the schema ID serializer for keys. This is used to serialize schema IDs in the message headers.
Type: string
Default: io.confluent.kafka.serializers.schema.id.PrefixSchemaIdSerializer
Importance: low
key.converter.key.subject.name.strategyHow to construct the subject name for key schema registration.
Type: string
Default: TopicNameStrategy
Importance: low
max.batch.sizeMaximum size of each batch of events that the connector processes. Defaults to 2048 with the allowed range is from 1 to 5000.
Type: int
Default: 2048
Valid Values: [1,…,5000]
Importance: low
poll.interval.msTime to wait for new change events to appear after receiving no events, given in milliseconds. Defaults to 500 ms.
Type: long
Default: 500
Valid Values: [200,…]
Importance: low
provide.transaction.metadataDetermines whether the connector generates events with transaction boundaries and enriches change event envelopes with transaction metadata.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
read.onlyControls whether the connector writes watermarks to the signal data collection to track incremental snapshot progress. Set the value to
trueto enable the connector to use an incremental snapshot watermarking strategy that does not require writing to the signal data collection (useful for read-only database connections).Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
skip.messages.without.changeEnable to skip publishing messages when there is no change in included columns. This would essentially filter messages to be sent when there is no change in columns included as per
column.include.listorcolumn.exclude.list. Set the value to true to prevent the connector from capturing records when no changes are present in the included columns.Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
skipped.operationsThe comma-separated list of operations to skip during streaming, defined as: ‘c’ for inserts/create; ‘u’ for updates; ‘d’ for deletes, ‘t’ for truncates, and ‘none’ to indicate nothing skipped. By default, only truncate operations will be skipped.
Type: list
Default: t
Importance: low
snapshot.delay.msAn interval in milliseconds that the connector should wait before performing a snapshot when the connector starts. Defaults to 0 ms.
Type: long
Default: 0
Valid Values: [0,…]
Importance: low
snapshot.lock.timeout.msThe maximum number of millis to wait for table locks at the beginning of a snapshot. If locks cannot be acquired in this time frame, the snapshot will be aborted. Defaults to 10 seconds.
Type: long
Default: 10000 (10 seconds)
Importance: low
streaming.delay.msA delay period after the snapshot is completed and the streaming begins, given in milliseconds. This delay helps prevent re-snapshotting in case the connector fails during the transition to streaming. Defaults to 60000 ms.
Type: long
Default: 60000 (1 minute)
Valid Values: [0,…]
Importance: low
topic.heartbeat.prefixSpecifies the prefix of the heartbeat topic to which the connector sends heartbeat messages. The topic name has this pattern:
<topic.heartbeat.prefix>.<topic.prefix>. Defaults to__debezium-heartbeat-{{.logicalClusterId}}.Type: string
Default: __debezium-heartbeat-{{.logicalClusterId}}
Importance: low
topic.transactionControls the name of the topic to which the connector sends transaction metadata messages. The final transaction topic name has this pattern:
<topic.prefix>.<topic.transaction>. Defaults to{{.logicalClusterId}}.transaction.Type: string
Default: {{.logicalClusterId}}.transaction
Importance: low
value.converter.decimal.formatSpecify the JSON/JSON_SR serialization format for Connect DECIMAL logical type values with two allowed literals:
BASE64 to serialize DECIMAL logical types as base64 encoded binary data and
NUMERIC to serialize Connect DECIMAL logical type values in JSON/JSON_SR as a number representing the decimal value.
Type: string
Default: BASE64
Importance: low
value.converter.flatten.singleton.unionsWhether to flatten singleton unions. Applicable for Avro and JSON_SR Converters.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
value.converter.ignore.default.for.nullablesWhen set to true, this property ensures that the corresponding record in Kafka is NULL, instead of showing the default column value. Applicable for AVRO,PROTOBUF and JSON_SR Converters.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
value.converter.reference.subject.name.strategySet the subject reference name strategy for value. Valid entries are DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy or QualifiedReferenceSubjectNameStrategy. Note that the subject reference name strategy can be selected only for PROTOBUF format with the default strategy being DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy.
Type: string
Default: DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy
Importance: low
value.converter.replace.null.with.defaultWhether to replace fields that have a default value and that are null to the default value. When set to true, the default value is used, otherwise null is used. Applicable for JSON Converter.
Type: boolean
Default: true
Importance: low
value.converter.schemas.enableInclude schemas within each of the serialized values. Input messages must contain schema and payload fields and may not contain additional fields. For plain JSON data, set this to false. Applicable for JSON Converter.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
value.converter.value.schema.id.serializerThe class name of the schema ID serializer for values. This is used to serialize schema IDs in the message headers.
Type: string
Default: io.confluent.kafka.serializers.schema.id.PrefixSchemaIdSerializer
Importance: low
value.converter.value.subject.name.strategyDetermines how to construct the subject name under which the value schema is registered with Schema Registry.
Type: string
Default: TopicNameStrategy
Importance: low
Auto-restart policy
auto.restart.on.user.errorEnable connector to automatically restart on user-actionable errors.
Type: boolean
Default: true
Importance: medium
Next Steps
For an example that shows fully-managed Confluent Cloud connectors in action with Confluent Cloud for Apache Flink, see the Cloud ETL Demo. This example also shows how to use Confluent CLI to manage your resources in Confluent Cloud.