Connect with Confluent for Confluent Cloud
This topic provides information for Confluent partners participating in the Connect with Confluent (CwC) program. If you would like to be a Confluent partner, get started by visiting the Confluent Partner Portal and signing up.
The CwC program gives your application direct access to Confluent Cloud, the cloud-native and complete data streaming platform that processes more than an exabyte of data per year. When you join and integrate with Confluent, you become a part of the largest data streaming network—making it easier for your customers to access and use real-time data streams to drive more consumption for your business. Together with guidance from Confluent’s Apache Kafka® experts, you’ll build your data streams integration and verify it for scaled use across your entire customer base.
Confluent partners can build and manage a verified integration to Confluent. Verified integrations are listed in our Connect with Confluent directory, and can be added to Confluent Marketplace if they provide a direct download or link to the Confluent-branded integration.
You can submit several types of integration into the program:
Client API integrations
Connectors which can be deployed across all relevant Confluent product options: Confluent Platform, Self Host and Custom Connect (but where Custom Connect is not applicable, this requirement will be waived).
If you have other questions, contact us at integrationonboarding@confluent.io
Client API integrations
Client API integrations (also known as native integrations) can customize the end-user experience using multiple configuration options, including any of the client configurations available to Confluent clients and applications. This allows partners to further tailor a data streaming experience to their specific requirements.
For a list of partner integrations, see Partner integration directory.
Native integrations simplify connecting to Confluent Cloud from a partner’s native platform. You can implement this in a couple of ways:
New Organization: Develop an integration that creates a new Confluent Cloud organization and adds your customer.
Existing Organization: Launch the customer into an existing Confluent Cloud organization.
These types of integrations must include the following specifics:
The native partner platform UI provides the end-user experience
Integrates Confluent Cloud authentication
Unlocks Schema Registry and Stream Governance capabilities in Confluent Cloud
Includes Confluent Cloud APIs to manage topics, configurations, and other details
Integrates producer and consumer clients
Integrates Confluent Cloud topics
What great integrations look like
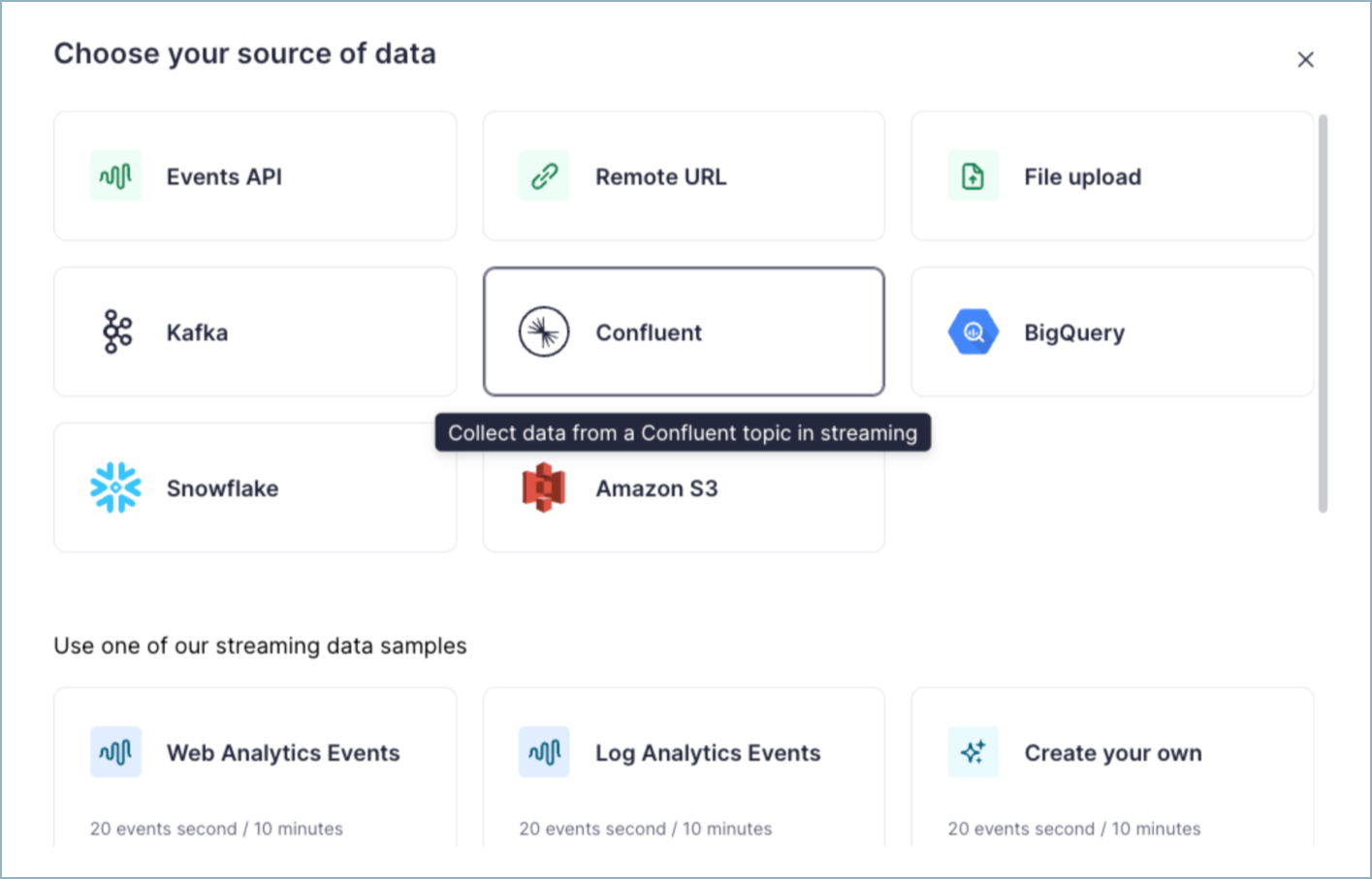
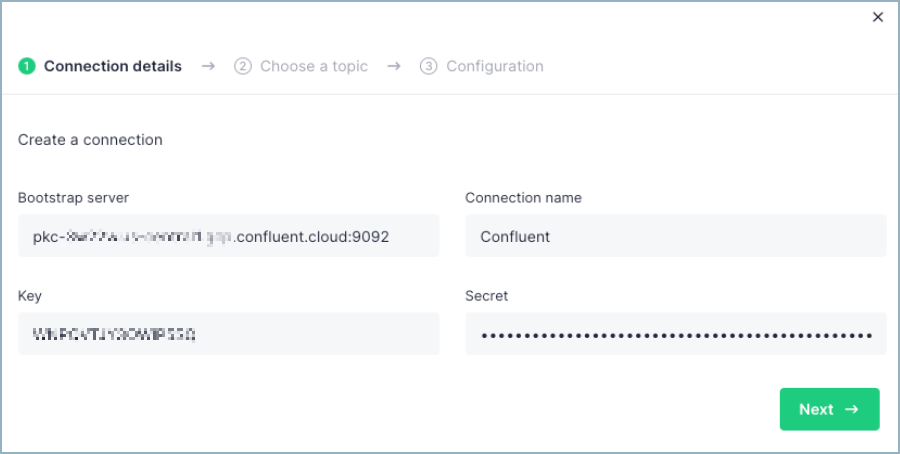
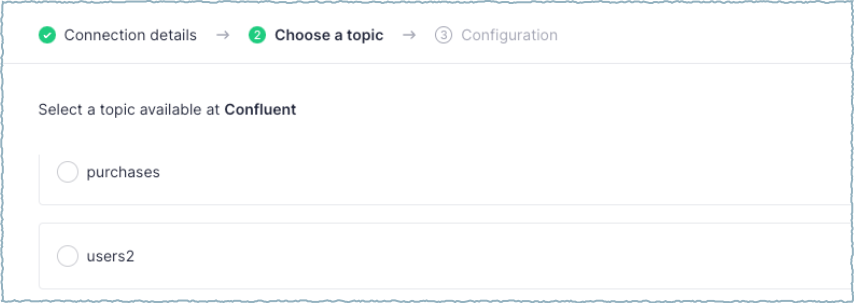
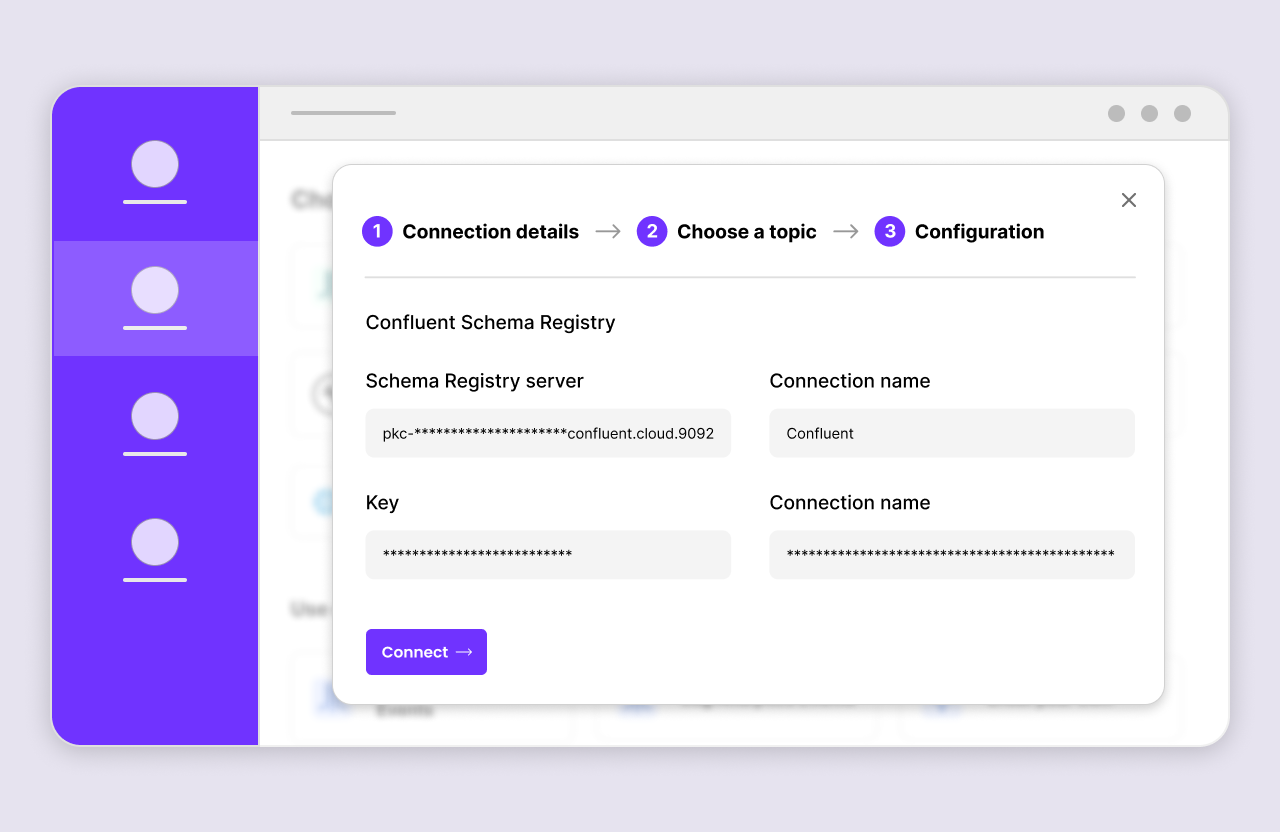
The most effective CwC integrations collect the necessary information from users as simply as possible. The integration should guide the user through how to obtain that information in Confluent Cloud.
The following information is typically collected though the UI:
Confluent Cloud cluster bootstrap server address
Confluent Cloud authentication details
Confluent Cloud topics to produce to or consume from
Schema Registry connection details
The following sample app mockup captures the typical user experience.
Native integration basics
Refer to the following information to understand what development tasks are required to configure an integration.
Integration authentication
Security and authentication are critical aspects of a CwC integration. To connect to a customer’s Confluent Cloud environment, the integration must prompt the end-user (customer) to provide authentication credentials. It is important that the integration’s authentication to Confluent Cloud is thoughtfully designed to require the least permissions necessary to enable all features and ensure the customer’s environment remains secure at all times. Typically, there are two options for an integration to authenticate to Confluent Cloud:
API keys
Confluent Cloud API keys can be used to control access to Confluent Cloud components and resources. Each API key consists of a key and a secret. Confluent recommends users set Use API Keys to Authenticate to Confluent Cloud.
How keys and secrets are stored is important. Do not store keys and secrets in plain text. A recommended practice is to dynamically inject secrets when connecting to Confluent Cloud using a secrets vault. For additional information, see Best Practices for Using API Keys on Confluent Cloud.
OAuth
Use OAuth/OIDC to Authenticate to Confluent Cloud supports short-lived credentials for an integration to authenticate with Confluent Cloud resources. OAuth 2.0 is an open-standard protocol that grants access to supported clients using a temporary access token. Supported clients use delegated authorization to attach and use Confluent Cloud resources and data on behalf of a user or application. It is important to be aware of OAuth limitations, notably usage limitations for cluster types and clients. For more information, see Limitations. For more information about authenticating to Confluent Cloud, see Security Protections for Authentication on Confluent Cloud.
End-user service account authentication
Confluent customers (end-users) in a production environment should use a dedicated service account. While a user account can be used for authentication, your integration should encourage authentication using a service account. Users can leave or change roles within a company (or user access may be revoked or changed) which results in an integration failure and loss of production time.
A partner integration does not know what RBAC roles and permissions are assigned for an authenticated service account. If the service account used for authentication has insufficient permissions, the partner integration should provide actionable error information so the Confluent customer knows what to do. Ideally, your integration should recommend proper roles or permissions that must be granted to the associated account.
At a minimum, the service account should have at least one of the following roles assigned to read, consume, write, and produce to Confluent Cloud. For a complete list of roles, see Predefined RBAC Roles in Confluent Cloud.
Role | Scope | Description |
|---|---|---|
DeveloperRead | Topic and Consumer Group | To read and consume data from a Confluent Cloud topic, the service account must have at least the |
DeveloperWrite | Topic | To write and produce data to a Confluent Cloud topic, the service account must have at least the |
If the integration has advanced features, additional roles may need to be assigned. For example, if an integration needs to create a topic to support a dead letter queue or for a new data stream, the integration may require the ability to create a new topic. In this case, the service account must have the DeveloperManage assigned role. For a complete list of roles, see Predefined RBAC Roles in Confluent Cloud.
Caution
When a Confluent Cloud customer deletes a user account or service account, all associated API keys are deleted. Any integrations using a deleted API key lose access.
Schema Registry and Stream Governance
Stream Governance on Confluent Cloud establishes trust in the data streams moving throughout your cloud environments and delivers an easy, self-service experience for more teams to put streaming data pipelines to work. CwC integrations are expected to connect to and use Schema Registry in order to fully unlock the capabilities of Stream Governance in Confluent Cloud.
At a minimum, this includes support for using Schema Registry with at least Avro schemas, preferably any schema supported by Confluent Cloud. Integrations are encouraged to provide support for the Confluent Stream Catalog, including tags and business metadata.
Confluent Cloud APIs
Basic integrations may simply connect to an existing topic and leverage existing schemas, but more feature-rich integrations may need to create and manage topics and schemas within Confluent Cloud.
For example, if an integration is connecting to Confluent Cloud to send data, it may be best for the integration to create and customize the target topic without requiring the user to do it separately. This creates a more seamless experience for the user and reduces the application switching to set up the integration.
For CRUD actions like this, you can leverage the Admin APIs within the Confluent Cloud Cluster or the REST API. For additional information, see Confluent Cloud APIs.
In a CwC integration, the integrated partner application is sending (producing) data to Confluent Cloud or reading (consuming) data from Confluent Cloud. To create this type of integration, the application uses Produce or Consume APIs with Confluent Cloud. For more information about setting up Producers and Consumers and other Kafka basics, see the related content.
Custom identifier
As part of your Confluent Cloud integration, additional custom configuration options are used help identify the integration. These custom configurations will be shared with you by your Partner Success Manager as part of the verification process. Typically, this involves a client.id prefix. Note that these additional configurations are unique identifiers to your CwC integration and are solely used to measure the adoption of the integration.
Verify an integration
When your integration with Confluent Cloud is built, the next step is to have it verified by Confluent. This verification ensures that your integration meets the security and governance expectations of any Confluent verified integration. To verify your integration, contact your Partner Success Manager or verification@confluent.io or apply as a new partner today using the Confluent Partner Portal.
Verified integration standards
The term verified integration is only currently available to approved Confluent Partners, and aims to give end-users confidence in the build quality, and the ease of deployment across Confluent product options (where applicable). The Confluent Marketplace terms of use still apply.
The checks made for verified integration are carried out at the time of testing and include:
The integration comes from a registered Confluent Partner.
The integration functioned from a user-perspective, at the time of testing, across applicable Confluent product options.
The integration provided suitable documentation for users.
The integration provided an appropriate license (open source, or non-conflicting third party proprietary).
The integration demonstrated adherence to essential best- practice standards, where relevant to the integration type.
Some key sample standards for connector-type integrations are shown below:
Best practice standards | Confluent documentation reference |
|---|---|
With regard to secrets management, credentials are stored securely and in line with best operational practices. Such management should employ a dedicated solution such as Vault, Secret Manager or Key Vault. | |
The client configuration can be set up using resource scoped API Keys and Secrets from Confluent Cloud to ensure “principle of least privilege” | |
If source integration (using producer API) there is a record key. | |
Data discovery is simple (the user is presented with a list of topics or entities) | |
Public Endpoint Support exists | |
Where applicable, schema registry is supported | |
Documentation provides information on the Kafka Client Library version used | |
Documentation is clear on the supported data types (JSON, AVRO, Protobuf) | Kafka Streams Data Types and Serialization | Confluent Documentation |
Custom Connect deployment effectively manages any required sensitive properties and secrets | |
The connector supports logging practices and ability to set logging levels | |
Documentation provides information on the Confluent platform supported versions* | Supported Versions and Interoperability for Confluent Platform |
Provides sample connector configuration for use by Kafka Connect | |
Connect configuration can be submitted through an API call | |
Documentation provides information on the Java version required | Supported Versions and Interoperability for Confluent Platform |
Documentation provides information about whether the connector supports single worker or multiple worker nodes | |
Works with CP Standalone and CP multiple nodes | How to Use Kafka Connect - Get Started | Confluent Documentation |
Supports SSL/SASL communication and ACL (Secure communication between worker nodes and the application) | Encrypt and authenticate Confluent Platform and resources with TLS |
Documentation provides a sample (connector) configuration for use by Custom Connect API | |
Provides a list of sensitive properties to set on connector setup | |
Provides a list of required endpoints to an allowlist so that Custom Connector will function correctly | |
The connector has a “Fail Fast & Abort” strategy | Kafka Connect Deep Dive – Error Handling and Dead Letter Queues | Confluent |
Publish an integration
After your native CwC integration is verified by Confluent, work with your Partner Success Manager to promote the integration and increase its visibility. Your Partner Success Manager will guide you through the options that both you and Confluent can do to support amplifying the integration.
Partner integration directory
The following table lists available native partner integrations available for CwC.
Partner | Category | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
SAP and Oracle integrator | SAP Kafka Integration: Real-time Data Flow for Business Agility | |
Streaming-native API infrastructure | ||
Analytics | ||
Analytics | ||
Serverless compute | ||
CDC | ||
Stream processing | ||
SAP integrator | ||
Analytics | - | |
ETL | ||
Analytics | ||
Operational database | - | |
Operational database | - | |
Data pipelines | ||
Stream processing | ||
Stream processing | - | |
MQTT | ||
Analytics | ||
IOT | ||
Real-time analytics | ||
Real-time analytics platform | ||
Real-time analytics | ||
Operational / Graph database | - | |
Data integration | - | |
Real-time analytics | ||
Lakehouse | The Ultimate Data Lakehouse for Streaming Data Using Onehouse + Confluent | |
SAP integrator | ||
Vector database | Building real-time AI applications with Pinecone and Confluent Cloud | |
CDC | - | |
CDC | ||
App development | ||
In-memory database | - | |
Real-time analytics | ||
Real-time analytics | ||
ERP data integration | ||
Real-time analytics | Ingest data from Confluent Cloud (Kafka) - SingleStore Spaces | |
Real-time analytics | ||
Middle-tier platform | ||
Low-code development | ||
Real-time analytics | ||
Real-time analytics | ||
Data pipelines | ||
IOT | ||
Vector database | - | |
Vector database | - |