Configure RBAC for Confluent Platform Using Confluent for Kubernetes
Confluent for Kubernetes (CFK) supports Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). RBAC is powered by Confluent’s Metadata Service (MDS), which integrates with an LDAP server and acts as the central authority for authorization and authentication data. RBAC leverages role bindings to determine which users and groups can access specific resources and what actions the users can perform on those resources.
Confluent provides audit logs, that record the runtime decisions of the permission checks that occur as users/applications attempt to take actions that are protected by ACLs and RBAC.
There are a set of principals and role bindings required for the Confluent components to function, and those are automatically generated when CFK is deployed.
When you deploy Confluent Platform with RBAC enabled, CFK automates the security setup. Here’s the end state architecture:
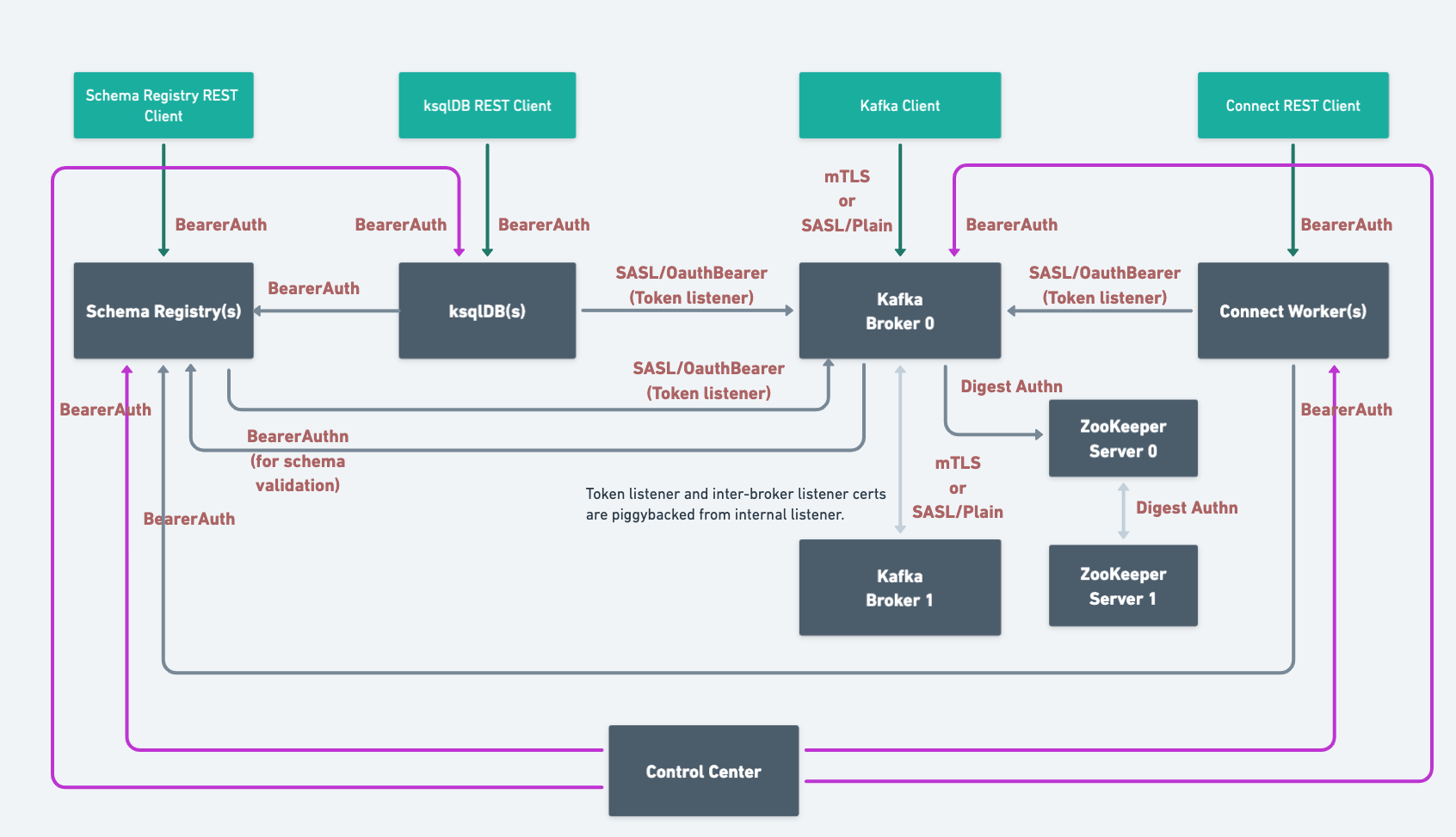
Based on the components and features you use, you need to configure the following additional role bindings:
Requirements and considerations
The following are the requirements for enabling and using RBAC with CFK:
You must have an LDAP server that Confluent Platform can use for authentication.
Currently, CFK only supports the
GROUPSLDAP search mode. The search mode indicates if the user-to-group mapping is retrieved by searching for group or user entries. If you need to use theUSERSsearch mode, specify using theconfigOverridessetting in the Kafka CR as below:spec: configOverrides: server: - ldap.search.mode=USERS
See Sample Configuration for User-Based Search for more information.
Confluent REST service is automatically enabled for RBAC and cannot be disabled when RBAC is enabled.
Use the Kafka bootstrap endpoint (same as the MDS endpoint) to access Confluent REST API.
You must create the user principals in LDAP that will be used by Confluent Platform components. These are the default user principals:
Kafka:
kafka/kafka-secretConfluent REST API:
erp/erp-secretConfluent Control Center (Legacy):
c3/c3-secretksqlDB:
ksql/ksql-secretSchema Registry:
sr/sr-secretReplicator:
replicator/replicator-secretConnect:
connect/connect-secret
Create the LDAP user/password for a user who has a minimum of LDAP read-only permissions to allow Metadata Service (MDS) to query LDAP about other users. For example, you’d create a user
mdswith passwordDeveloper!Create a user for the Admin REST service in LDAP and provide the username and password.
RBAC with CFK can be enabled only for new installations. You cannot upgrade an existing cluster and enable it with RBAC.
Configure RBAC with CFK
The comprehensive security tutorial walks you through an end-to-end setup of role-based access control (RBAC) for Confluent with CFK. We recommend you take the CustomResource spec and the steps outlined in the scenario as a starting point and customize for your environment.
Enable RBAC for Kafka
To configure and deploy Kafka with the Confluent RBAC:
Specify the MDS and LDAP settings in your Kafka Custom Resource (CR):
kind: Kafka spec: services: mds: --- [1] tokenKeyPair: --- [2] provider: type: ldap --- [3] ldap: --- [4] address: ldap://ldap.confluent.svc.cluster.local:389 authentication: type: simple simple: secretRef: credential configurations: groupNameAttribute: cn groupObjectClass: group groupMemberAttribute: member groupMemberAttributePattern: CN=(.*),DC=test,DC=com groupSearchBase: dc=test,dc=com userNameAttribute: cn userMemberOfAttributePattern: CN=(.*),DC=test,DC=com userObjectClass: organizationalRole userSearchBase: dc=test,dc=com
[1] Required.
[2] Required. The token key pair to authenticate to MDS.
For details, see MDS authentication token keys.
[3] Required for LDAP.
[4] Required. A few examples properties are given above.
Specify the RBAC settings in your Kafka Custom Resource (CR):
kind: Kafka spec: authorization: type: rbac --- [1] superUsers: --- [2] dependencies: kafkaRest: --- [3] authentication: type: bearer --- [4] bearer: secretRef: --- [5] directoryPathInContainer: --- [6]
[1] Required.
[2] Required. The super users to be given the admin privilege on the Kafka cluster.
These users have no access to resources in other Confluent Platform clusters unless they also configured with specific role bindings on the clusters.
This list is in the
User:<user-name>format. For example:superUsers: - "User:kafka" - "User:testadmin"
[3] Required. The REST client configuration for MDS when RBAC is enabled.
[4] Required.
[5] or [6] Required.
When RBAC is enabled (
spec.authorization.type: rbac), CFK always uses the Bearer authentication for Confluent components, ignoring thespec.authenticationsetting. It is not possible to set the component authentication type to mTLS when RBAC is enabled.[5] The username and password are loaded through secretRef.
The expected key is
bearer.txt.The value for the key is:
username=<username> password=<password>
[6] Provide the path where required credentials are injected by Vault. See [5] for the expected key and the value.
Configure the Admin REST Class CR.
You need to use the
bearerauthentication for the Admin Rest Class as shown below.For the rest of the configuration details for the Admin REST Class, see Manage Confluent Admin REST Class for Confluent Platform Using Confluent for Kubernetes.
kind: KafkaRestClass metadata: name: --- [1] namespace: spec: kafkaRest: authentication: type: bearer --- [2] bearer: secretRef: --- [3] directoryPathInContainer: --- [4]
[1] Optional. If not specified,
defaultis used as the name of this REST class.[2] Required for RBAC.
[3] or [4] Required.
[3] The username and password are loaded through secretRef.
The expected key is
bearer.txt.The value for the key is:
username=<username> password=<password>
[4] Provide the path where required credentials are injected by Vault. See [2] for the expected key and the value.
When RBAC is enabled (
spec.authorization.type: rbac), CFK always uses the Bearer authentication for Confluent components, ignoring thespec.authenticationsetting. It is not possible to set the component authentication type to mTLS when RBAC is enabled.
MDS authentication token keys
To sign the token generated by the MDS server, you can use the PKCS#1 or PKCS#8 PEM key format. When using PKCS#8, the private key can be unencrypted or encrypted with a passphrase.
To provide the MDS token keys:
Create a PEM key pair as described in Create a PEM key pair for MDS.
If using an encrypted private key:
Create a passphrase file with the name,
mdsTokenKeyPassphrase.txt.In the
mdsTokenKeyPassphrase.txtfile, add the key-value pair with themdsTokenKeyPassphrasekey and the passphrase that the private key was encrypted with:
mdsTokenKeyPassphrase=<passphrase>
Add the public key and the token key pair to a secret or inject it in a directory path in the container using Vault.
To use an encrypted private key, add the passphrase value to the secret or the directory path in the container, as well.
An example command to create a secret with an unencrypted private key:
kubectl create secret generic mds-token \ --from-file=mdsPublicKey.pem=mds-publickey.txt \ --from-file=mdsTokenKeyPair.pem=mds-tokenkeypair.txt \ --namespace confluent
An example command to create a secret with an encrypted private key:
kubectl create secret generic mds-token \ --from-file=mdsPublicKey.pem=mds-publickey.txt \ --from-file=mdsTokenKeyPair.pem=mds-tokenkeypair.txt \ --from-file=mdsTokenKeyPassphrase.pem=mdsTokenKeyPassphrase.txt \ --namespace confluent
In the Kafka CR, specify the token key pair to authenticate to MDS:
kind: Kafka spec: services: mds: tokenKeyPair: secretRef: --- [1] directoryPathInContainer: --- [2] encryptedTokenKey: --- [3]
[1] The name of the Kubernetes secret that contains the public key and the token key pair to sign the token generated by the MDS server.
[2] The directory path in the container where the required public key and the token key pair are injected by Vault.
[3] Optional. Set to
trueto use an encrypted private key. The default value isfalse.
Enable RBAC for KRaft controller
To enable the Confluent RBAC for a KRaft-based deployment:
Configure MDS as shown above in Enable RBAC for Kafka.
Configure the KraftController CR:
kind: KRaftController spec: dependencies: mdsKafkaCluster: bootstrapEndpoint: --- [1] authentication: --- [2] type: --- [3] jaasConfig: --- [4] jaasConfigPassThrough: --- [5] oauthbearer: --- [6] secretRef: —-- [7] directoryPathInContainer: --- [8] tls: --- [9] enabled: --- [10]
[1] Required. Specify the MDS Kafka bootstrap endpoint.
[2] Specify the client-side authentication for the MDS Kafka cluster.
[3] Required. Specify the client-side authentication type for the MDS Kafka. Valid options are
plain,oauthbearer, andmtls.[4] When the authentication type (
type) is set toplain, specify the credential using JAAS config. For details, see Create client-side SASL/PLAIN credentials using JAAS config.[5] When the authentication type (
type) is set toplain, specify the credential using JAAS config passthrough. For details, see Create client-side SASL/PLAIN credentials using JAAS config pass-through.[6] Use Oauth Bearer Token to provide principals to authenticate with MDS Kafka.
[7] The Oauth username and password are loaded through secretRef. The expected key is
bearer.txt, and the value for the key is:username=<username> password=<password>
An example command to create a secret to use for this property:
kubectl create secret generic oauth-client \ --from-file=bearer.txt=/some/path/bearer.txt \ --namespace confluent
[8] The directory in the Confluent Control Center (Legacy) container where the expected Bearer credentials are injected by vault. See above ([7]) for the expected format.
See Provide secrets for Confluent Platform component CR for providing the credential and required annotations when using Vault.
[9] The client-side TLS setting for the MDS Kafka cluster. For details, see Client-side mTLS authentication for Kafka.
[10] Required for mTLS authentication. Set to
true.
An example KRaftController CR:
kind: KRaftController spec: dependencies: mdsKafkaCluster: bootstrapEndpoint: kafka.operator.svc.cluster.local:9092 authentication: type: plain jaasConfig: secretRef: credential tls: enabled: true
Enable RBAC for other Confluent Platform components
To configure and deploy other non-Kafka components with the Confluent RBAC:
Specify the settings in the component CR:
spec: authorization: type: rbac --- [1] kafkaRestClassRef: --- [2] name: default dependencies: mds: endpoint: --- [3] tokenKeyPair: --- [4] secretRef: directoryPathInContainer authentication: type: bearer --- [5] bearer: secretRef: --- [6] directoryPathInContainer: --- [7]
[1] Required for RBAC.
[2] If
kafkaRestClassRefis not configured, the kafkaRestClass with the name,default, in the current namespace is used.[3] Required. MDS endpoint.
[4] Required. The token key pair and the public key to authenticate to the MDS. Use
secretRefordirectoryPathInContainerto specify.You need to add the public key and the token key pair to the secret or directoryPathInContainer. For details, see Create a PEM key pair for MDS.
An example command to create a secret is:
kubectl create secret generic mds-token \ --from-file=mdsPublicKey.pem=mds-publickey.txt \ --from-file=mdsTokenKeyPair.pem=mds-tokenkeypair.txt \ --namespace confluent
[5] Required.
[6] or [7] Required.
When RBAC is enabled (
spec.authorization.type: rbac), CFK always uses the Bearer authentication for Confluent components, ignoring thespec.authenticationsetting. It is not possible to set the component authentication type to mTLS when RBAC is enabled.[6] The username and password are loaded through secretRef.
The expected key is
bearer.txt.The value for the key is:
username=<username> password=<password>
[7] Provide the path where required credentials are injected by Vault. See [2] for the expected key and the value.
Use an existing Admin REST Class or create a new Admin REST Class CR as described in the previous section.
Automated creation of role bindings for Confluent Platform component principals
CFK automatically creates all required role bindings for Confluent Platform components as ConfluentRoleBinding custom resources (CRs).
Review the role bindings created by CFK:
kubectl get confluentrolebinding
Grant role to Kafka user to access Schema Registry
Use the following ConfluentRolebinding CR to create the required role binding to access Schema Registry:
apiVersion: platform.confluent.io/v1beta1
kind: ConfluentRolebinding
metadata:
name: internal-schemaregistry-schema-validation
namespace: <namespace>
spec:
principal:
name: <user-id>
type: user
clustersScopeByIds:
schemaRegistryClusterId: <schema-registry-group-id>
kafkaClusterId: <kafka-cluster-id>
resourcePatterns:
- name: "*"
patternType: LITERAL
resourceType: Subject
role: DeveloperRead
Grant roles to a Confluent Control Center (Legacy) user to administer Confluent Platform
Control Center (Legacy) users require separate roles for each Confluent Platform component and resource they wish to view and administer in the Control Center (Legacy) UI. Grant explicit permissions to the users as shown below.
In the following example, the testadmin principal is used as a Control Center (Legacy) UI user.
Grant permission to view and administer Confluent Platform components
The rolebinding CRs in the examples GitHub repo specifies the permissions needed in CFK. Create the rolebindings with the following command:
kubectl apply -f \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/confluentinc/confluent-kubernetes-examples/master/security/production-secure-deploy/controlcenter-testadmin-rolebindings.yaml
Check the roles created:
kubectl get confluentrolebinding
Troubleshooting: Verify MDS configuration
Log into MDS to verify the correct configuration and to get the Kafka cluster ID. You need the Kafka cluster ID for component role bindings.
Replace https://<mds_endpoint> in the below commands with the value you set in the spec.dependencies.mds.endpoint in the Kafka CR.
Log into MDS as the Kafka super user as below:
confluent login \ --url https://<mds_endpoint> \ --ca-cert-path <path-to-cacerts.pem>
You need to pass the
--ca-cert-pathflag if:You have configured MDS to serve HTTPS traffic (
kafka.spec.dependencies.mds.tls.enabled: true).The CA used to issue the MDS certificates is not trusted by system where you are running these commands.
Provide the Kafka username and password when prompted, in this example,
kafkaandkafka-secret.You get a response to confirm a successful login.
Verify that the advertised listeners are correctly configured using the following command:
curl -ik \ -u '<kafka-user>:<kafka-user-password>' \ https://<mds_endpoint>/security/1.0/activenodes/https
Get the Kafka cluster ID using one of the following commands:
confluent cluster describe --url https://<mds_endpoint>
curl -ik \ https://<mds_endpoint>/v1/metadata/id