Install ksqlDB for Confluent Platform
ksqlDB is available as a component of Confluent Platform and Confluent Cloud. For Confluent Platform the ksqlDB binaries are located at https://www.confluent.io/download/ as a part of the Confluent Platform bundle.
ksqlDB must have access to a running Apache Kafka® cluster, which can be in your data center, in a public cloud, Confluent Cloud, etc.
Ready to get started?
Sign up for Confluent Cloud, the fully managed cloud-native service for Apache Kafka® and get started for free using the Cloud quick start.
Download Confluent Platform, the self managed, enterprise-grade distribution of Apache Kafka and get started using the Confluent Platform quick start.
- Docker support
You can deploy ksqlDB by using Docker containers. Starting with Confluent Platform 4.1.2, Confluent maintains images at Docker Hub.
Watch the screencast of Installing and Running KSQL on YouTube.
Supported Versions and Interoperability
For ksqlDB compatibility with Confluent Platform and Kafka Streams, see Supported Versions and Interoperability.
Installation Instructions
Follow the instructions at Quick Start for Confluent Platform.
Also, you can install ksqlDB individually by using the confluent-ksql package. For more information, see Confluent Platform Packages.
Scale Your ksqlDB Server Deployment
You can scale ksqlDB by adding more capacity per server (vertically) or by adding more servers (horizontally). Also, you can scale ksqlDB clusters during live operations without loss of data. For more information, see Scaling ksqlDB.
Starting the ksqlDB Server
The ksqlDB servers are run separately from the ksqlDB CLI client and Kafka brokers. You can deploy servers on remote machines, VMs, or containers and then the CLI connects to these remote servers.
You can add or remove servers from the same resource pool during live operations, to elastically scale query processing. You can use different resource pools to support workload isolation. For example, you could deploy separate pools for production and for testing.
You can only connect to one ksqlDB server at a time. The ksqlDB CLI does not support automatic failover to another ksqlDB server.
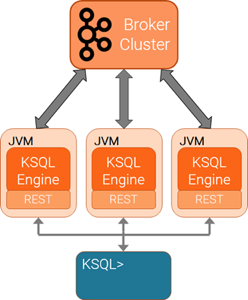
Follow these instructions to start ksqlDB server using the ksql-server-start script.
Tip
These instructions are based on the assumption that you are installing Confluent Platform by using ZIP or TAR archives. For more information, see Install Confluent Platform On-Premises.
Specify your ksqlDB server configuration parameters. You can also set any property for the Kafka Streams API, the Kafka producer, or the Kafka consumer. The required parameters are
bootstrap.serversandlisteners. You can specify the parameters in the ksqlDB properties file or theKSQL_OPTSenvironment variable. Properties set withKSQL_OPTStake precedence over those specified in the properties file.A recommended approach is to configure a common set of properties using the ksqlDB configuration file and override specific properties as needed, using the
KSQL_OPTSenvironment variable.Here are the default settings:
bootstrap.servers=localhost:9092 listeners=http://0.0.0.0:8088
For more information, see Configure ksqlDB Server.
Start a server node with this command:
ksql-server-start ${CONFLUENT_HOME}/etc/ksqldb/ksql-server.properties
Tip
You can view the ksqlDB server help text by running
ksql-server-start --help.NAME server - KSQL Cluster SYNOPSIS server [ {-h | --help} ] [ --queries-file <queriesFile> ] [--] <config-file> OPTIONS -h, --help Display help information --queries-file <queriesFile> Path to the query file on the local machine. -- This option can be used to separate command-line options from the list of arguments (useful when arguments might be mistaken for command-line options) <config-file> A file specifying configs for the KSQL Server, KSQL, and its underlying Kafka Streams instance(s). Refer to KSQL documentation for a list of available configs.Have a look at this page for instructions on running ksqlDB in non-interactive (aka headless) mode.
Starting the ksqlDB CLI
The ksqlDB CLI is a client that connects to the ksqlDB servers.
You can start the ksqlDB CLI by providing the connection information to the ksqlDB server.
LOG_DIR=./ksql_logs ${CONFLUENT_HOME}/bin/ksql http://localhost:8088
Important
By default ksqlDB attempts to store its logs in a directory called logs that is relative to the location of the ksql executable. For example, if ksql is installed at /usr/local/bin/ksql, then it would attempt to store its logs in /usr/local/logs. If you are running ksql from the default Confluent Platform location, $CONFLUENT_HOME/bin, you must override this default behavior by using the LOG_DIR variable.
After ksqlDB is started, your terminal should resemble this.
===========================================
= _ _ ____ ____ =
= | | _____ __ _| | _ \| __ ) =
= | |/ / __|/ _` | | | | | _ \ =
= | <\__ \ (_| | | |_| | |_) | =
= |_|\_\___/\__, |_|____/|____/ =
= |_| =
= The Database purpose-built =
= for stream processing apps =
===========================================
Copyright 2017-2022 Confluent Inc.
CLI v8.1.1, Server v8.1.1 located at http://localhost:8088
Server Status: RUNNING
Having trouble? Type 'help' (case-insensitive) for a rundown of how things work!
ksql>
Tip
You can view the ksqlDB CLI help text by running ksql --help.
NAME
ksql - KSQL CLI
SYNOPSIS
ksql [ --config-file <configFile> ]
[ --confluent-api-key <ccloudApiKey> ]
[ --confluent-api-secret <ccloudApiSecret> ]
[ {--define | -d} <definedVars>... ]
[ {--execute | -e} <execute> ] [ {--file | -f} <scriptFile> ]
[ {-h | --help} ] [ --output <outputFormat> ]
[ {--password | -p} <password> ]
[ --query-row-limit <streamedQueryRowLimit> ]
[ --query-timeout <streamedQueryTimeoutMs> ]
[ {--token | -t} <token> ] [ {--user | -u} <userName> ] [--] [ <server> ]
OPTIONS
--config-file <configFile>
A file specifying configs for Ksql and its underlying Kafka Streams
instance(s). Refer to KSQL documentation for a list of available
configs.
--confluent-api-key <ccloudApiKey>
If you're connecting to a Confluent Cloud ksqlDB server and would
like to use ksqlDB's connector management capabilities, then
provide your Confluent Cloud API key here. The API key secret must
be specified separately with the --confluent-api-secret flag
--confluent-api-secret <ccloudApiSecret>
If you're connecting to a Confluent Cloud ksqlDB server and would
like to use ksqlDB's connector management capabilities, then
provide your Confluent Cloud API key secret here. The API key
itself must be specified separately with the --confluent-api-key
flag
--define <definedVars>, -d <definedVars>
Define variables for the CLI session (equivalent to the DEFINE
statement).
--execute <execute>, -e <execute>
Execute one or more SQL statements and quit.
--file <scriptFile>, -f <scriptFile>
Execute commands from a file and exit.
-h, --help
Display help information
--output <outputFormat>
The output format to use (either 'JSON' or 'TABULAR'; can be
changed during REPL as well; defaults to TABULAR)
--password <password>, -p <password>
If your KSQL server is configured for authentication, then provide
your password here. The username must be specified separately with
the -u/--user flag
--query-row-limit <streamedQueryRowLimit>
An optional maximum number of rows to read from streamed queries
This options value must fall in the following range: value >= 1
--query-timeout <streamedQueryTimeoutMs>
An optional time limit (in milliseconds) for streamed queries
This options value must fall in the following range: value >= 1
--token <token>, -t <token>
If your KSQL server is configured for authentication, then provide
the confluent token retrieved from confluent cli here.
--user <userName>, -u <userName>
If your KSQL server is configured for authentication, then provide
your user name here. The password must be specified separately with
the -p/--password flag
--
This option can be used to separate command-line options from the
list of arguments (useful when arguments might be mistaken for
command-line options)
<server>
The address of the Ksql server to connect to (ex:
http://confluent.io:9098)
This option may occur a maximum of 1 times
Configuring ksqlDB for Confluent Cloud
You can use ksqlDB with a Kafka cluster in Confluent Cloud. For more information, see Connecting ksqlDB to Confluent Cloud.