Deploy Secure Standalone REST Proxy in Confluent Platform
REST Proxy has two separate connections, one to a client and another to the broker. They are separate and distinct, and each of these connections requires a completely separate and different security configuration. You must configure security twice: once for the client-REST Proxy connection, and again for the REST Proxy-broker connection.
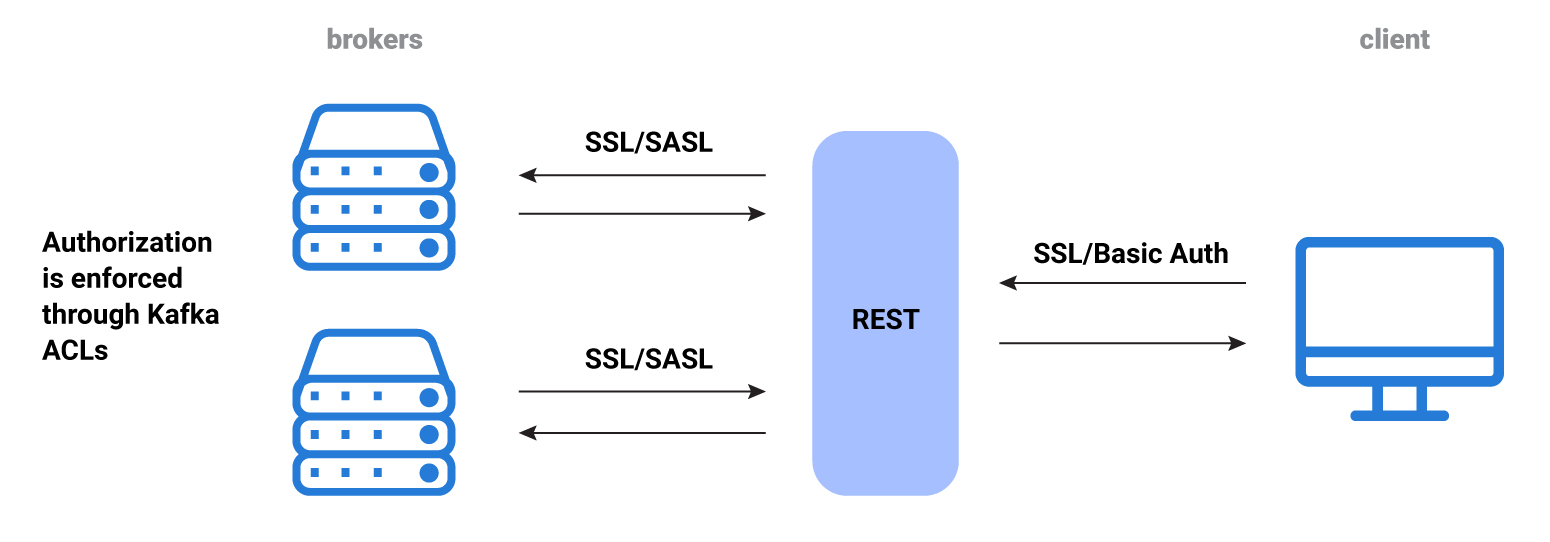
REST Proxy security workflow
When a connection is initialized, there is a basic work request to REST Proxy. Such requests are plain text/JSON, and contain metadata and content to be stored in Kafka, or requests to retrieve data from Kafka. REST Proxy receives these requests, translates them into Kafka requests, and satisfies them with the Kafka broker.
No authorization actually occurs on REST Proxy (unlike in Schema Registry) so you must set broker ACLs to enforce any restrictions.
REST Proxy Authentication
You can use HTTP Basic Authentication or mutual TLS (mTLS) authentication for communication between a client and REST Proxy. You can use SASL or mTLS for communication between REST Proxy and the brokers.
HTTP Basic Authentication
With HTTP Basic Authentication you can authenticate with REST Proxy using a username and password pair. They are presented to the REST Proxy server using the Authorization HTTP header.
To enable HTTP Basic Authentication:
Add the following configuration to your REST Proxy properties file (
etc/kafka-rest/kafka-rest.properties):authentication.method=BASIC authentication.realm=KafkaRest authentication.roles=thisismyrole
Create a JAAS configuration file. For an example, see
<CONFLUENT_HOME/etc/kafka-rest/rest-jaas.properties:KafkaRest { org.eclipse.jetty.jaas.spi.PropertyFileLoginModule required debug="true" file="${CONFLUENT_HOME}/etc/kafka-rest/password.properties"; };Tip
KafkaRestis in line with the realm specified asauthentication.realminkafka-rest.properties.Create a password properties file (
${CONFLUENT_HOME}/etc/kafka-rest/password.properties). For example:thisismyusername: thisismypass,thisismyrole
Start REST Proxy with HTTP Basic auth:
KAFKAREST_OPTS="-Djava.security.auth.login.config=${CONFLUENT_HOME}/etc/kafka-rest/rest-jaas.properties" \ kafka-rest-start etc/kafka-rest/kafka-rest.properties
Login to your REST Proxy with the username
thisismyusernameand the passwordthisismypass. The password in yourpassword.propertiesfile can also be hashed. For more information, see this link.
Configuration Options
authentication.methodWhich method should REST Proxy use to authenticate requests. One of
NONEorBASIC. To activate HTTP Basic Authentication, you must set it toBASIC.Type: string
Default: “NONE”
Importance: high
authentication.realmIf
authentication.method = BASIC, this configuration tells which section from the system JAAS configuration file to use to authenticate HTTP Basic Authentication credentials.Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: high
authentication.rolesIf
authentication.method = BASIC, this configuration tells which user roles are allowed to authenticate with REST Proxy through HTTP Basic Authentication. If set to*, any role will be allowed to authenticate.Type: string
Default: “*”
Importance: medium
Mutual TLS authentication
With mutual TLS (mTLS) authentication, you can authenticate with a HTTPS enabled REST Proxy using a client side X.509 certificate.
To enable mTLS, you must first enable HTTPS on REST Proxy. See REST Proxy Configuration Options for HTTPS for the configuration options you must set.
After HTTPS is configured, you must configure the REST Proxy truststore to be able to verify the incoming client X.509 certificates. For example, you can configure the REST Proxy truststore to point to a keystore with the root CA certificate used to sign the client certificates loaded into it.
Finally, you can turn mTLS on by setting ssl.client.authentication to REQUIRED.
Configuration Options
ssl.client.authDEPRECATED: Used for HTTPS. Whether or not to require the HTTPS client to authenticate using the server’s trust store. To enable mTLS, the value must be set to
true. Usessl.client.authenticationinstead.Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: medium
ssl.client.authenticationUsed for HTTPS. Whether to require the HTTPS client to authenticate using the server’s trust store. To enable mTLS, the value must be set to
REQUIRED.This configuration overrides the deprecated
ssl.client.auth.Valid values are NONE, REQUESTED or REQUIRED. NONE disables TLS client authentication, REQUESTED requests but does not require TLS client authentication, and REQUIRED requires TLS HTTPS clients to authenticate using the server’s truststore.
Type: string
Default: NONE
Importance: medium
ssl.truststore.locationLocation of the trust store.
Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: high
ssl.truststore.passwordThe password for the trust store file.
Type: password
Default: “”
Importance: high
ssl.truststore.typeThe type of trust store file.
Type: string
Default: JKS
Importance: medium
Authentication between REST Proxy and Kafka Brokers
If you are using REST Proxy to communicate with a secured Kafka broker, you must configure REST Proxy with appropriate credentials so that it can authenticate with Kafka. Kafka can be configured to authenticate with SASL and mTLS. The following section provides details on how to configure REST Proxy for each case.
SASL Authentication
Kafka SASL configurations are described here.
Note that all the SASL configurations (for REST Proxy to broker communication) are prefixed with client.. If you want the configuration to apply just to admins, consumers or producers, replace the prefix with admin., consumer. or producer..
Important
Make sure the bootstrap.servers configuration is set with SASL_PLAINTEXT://host:port (or SASL_SSL://host:port) end-points, or you will accidentally open a SASL connection to a non-SASL port.
To enable SASL authentication with the Kafka broker set client.security.protocol to either SASL_PLAINTEXT or SASL_SSL.
Then set client.sasl.jaas.config with the credentials to be used by REST Proxy to authenticate with Kafka. For example:
client.sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username="kafkarest" password="kafkarest";
Alternatively you can create a JAAS config file, for example etc/kafka-rest/etc/kafka-rest/rest-jaas.properties:
KafkaClient {
org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required
username="kafkarest"
password="kafkarest";
};
The name of the section in the JAAS file must be KafkaClient. Then pass it as a JVM argument:
export KAFKAREST_OPTS="-Djava.security.auth.login.config=${CONFLUENT_HOME}/etc/kafka-rest/rest-jaas.properties"
For details about configuring Kerberos see JDK’s Kerberos Requirements.
Configuration Options
client.security.protocolProtocol used to communicate with brokers. Valid values are:
PLAINTEXT,SSL,SASL_PLAINTEXT,SASL_SSL.Type: string
Default: PLAINTEXT
Importance: high
client.sasl.jaas.configJAAS login context parameters for SASL connections in the format used by JAAS configuration files. JAAS configuration file format is described in Oracle’s documentation. The format for the value is: ‘(=)*;’
Type: string
Default: null
Importance: high
client.sasl.kerberos.service.nameThe Kerberos principal name that Kafka runs as. This can be defined either in Kafka’s JAAS config or in Kafka’s configuration.
Type: string
Default: null
Importance: medium
client.sasl.mechanismSASL mechanism used for client connections. This may be any mechanism for which a security provider is available. GSSAPI is the default mechanism.
Type: string
Default: GSSAPI
Importance: medium
client.sasl.kerberos.kinit.cmdKerberos kinit command path.
Type: string
Default: /usr/bin/kinit
Importance: low
client.sasl.kerberos.min.time.before.reloginLogin thread sleep time between refresh attempts.
Type: long
Default: 60000
Importance: low
client.sasl.kerberos.ticket.renew.jitterPercentage of random jitter added to the renewal time.
Type: double
Default: 0.05
Importance: low
client.sasl.kerberos.ticket.renew.window.factorLogin thread will sleep until the specified window factor of time from last refresh to ticket’s expiry has been reached, at which time it will try to renew the ticket.
Type: double
Default: 0.8
Importance: low
Mutual TLS authentication
Kafka TLS configurations are described here.
REST Proxy to Kafka TLS configurations are described here.
To enable mTLS with the Kafka broker you must set client.security.protocol to SSL or SASL_SSL.
If the Kafka broker is configured with ssl.client.authentication=required, and you configure client certificates for REST Proxy with client.ssl.keystore.*, that should make REST Proxy do TLS authentication with the Kafka broker.
Principal Propagation
This is a commercial component of Confluent Platform.
Important
To use Principal Propagation, the REST Proxy Security Plugins are required.
Principal propagation takes the principal from the authentication mechanism configured for a client to authenticate with REST Proxy and propagates this principal when making requests to the Kafka broker. Without principal propagation, authentication terminates at the REST Proxy. This means that all requests to Kafka are made as the REST Proxy user.
From a security perspective, the propagation process is:
The first JSON request (over HTTP) is authenticated using the configured mechanism.
REST Proxy translates the principal used in the HTTP authentication into a principal that can be authenticated (SSL/SASL) against the Kafka broker.
For example, if you use TLS for both stages then you must have the client TLS certificates for REST Proxy too.
Credentials for all principals that will propagate must be present on the REST Proxy server. Note that this is both a technical challenge (for example, TLS principals must map to Kerberos principals) and a security challenge (everything required to impersonate a user is stored in REST Proxy outside the user’s control).
Note
A Kafka consumer is bound to the principal used to create the REST Proxy consumer instance. A consumer name only identifies the consumer instance created using REST, and may not be unique in a consumer group, if the same consumer name is used to create a consumer using a different principal.
The following sections provide further details and configuration examples.
HTTP Basic Authentication to SASL Authentication
To enable HTTP Basic Authentication to SASL Authentication credentials propagation, you must set authentication.method to BASIC, confluent.rest.auth.propagate.method to JETTY_AUTH, and client.security.protocol to either SASL_PLAINTEXT or SASL_SSL.
Security plugin supports all the sasl.mechanism supported by Kafka clients. Just like a regular Kafka client, the plugin also expects a JAAS config file to be configured through -Djava.security.auth.login.config. It is required for all the principals to be specified in the JAAS config file under the section KafkaClient.
In the JAAS config file, all of the principals must be explicitly specified. The plugin supports specifying principals using following supported mechanisms: GSSAPI, PLAIN, SCRAM-SHA-256 and SCRAM-SHA-512. Also, the plugin ignores any configured sasl.mechanism and picks it automatically based on the LoginModule specified for the principal.
The JAAS file should also include the Basic Authentication logic documented here. In the example, the KafkaClient {...} block provides the SASL authentication and the KafkaRest {...} block at the end provides the basic authentication logic.
KafkaClient {
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required
useKeyTab=true
storeKey=true
keyTab="/etc/security/keytabs/restproxy-localhost.keytab"
principal="CN=restproxy/localhost@EXAMPLE.COM";
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required
useKeyTab=true
storeKey=true
keyTab="/etc/security/keytabs/kafka_client_2.keytab"
principal="kafka-client-2@EXAMPLE.COM";
org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required
username="alice-plain"
password="alice-secret";
org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required
username="alice-scram"
password="alice-secret";
org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required
username="alice-scram-256"
password="alice-secret"
mechanism="SCRAM-SHA-256";
};
KafkaRest {
org.eclipse.jetty.jaas.spi.PropertyFileLoginModule required
debug="true"
file="${CONFLUENT_HOME}/etc/kafka-rest/password.properties";
};
Here is the mapping of sasl.mechanism for the configured login modules:
Principal’s Login Module | SASL Mechanism |
|---|---|
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule | GSSAPI |
org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule | PLAIN |
org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule | SCRAM-SHA-512 For SCRAM-SHA-256 set mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-256as an option in ScramLoginModule |
All the mechanisms except SCRAM-SHA-256 would be automatically detected by the plugin and SCRAM-SHA-256 can be explicitly mentioned as an option in the ScramLoginModule.
Configuration Options
confluent.rest.auth.propagate.methodThe mechanism used to authenticate REST Proxy requests. When broker security is enabled, the principal from this authentication mechanism is propagated to Kafka broker requests. Either
JETTY_AUTHorSSL.Type: string
Default: “SSL”
Importance: low
mTLS to SASL Authentication
To enable mTLS to SASL Authentication, you must set ssl.client.auth to true, confluent.rest.auth.propagate.method to SSL, and client.security.protocol to either SASL_PLAINTEXT or SASL_SSL.
The incoming X500 principal from the client is used as the principal while interacting with the Kafka broker. You can use confluent.rest.auth.ssl.principal.mapping.rules to map the DN from the client certificate to a name that can be used for principal propagation. For example, a rule like RULE:^CN=(.*?)$/$1/, would strip off the CN= portion of the DN.
Requires JAAS config file with KafkaClient section containing all principals along with its login module and options; configured via -Djava.security.auth.login.config.
Configuration Options
confluent.rest.auth.propagate.methodThe mechanism used to authenticate REST Proxy requests. When broker security is enabled, the principal from this authentication mechanism is propagated to Kafka broker requests.
Type: string
Default: “SSL”
Importance: low
confluent.rest.auth.ssl.principal.mapping.rulesA list of rules for mapping distinguished name (DN) from the client certificate to short name. The rules are evaluated in order and the first rule that matches a principal name is used to map it to a short name. Any later rules in the list are ignored. By default, DN of the X.500 certificate is the principal. Each rule starts with “RULE:” and contains an expression using the formats below. The default rule returns string representation of the X.500 certificate DN. If the DN matches the pattern, then the replacement command is run over the name. This also supports lowercase/uppercase options, to force the translated result to be all lower/uppercase case. This is done by adding a “/L” or “/U’ to the end of the rule:
Type: list
Default: DEFAULT
Importance: low
Note
Only use
confluent.rest.auth.ssl.principal.mapping.rulesto configure mTLS (SSL) to SASL propagation with REST Proxy. Do not use it to configure TLS/SSL to TLS/SSL propagation with REST Proxy.
TLS Authentication to TLS Authentication
To enable mTLS to mTLS, you must set ssl.client.authentication to REQUIRED, and confluent.rest.auth.propagate.method to SSL.
For TLS propagation to work, it is required to load all the certificates corresponding to the required principals in a single client keystore file. Once this is done, the plugin would pick the appropriate certificate alias based on the logged on principal while making requests to Kafka. Currently, the logged on principal must exactly match the X.509 Principal of the certificate.
For example, if there were two clients integrated to REST Proxy the setup could be as simple as below:
Client Aauthenticates to REST Proxy using its keystore which containsCertificate-AClient Bauthenticates to REST Proxy using its keystore which containsCertificate-BREST Proxy’s keystore
client.ssl.keystore.locationis loaded withCertificate-AandCertificate-B. The certificate is then chosen by the plugin based on who the client is.
Configuration Options
confluent.rest.auth.propagate.methodThe mechanism used to authenticate REST Proxy requests. When broker security is enabled, the principal from this authentication mechanism is propagated to Kafka broker requests.
Type: string
Default: “SSL”
Importance: low
Note
Use confluent.rest.auth.ssl.principal.mapping.rules to configure mTLS to SASL propagation with REST Proxy only. Do not use it to configure TLS to TLS propagation with REST Proxy.
License Client Configuration
A Kafka client is used to check the license topic for compliance. Review the following information about how to configure this license client when using principal propagation.
- Configure license client authentication
When using principal propagation and the following security types, you must configure client authentication for the license topic. For more information, see the following documentation:
- Configure license client authorization
When using principal propagation and RBAC or ACLs, you must configure client authorization for the license topic.
Note
The
_confluent-commandinternal topic is available as the preferred alternative to the_confluent-licensetopic for components such as Schema Registry, REST Proxy, and Confluent Server (which were previously using_confluent-license). Both topics will be supported going forward. Here are some guidelines:New deployments (Confluent Platform 6.2.1 and later) will default to using
_confluent-commandas shown below.Existing clusters will continue using the
_confluent-licenseunless manually changed.Newly created clusters on Confluent Platform 6.2.1 and later will default to creating the
_confluent-commandtopic, and only existing clusters that already have a_confluent-licensetopic will continue to use it.
RBAC authorization
Run this command to add
ResourceOwnerfor the component user for the Confluent license topic resource (default name is_confluent-command).confluent iam rbac role-binding create \ --role ResourceOwner \ --principal User:<service-account-id> \ --resource Topic:_confluent-command \ --kafka-cluster <kafka-cluster-id>
ACL authorization
Run this command to configure Kafka authorization, where bootstrap server, client configuration, service account ID is specified. This grants create, read, and write on the
_confluent-commandtopic.kafka-acls --bootstrap-server <broker-listener> --command-config <client conf> \ --add --allow-principal User:<service-account-id> --operation Create --operation Read --operation Write \ --topic _confluent-command
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
This is a commercial component of Confluent Platform.
Prerequisites:
RBAC-enabled Kafka and Schema Registry clusters. For details about RBAC, see Authorize using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in Confluent Platform.
HTTPS is recommended, but not required.
Confluent REST Proxy supports the cross-component, proprietary role-based access control (RBAC) solution to enforce access controls across Confluent Platform. The REST Proxy security plugin supports a bearer token-based authentication mechanism. With token authentication, REST Proxy can impersonate the user requests when communicating with Kafka brokers and Schema Registry clusters.
RBAC REST Proxy security resolves a number of usability challenges, including:
Local configuration of principals. With RBAC REST Proxy security, principals are no longer configured locally; instead, principals are handled by the Metadata Service (MDS).
Existing REST Proxy security capabilities do not scale for very large deployments without significant manual operations; in RBAC REST Proxy security, the MDS binds and enforces an Kafka cluster configuration across different resources (Topics, Connectors, Schema Registry, etc.), thereby saving users the time and challenge associated with reconfiguring ACLs and roles separately for each Kafka cluster resource.
RBAC REST Proxy workflow
Here is a summary of the RBAC REST Proxy security workflow:
A user makes REST API call to REST Proxy using LDAP credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication.
REST Proxy authenticates the user with the MDS by acquiring a token for the authenticated user.
The generated token is used to impersonate the user request and authenticate between Kafka clients and the Kafka cluster. For Kafka clients, the
SASL_PLAINTEXT/SASL_SSLsecurity protocol is used and the proprietary callback handler passes the token to the Kafka cluster. Similarly, when communicating with Schema Registry, the authentication token is passed to the Schema Registry client using a proprietary implementation of theBearerAuthCredentialProviderinterface.If the user does not have the requisite role or ACL permission for the requested resource (for example, topic, group, or cluster), then the REST API call fails and returns an error with the HTTP 403 status code.
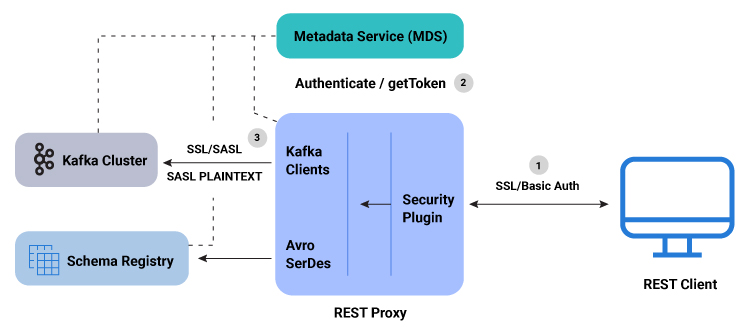
RBAC REST Proxy security workflow
Configuring RBAC REST Proxy security
To use RBAC with REST Proxy, the REST Proxy Security Plugins are required.
To enable token authentication (in the kafka-rest.properties file) set rest.servlet.initializor.classes to io.confluent.common.security.jetty.initializer.InstallBearerOrBasicSecurityHandler and kafka.rest.resource.extension.class to io.confluent.kafkarest.security.KafkaRestSecurityResourceExtension.
rest.servlet.initializor.classes=io.confluent.common.security.jetty.initializer.InstallBearerOrBasicSecurityHandler
kafka.rest.resource.extension.class=io.confluent.kafkarest.security.KafkaRestSecurityResourceExtension
When token authentication is enabled, the generated token is used to impersonate the API requests. REST Proxy Kafka clients use the SASL_PLAINTEXT or SASL_SSL authentication mechanism to authenticate with Kafka brokers.
Provide the credentials to use with the metadata service (MDS). These should usually match those used for talking to Kafka.
confluent.metadata.basic.auth.user.info=<username>:<password>
confluent.metadata.http.auth.credentials.provider=BASIC
Note
If you have high latency from Schema Registry to MDS for requests, increase the timeout value of the optional setting confluent.metadata.http.request.timeout.ms to account for the extra latency. You may want to increase the value specified for the optional setting confluent.metadata.request.timeout.ms proportionally so that any retries have a sufficient buffer in time. For details about these optional configuration settings, refer to RBAC REST Proxy Configuration Options.
See also Configure Token Authentication in Confluent Platform.
Configuration Options
rest.servlet.initializor.classesList of custom initialization classes for REST Proxy. To use RBAC, set it to
io.confluent.common.security.jetty.initializer.InstallBearerOrBasicSecurityHandler.Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: high
kafka.rest.resource.extension.classList of custom extension classes for REST Proxy. To use RBAC, set it to
io.confluent.kafkarest.security.KafkaRestSecurityResourceExtension.Type: string
Default: PLAINTEXT
Importance: high
client.security.protocolProtocol used to communicate with brokers. Valid values are:
PLAINTEXT,SSL,SASL_PLAINTEXT,SASL_SSL. To use RBAC, set it to eitherSASL_PLAINTEXTorSASL_SSL.Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: high
public.key.pathLocation of the PEM encoded public key file to be used for verifying tokens.
Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: high
confluent.metadata.bootstrap.server.urlsComma-separated list of bootstrap metadata service URLs to which this REST Proxy connects. For example: http://localhost:8080,http://localhost:8081
Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: high
confluent.metadata.basic.auth.user.infoService user credentials information in the format:
user:password.Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: high
confluent.metadata.http.auth.credentials.providerMetadata Server (MDS) authentication provider; for example:
BASIC.Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: high
You can use the following optional settings to internally configure the HTTP client used to call MDS to authorize the REST Proxy client.
confluent.metadata.http.request.timeout.msOptional. Controls the maximum amount of time the client will wait for the response to an HTTP request. If the response is not received before the timeout elapses, the client will resend the request or fail the request if all URLs are exhausted. The value should be less than or equal to the value of
confluent.metadata.request.timeout.ms.Type: string
Default: 10000 ms (10 seconds)
Importance: low
confluent.metadata.request.timeout.msOptional. Controls the maximum amount of time the client will wait for the response to each authorizer request.
Type: string
Default: 30000 ms (30 seconds)
Importance: low