Tutorial: Link Confluent Platform and Confluent Cloud Clusters
This tutorial provides an example of how to use Cluster Linking for hybrid use cases that link Confluent Platform and Confluent Cloud clusters.
What the tutorial covers
By the end of this tutorial, you will have configured two clusters, one on Confluent Platform and one on Confluent Cloud, and successfully used Cluster Linking to share topic data bidirectionally across the clusters, all without opening up your firewall to Confluent Cloud.
You will create a deployment with data flowing in both directions:
From Confluent Cloud to Confluent Platform
From Confluent Platform to Confluent Cloud
In both cases, Confluent Platform brokers will initiate the connection to Confluent Cloud brokers. Therefore, you will not have to open up your firewall to let Confluent Cloud connect to your Confluent Platform brokers.
In the process, you will create various security credentials and configuration files to use with the Confluent Platform and Confluent Cloud commands. For a handy list of these, see the Configuration summary at the end of this tutorial.
To see what clusters can use Cluster Linking, see Supported Cluster Types.

Install Confluent Platform and configure environment variables
Download and extract Confluent Platform version 7.1.0.
Configure environment variables.
Important
Add these two lines to your
.bashrcor.bash-profileso that they are executed whenever you open a new terminal window.The rest of the tutorial expects these environment variables to be set for KRaft mode:
export CONFLUENT_HOME=<CP installation directory>
export CONFLUENT_CONFIG=$CONFLUENT_HOME/etc/kafka/kraft
The rest of the tutorial expects these environment variables to be set for ZooKeeper mode:
export CONFLUENT_HOME=<CP installation directory>
export CONFLUENT_CONFIG=$CONFLUENT_HOME/etc/kafka
About prerequisites and command examples
Note
As a general guideline (not just for this tutorial), any customer-owned firewall that allows the cluster link connection from source cluster brokers to destination cluster brokers must allow the TCP connection to persist in order for Cluster Linking to work.
These instructions assume you have a local installation of Confluent Platform 7.1.0 or later, and Java 8, 11, or 17 (recommended) (needed for Confluent Platform). Install instructions for self-managed deployments are available in the documentation. If you are new to Confluent Platform, you may want to first work through the Quick Start for Apache Kafka using Confluent Platform, and/or the basic Cluster Linking tutorial then return to this tutorial.
This tutorial and the source-initiated link feature require Confluent Enterprise, and are not supported in Confluent Community or Apache Kafka®.
With a default install of Confluent Platform, the Confluent CLI. and Cluster Linking commands should be available in
$CONFLUENT_HOME/binand properties files will be in the directoryCONFLUENT_CONFIG($CONFLUENT_HOME/etc/kafka/). You must have Confluent Platform running to access these commands. Once Confluent Platform is configured and running, you can type any command with no arguments to get help (for example,kafka-cluster-links).This tutorial requires a Confluent Cloud login and the Confluent CLI. To learn more, see Get the latest version of Confluent Cloud in the Confluent Cloud Cluster Linking Quick Start as well as Migrate Confluent CLI. If you are new to Confluent Cloud, you might want to walk through that Quick Start first, and then return to this tutorial.
This tutorial requires that you run a Dedicated cluster in Confluent Cloud, which will incur Confluent Cloud charges.
The parameter
password.encoder.secretis used to encrypt the credentials which will be stored in the cluster link. To learn more about this parameter, see Multi-Region Clusters.
KRaft and ZooKeeper
Important
As of Confluent Platform 7.5, ZooKeeper is deprecated for new deployments. Confluent recommends KRaft mode for new deployments. To learn more about running Kafka in KRaft mode, see KRaft Overview.
This tutorial provides examples for both KRaft mode and ZooKeeper mode.
For KRaft, the examples show a combined mode configuration, where for each cluster the broker and controller run on the same server. Currently, combined mode is not intended for production use but is shown here to simplify the tutorial. If you want to run controllers and brokers on separate servers, use KRaft in isolated mode. To learn more, see KRaft Overview and Kraft mode under Configure Confluent Platform for production.
Configure Kafka brokers, controllers, and ZooKeeper files
Create and update configuration files as shown below. A summary of server configurations and files is provided at the end of this document for reference.
Make sure you have set the environment variables as described in Install Confluent Platform and configure environment variables. These are used throughout the tutorial.
Ports mapping
The example deployment in this tutorial uses the following default port and feature configurations, and assumes that services will run on localhost.
Confluent Platform | |
|---|---|
Kafka broker | 9092 |
KRaft controller | 9093 |
Confluent Platform | |
|---|---|
Kafka Brokers | 9092 |
ZooKeeper | 2181 |
These are example ports that are used for the purposes of this tutorial. Cluster Linking does not require you to use these ports.
If you have other processes using these ports, either quit the other processes, or modify the tutorial steps to use different ports.
Configure ports, data directories, authentication, and Cluster Linking specifics
The sections below provide quick, copy-paste steps for setting up your Kafka brokers and controllers (KRaft) or ZooKeeper files. Configure the following files in $CONFLUENT_CONFIG, to set up the Confluent Platform cluster.
Copy
$CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server.propertiesto use as a basis forserver-clusterlinking.properties:cp $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server.properties $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
Modify the
listenersandadvertised.listenersconfigurations to use SASL_PLAINTEXT, instead of the default PLAINTEXT. You can update both of these configurations simultaneously with the following command.sed -i '' -e "s/listeners=PLAINTEXT/listeners=SASL_PLAINTEXT/g" $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
Make the following update to the
advertised.listenersport configuration:sed -i '' -e "s/your.host.name:9092/:9092/g" $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
Update Kafka data directories.
sed -i '' -e "s/kraft-combined-logs/kraft-combined-logs-1/g" $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
Append the following lines to the end of the server properties file to set Cluster Linking specific configurations:
echo "inter.broker.listener.name=SASL_PLAINTEXT" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
echo "sasl.enabled.mechanisms=SCRAM-SHA-512" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
echo "sasl.mechanism.inter.broker.protocol=SCRAM-SHA-512" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
echo "listener.name.sasl_plaintext.scram-sha-512.sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="kafka" password="kafka-secret";" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
echo "confluent.reporters.telemetry.auto.enable=false" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
echo "confluent.cluster.link.metadata.topic.replication.factor=1" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
echo "confluent.cluster.link.enable=true" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
echo "password.encoder.secret=encoder-secret" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
Copy
$CONFLUENT_CONFIG/zookeeper.propertiesto use as a basis forzookeeper-clusterlinking.properties:cp $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/zookeeper.properties $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/zookeeper-clusterlinking.properties
Update the ZooKeeper data directories.
sed -i '' -e "s/zookeeper/zookeeper-clusterlinking/g" $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/zookeeper-clusterlinking.properties
Copy
$CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server.propertiesto use as a basis for server-clusterlinking.properties:cp $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server.properties $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
Uncomment the listeners port configuration and update it to use SASL_PLAINTEXT.
sed -i '' -e "s/#listeners=PLAINTEXT/listeners=SASL_PLAINTEXT/g" $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
Modify the following configurations in
$CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties:Configure
listenersto use SASL_PLAINTEXT instead of the default, PLAINTEXT.sed -i '' -e "s/#listeners=PLAINTEXT/listeners=SASL_PLAINTEXT/g" $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
Configure
advertised.listenersto use SASL instead of the default PLAINTEXT:sed -i '' -e "s/#advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT/advertised.listeners=SASL_PLAINTEXT/g" $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
sed -i '' -e "s/your.host.name:9092/:9092/g" $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
Update Kafka data directories.
sed -i '' -e "s/kafka-logs/kafka-logs-1/g" $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
Append the following lines to the end of the server properties file to set Cluster Linking specific configurations:
echo "inter.broker.listener.name=SASL_PLAINTEXT" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
echo "sasl.enabled.mechanisms=SCRAM-SHA-512" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
echo "sasl.mechanism.inter.broker.protocol=SCRAM-SHA-512" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
echo "listener.name.sasl_plaintext.scram-sha-512.sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="kafka" password="kafka-secret";" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
echo "confluent.reporters.telemetry.auto.enable=false" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
echo "confluent.cluster.link.enable=true" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
echo "password.encoder.secret=encoder-secret" >> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
Tip
If you check your
server-clusterlinking.propertiesfile after these edits, you should see the above seven lines at the end of the file, and the other configs upated per the previous steps.This example configures only one Confluent Server broker, secured with SSL, along with one KRaft controller or ZooKeeper, depending on your use case. This is fine for testing on your local machine, but in a production setting, you should have more brokers (and requisite KRaft controllers or ZooKeepers), spread across different machines for fault tolerance and high availability, all secured with authentication and encryption.
The replication factors for important internal topics are set to
1, because this is a testing setup with only one broker. For production deployments, do not set the replication factor of these topics to1. Generally, replication factors should be set to 3 or more, depending on the number of brokers.The parameter
password.encoder.secretis needed to encrypt the credentials which will be stored in the cluster link. To learn more about this parameter, see Multi-Region Clusters.
Create credentials on the cluster
To learn more about authenticating to Confluent Platform clusters, see Configure SASL/SCRAM authentication for Confluent Platform. Both KRaft and ZooKeeper mode are covered in the document.
You must run the first two KRaft commands below (kafka-storage) from $CONFLUENT_HOME, the top of your Confluent Platform install directory.
Change directories into $CONFLUENT_HOME.
cd $CONFLUENT_HOME
Generate a
random-uuidusing the kafka-storage tool.KAFKA_CLUSTER_ID="$(bin/kafka-storage random-uuid)"
Format log directories for this server and create SASL SCRAM credentials on the cluster: a user called “kafka” that will be used by the Kafka cluster itself, and another for a user called “admin” that you will use to run commands against this cluster. For KRaft, both credentials must be applied together in a single command.
kafka-storage format -t $KAFKA_CLUSTER_ID -c $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties -S 'SCRAM-SHA-512=[name=kafka,iterations=8192,password=kafka-secret]' -S 'SCRAM-SHA-512=[name=admin,iterations=8192,password=admin-secret]' --ignore-formatted
Tip
The
kafka-storagecommand is run only once per broker/controller. You cannot use this command to update an existing cluster. If you make a mistake in configurations at this point, you must recreate the directories from scratch, and work through the steps again.Create a file with the admin credentials to authenticate when you run commands against the Confluent Platform cluster.
Open a text editor, create a file called
$CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.configand copy-paste in the following content:sasl.mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-512 security.protocol=SASL_PLAINTEXT sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required \ username="admin" \ password="admin-secret";
In a new command window, start the ZooKeeper server for the Confluent Platform cluster.
zookeeper-server-start $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/zookeeper-clusterlinking.properties
Run commands to create SASL SCRAM credentials on the cluster for two users: one to be used by the Kafka cluster, and the other for running commands against the cluster.
Run this command to create credentials on the cluster for a user called “kafka” that will be used by the Kafka cluster itself.
kafka-configs --zookeeper localhost:2181 --alter --add-config \ 'SCRAM-SHA-512=[iterations=8192,password=kafka-secret]' \ --entity-type users --entity-name kafka
Run this command to create credentials on the cluster for a user called “admin” that you will use to run commands against this cluster.
kafka-configs --zookeeper localhost:2181 --alter --add-config \ 'SCRAM-SHA-512=[iterations=8192,password=admin-secret]' \ --entity-type users --entity-name admin
Create a file with the admin credentials to authenticate when you run commands against the Confluent Platform cluster.
Open a text editor, create a file called
$CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.configand copy-paste in the following content:sasl.mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-512 security.protocol=SASL_PLAINTEXT sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required \ username="admin" \ password="admin-secret";
Start the Confluent Platform cluster
Run the following commands in separate command windows.
The commands used to run the KRaft controller, ZooKeeper, and Kafka brokers do not “complete” until you stop them, so these windows need to stay open while the applications are running.
Use another command window to serve as your main terminal in which to run commands that you expect to complete. (Examples of these are kafka-configs, kafka-topics, kafka-cluster-links, and in certain cases kafka-console-producer and kafka-console-consumer, although sometimes you may want to leave these last two running as well.)
In a new command window, start a Confluent Server broker for the source cluster, passing the credentials as a part of the command.
kafka-server-start $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/server-clusterlinking.properties
Get the Confluent Platform cluster ID.
kafka-cluster cluster-id --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
Your output should resemble:
Cluster ID: G1pnOMOxSjWYIX8xuR2cfQ
In this case,
G1pnOMOxSjWYIX8xuR2cfQis the Confluent Platform cluster ID, referred to in these examples as$CP_CLUSTER_ID.Optionally, set an environment variable for this either in the local shell, or in a zsh or bash profile so that you can directly cut-and-paste commands in later steps:
export CP_CLUSTER_ID=<CP-CLUSTER-ID>
Start the Confluent Cloud cluster
You need a Dedicated Confluent Cloud cluster with Public internet in order to run the rest of the commands. You may create one just for the purpose of this demo, and then delete it after the tutorial is over. You will incur charges for this cluster.
Log on to Confluent Cloud using either the unified CLI or the Confluent Cloud CLI (see About prerequisites and command examples).
This example uses the unified CLI command:
confluent loginView environments, and select the one you want to use by environment ID.
confluent environment list
An asterisk indicates the currently selected environment in the list. You can select a different environment as follows.
confluent environment use <environment-ID>
Use an existing Dedicated cluster in Confluent Cloud, or create a new one either from the Confluent Cloud Console or directly from the Confluent CLI as shown below:
confluent kafka cluster create CLOUD-DEMO --type dedicated --cloud aws --region us-east-1 --cku 1 --availability single-zone
Your output should resemble:
It may take up to 5 minutes for the Kafka cluster to be ready. +--------------+---------------+ | Id | lkc-59oyn | | Name | MY-CLOUD-DEMO | | Type | DEDICATED | | Ingress | 50 | | Egress | 150 | | Storage | Infinite | | Provider | aws | | Availability | single-zone | | Region | us-east-1 | | Status | PROVISIONING | | Endpoint | | | ApiEndpoint | | | RestEndpoint | | | ClusterSize | 1 | +--------------+---------------+
If you created a new Confluent Cloud cluster, you must wait for the cluster to be provisioned. This typically takes a few minutes, but can take longer. You will be notified in email when the cluster is ready for use.
View your clusters.
confluent kafka cluster list
An asterisk indicates the currently selected cluster. You can select a different cluster as follows:
confluent kafka cluster use <CC-CLUSTER-ID>
Tip
You can get information or take several types of actions on a cluster that is not currently selected by specifying its cluster ID. For example,
confluent kafka cluster describe <cluster-ID>.Note the cluster ID for your Dedicated cluster, referred to as
$CC-CLUSTER-IDin this tutorial.Optionally, set an environment variable for this either in the local shell, or in a zsh or bash profile so that you can directly cut-and-paste commands in later steps:
export CC_CLUSTER_ID=<CC-CLUSTER-ID>
Populate the Confluent Platform cluster
These commands use the Confluent Platform CLI.
Create a topic on the Confluent Platform cluster with a single partition so ordering is easier to see.
kafka-topics --create --topic from-on-prem --partitions 1 --replication-factor 1 --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
You should get confirmation that the topic was successfully created.
Created topic from-on-prem.
You can get a list of existing topics as follows:
kafka-topics --list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
And get detailed information on a topic with the
--describeoption:kafka-topics --describe --topic from-on-prem --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
Send some messages to the from-on-prem topic on the source cluster, and fill it with data.
seq 1 5 | kafka-console-producer --topic from-on-prem --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --producer.config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
The command should terminate without any output.
Consume from the topic on the source cluster.
Run a consumer to consume messages from the
from-on-premtopic.kafka-console-consumer --topic from-on-prem --from-beginning --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --consumer.config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
If the topic successfully consumes the messages, your output will be:
1 2 3 4 5
Use keyboard command Ctrl+C to get the prompt back.
Set up privileges for the Confluent Cloud cluster
On Confluent Cloud:
Create a user API key for your Confluent Cloud cluster to act as the destination in Confluent Platform to Confluent Cloud topic data mirroring.
confluent api-key create --resource $CC_CLUSTER_ID
Save the resulting API key and secret in a safe place. This tutorial refers to these as
<CC-link-api-key>and<CC-link-api-secret>. This is the API key and secret associated with the Confluent Cloud cluster that you will use to create the Confluent Platform to Confluent Cloud link. You will add these to a configuration file in the next step.Important
If you are setting this up in production, you should use a service account API key instead of a user-associated key. A guide on how to set up privileges to access Confluent Cloud clusters with a service account is provided in the topic data sharing tutorial. For source-initiated links, the only ACL your service account will need is ALTER on the destination cluster (Cluster: Alter ACL). To learn more about ACLs for cluster linking, see the Security for Cluster Linking on Confluent Platform and the Security for Cluster Linking on Confluent Cloud
Mirror data from on-premises to Confluent Cloud
The following sections describe how to set up and test the Confluent Platform to Confluent Cloud link.
Tip
If you want to mirror consumer offset groups, you must enable consumer offset sync and pass in a JSON file to identify which groups to sync (excluding any groups already used on the destination). This tutorial particular tutorial does not show this configuration.
Create a Confluent Platform to Confluent Cloud link
Set up the cluster link that mirrors data from Confluent Platform to Confluent Cloud.
Tip
This tutorial shows how to create a cluster link from Confluent Platform to Confluent Cloud. That said, you can use the same general configuration if the destination is Confluent Platform 7.0 or later; you would create cluster link in the same way.
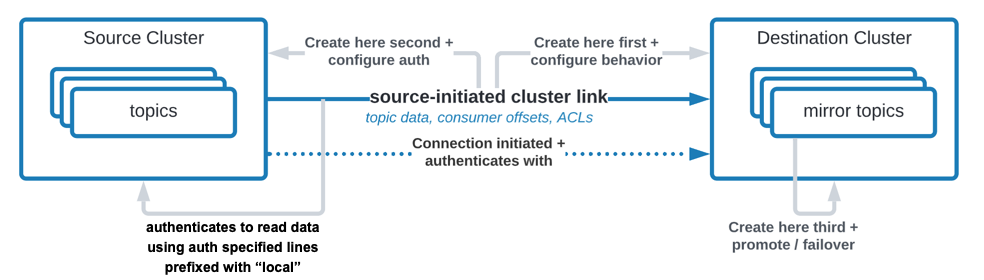
This is a source initiated link, meaning that its connection will come from Confluent Platform and go to Confluent Cloud. As such, you won’t have to open your on-premise firewall.
To create this source initiated link, you must create both halves of the cluster link: the first half on Confluent Cloud, the second half on Confluent Platform.
Create a cluster link on the Confluent Cloud cluster.
Create a link configuration file
$CONFLUENT_CONFIG/clusterlink-hybrid-dst.configwith the following entries:link.mode=DESTINATION connection.mode=INBOUND
The combination of the configurations
link.mode=DESTINATIONandconnection.mode=INBOUNDtell the cluster link that it is the Destination half of a source initiated cluster link. These two configurations must be used together.Note
This tutorial example is based on the assumption that there is only one listener. If you configure multiple listeners (for example, INTERNAL, REPLICATION and EXTERNAL) and want to switch to a different listener than the default, you must add one more parameter to the configuration:
local.listener.name=EXTERNAL. To learn more, see the Confluent Platform documentation on Configuration Options and Understanding Listeners in Cluster LinkingIf you want to add any configurations to your cluster link (such as consumer offset sync or auto-create mirror topics)
clusterlink-hybrid-dst.configis the file where you would add them. Cluster link configurations are always set on the Destination cluster link (not the Source cluster link).
Create the destination cluster link on Confluent Cloud.
confluent kafka link create from-on-prem-link --cluster $CC_CLUSTER_ID \ --source-cluster $CP_CLUSTER_ID \ --config-file $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/clusterlink-hybrid-dst.config
Tip
--source-cluster-idwas replaced with--source-clusterin version 3 of confluent CLI, as described in the command reference for confluent kafka link create.The output from this command should indicate that the link was created.
Created cluster link "from-on-prem-link".
Tip
You can list and describe the cluster links on Confluent Cloud with the following commands:
confluent kafka link list --cluster $CC_CLUSTER_ID
confluent kafka --cluster $CC_CLUSTER_ID link configuration list <link-name>
Create security credentials for the cluster link on Confluent Platform. This security credential will be used to read topic data and metadata from the source cluster.
kafka-configs --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --alter --add-config \ 'SCRAM-SHA-512=[iterations=8192,password=1LINK2RUL3TH3MALL]' \ --entity-type users --entity-name cp-to-cloud-link \ --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
Your output should resemble:
Completed updating config for user cp-to-cloud-link.
Create a link configuration file
$CONFLUENT_CONFIG/clusterlink-CP-src.configfor the source cluster link on Confluent Platform with the following entries:link.mode=SOURCE connection.mode=OUTBOUND bootstrap.servers=<CC-BOOTSTRAP-SERVER> ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm=https security.protocol=SASL_SSL sasl.mechanism=PLAIN sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username='<CC-link-api-key>' password='<CC-link-api-secret>'; local.listener.name=SASL_PLAINTEXT local.security.protocol=SASL_PLAINTEXT local.sasl.mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-512 local.sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="cp-to-cloud-link" password="1LINK2RUL3TH3MALL";
The combination of configurations
link.mode=SOURCEandconnection.mode=OUTBOUNDtell the cluster link that it is the source-half of a source initiated cluster link. These configurations must be used together.The middle section tells the cluster link the
bootstrap.serversof the Confluent Cloud destination cluster for it to reach out to, and the authentication credentials to use. Cluster Linking to Confluent Cloud uses TLS and SASL_PLAIN. This is needed so that the Confluent Cloud cluster knows to accept the incoming request. The Confluent Cloud bootstrap server is shown as the Endpoint in the output forconfluent kafka cluster describe $CC_CLUSTER_ID, or in cluster settings on the Confluent Cloud console. If you use the Endpoint from the CLI output, remove the protocol prefix. For example, if the endpoint shows asSASL_SSL://pkc-r2ymk.us-east-1.aws.confluent.cloud:9092, your entry in$CONFLUENT_CONFIG/clusterlink-CP-src.configshould bebootstrap.servers=pkc-r2ymk.us-east-1.aws.confluent.cloud:9092.The last section, where lines are prefixed with
local, contains the security credentials to use with the source cluster (Confluent Platform) to read data.Note that the authentication mechanisms and security protocols for Confluent Platform map to what is defined in the broker. Those for Confluent Cloud map to what will be defined in a file called
clusterlink-cloud-to-CP.configin a subsequent step. To learn more about the authentication and security protocols used, see Configure SASL/SCRAM authentication for Confluent Platform, and the JAAS section in particular.
Caution
Do not add any cluster link configurations (such as consumer offset sync or auto-create mirror topics) to
clusterlink-CP-src.config. These configurations must be set on the Destination’s cluster link (not the Source cluster’s cluster link).Create the source cluster link on Confluent Platform, using the following command, specifying the configuration file from the previous step.
kafka-cluster-links --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \ --create --link from-on-prem-link \ --config-file $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/clusterlink-CP-src.config \ --cluster-id $CC_CLUSTER_ID --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
Your output should resemble:
Cluster link 'from-on-prem-link' creation successfully completed.
Tip
You can list cluster links on Confluent Platform with this command:
kafka-cluster-links --list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
The command to create the cluster link uses the Confluent Platform kafka-cluster-links to talk with the Confluent Platform cluster, which is different from the unified Confluent CLI used to talk with the Confluent Cloud cluster.
Create topics and mirror data to Confluent Cloud
Note
When using Schema Linking: To use a mirror topic that has a schema with Confluent Cloud Connect, ksqlDB, broker-side schema ID validation, or the topic viewer, make sure that make sure that Schema Linking puts the schema in the default context of the Confluent Cloud Schema Registry. To learn more, see How Schemas work with Mirror Topics.
Before running the first command in the steps below, make sure that you are still logged in to Confluent Cloud and have the appropriate environment and cluster selected. To list and select these resources, use the commands
confluent kafka environment list,confluent kafka environment use,confluent kafka cluster list, andconfluent kafka cluster use. A selected environment or cluster is indicated by an asterisk next to it in the output of list commands. The commands won’t work properly if no resources are selected (or if the wrong ones are selected).
Perform the following tasks logged in to Confluent Cloud.
Create a mirror topic.
The following command establishes a mirror of the original
from-on-premtopic, using the cluster linkfrom-on-prem-link.confluent kafka mirror create from-on-prem --link from-on-prem-link
The command output will be:
Created mirror topic "from-on-prem".
The mirror topic name must match the original topic name. To learn more, see all Known Limitations.
A mirror topic must specify the link to its source topic at creation time. This ensures that the mirror topic is a clean slate, with no conflicting data or metadata.
List the mirror topics on the link.
confluent kafka mirror list --cluster $CC_CLUSTER_ID
Your output will resemble:
Link Name | Mirror Topic Name | Num Partition | Max Per Partition Mirror Lag | Source Topic Name | Mirror Status | Status Time Ms +-------------------+-------------------+---------------+------------------------------+-------------------+---------------+----------------+ from-on-prem-link | from-on-prem | 1 | 0 | from-on-prem | ACTIVE | 1633640214250
Consume from the mirror topic on the destination cluster to verify it.
Still on Confluent Cloud, run a consumer to consume messages from the mirror topic to consume the messages you originally produced to the Confluent Platform topic in previous steps.
confluent kafka topic consume from-on-prem --from-beginning
Your output should be:
1 2 3 4 5
Note
If when you attempt to run the consumer you get an error indicating “no API key selected for resource”, run this command to specify the
<CC-API-KEY>for the Confluent Cloud destination cluster, then re-run the consumer command:confluent api-key use <CC-API-KEY> --resource $CC_CLUSTER_ID, or follow the instructions on the CLI provided with the error messages.
Mirror data from Confluent Cloud to on-premises
The following sections describe how to set up and test the Confluent Cloud to Confluent Platform link.
Tip
If you want to mirror consumer offset groups, you must enable consumer offset sync and pass in a JSON file to identify which groups to sync (excluding any groups already used on the destination). This tutorial particular tutorial does not show this configuration.
Create the Confluent Cloud to Confluent Platform link
Create another user API key for this cluster link on your Confluent Cloud cluster.
confluent api-key create --resource $CC_CLUSTER_ID
You use the same cluster that served as the destination in previous steps as the source cluster in the following steps, therefore, you create a different API key and secret for the same cluster to serve in this new role.
Keep the resulting API key and secret in a safe place. This tutorial refers to these as
<CC-src-api-key>and<CC-src-api-secret>. You will add these to a configuration file in the next step.Important
If you are setting this up in production, you should use a service account API key instead of a user-associated key. To do this, you would create a service account for your cluster link, give the service account the requisite ACLs, then create an API key for the service account. It’s best practice for each cluster link to have its own API key and service account. A guide on how to set up privileges to access Confluent Cloud clusters with a service account is provided in the topic data sharing tutorial.
Use
confluent kafka cluster describeto get the Confluent Cloud cluster Endpoint URL.confluent kafka cluster describe $CC_CLUSTER_ID
This Endpoint URL will be referred to as
<CC-BOOTSTRAP-SERVER>in the following steps.Save your API key and secret along with the following configuration entries in a file called
$CONFLUENT_CONFIG/clusterlink-cloud-to-CP.configthat the Confluent Platform commands will use to authenticate into Confluent Cloud:<vi | emacs> $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/clusterlink-cloud-to-CP.config
The configuration entries you need in this file are as follows:
bootstrap.servers=<CC-BOOTSTRAP-SERVER> security.protocol=SASL_SSL sasl.mechanism=PLAIN sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username='<CC-src-api-key>' password='<CC-src-api-secret>';
Tip
A copy-paste of this file into a vi or Emacs editor should result in each of these statements being on one line. Make sure that the lines are not broken up. The last line starting with
sasl.jaas.config=should show all on one line in your file (as should the others). Supply values for your Confluent Cloud bootstrap server, and API key and secret, then save the file.Note that the values for
security.protocolandsasl.mechanismmap to what you defined for Confluent Cloud inclusterlink-CP-src.config.
Create the cluster link to Confluent Platform.
If you want to follow this example exactly, name the cluster link
from-cloud-linkbut you have the option to name it whatever you like. You will use the cluster link name to create and manipulate mirror topics. You cannot rename a cluster link once it’s created.The following command creates the cluster link on an unsecured Confluent Platform cluster. If you have security set up on your Confluent Platform cluster, you must pass security credentials to this command with
--command-configas shown in Setting Properties on a Cluster Link.kafka-cluster-links --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \ --create --link from-cloud-link \ --config-file $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/clusterlink-cloud-to-CP.config \ --cluster-id $CC_CLUSTER_ID --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
Your output should resemble the following:
Cluster link 'from-cloud-link' creation successfully completed.
Check that the link exists with the
kafka-cluster-links --listcommand, as follows.kafka-cluster-links --list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
Your output should resemble the following, showing the previous
from-on-prem-linkyou created along with the newfrom-cloud-linkLink name: 'from-on-prem-link', link ID: '7eb4304e-b513-41d2-903e-147dea62a01c', remote cluster ID: 'lkc-1vgo6', local cluster ID: 'G1pnOMOxSjWYIX8xuR2cfQ' Link name: 'from-cloud-link', link ID: 'b1a56076-4d6f-45e0-9013-ff305abd0e54', remote cluster ID: 'lkc-1vgo6', local cluster ID: 'G1pnOMOxSjWYIX8xuR2cfQ'
Create topics and mirror data to on-premises
In Confluent Cloud, use the unified Confluent CLI to create a topic with one partition called
cloud-topic.confluent kafka topic create cloud-topic --partitions 1
In another command window on Confluent Cloud, start a producer to send some data into
cloud-topic.confluent kafka topic produce cloud-topic --cluster $CC_CLUSTER_ID
Verify that the producer has started. Your output will resemble the following to show that the producer is ready.
$ confluent kafka topic produce cloud-topic --cluster lkc-1vgo6 Starting Kafka Producer. Use Ctrl-C or Ctrl-D to exit.
Type some entries of your choice into the producer window, hitting return after each entry to send.
Riesling Pinot Blanc Verdejo
Mirror the
cloud-topicon Confluent Platform, using the commandkafka-mirrors --create --mirror-topic <topic-name>.The following command establishes a mirror of the original
cloud-topic, using the cluster linkfrom-cloud-link.kafka-mirrors --create --mirror-topic cloud-topic --link from-cloud-link --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
You should get this verification that the mirror topic was created.
Created topic cloud-topic.
On Confluent Platform, check the mirror topic status by running
kafka-mirrors --describeon thefrom-cloud-link.kafka-mirrors --describe --link from-cloud-link --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
Your output will show the status of any mirror topics on the specified link.
Topic: cloud-topic LinkName: from-cloud-link LinkId: b1a56076-4d6f-45e0-9013-ff305abd0e54 MirrorTopic: cloud-topic State: ACTIVE StateTime: 2021-10-07 16:36:20 Partition: 0 State: ACTIVE DestLogEndOffset: 2 LastFetchSourceHighWatermark: 2 Lag: 0 TimeSinceLastFetchMs: 384566
Consume the data from the on-prem mirror topic.
kafka-console-consumer --topic cloud-topic --from-beginning --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --consumer.config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
Your output should match the entries you typed into the Confluent Cloud producer in step 8.

View the configuration of your cluster link:
kafka-configs --describe --cluster-link from-cloud-link --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
The output for this command is a list of configurations, partially shown in the following example.
Dynamic configs for cluster-link from-cloud-link are: metadata.max.age.ms=300000 sensitive=false synonyms={} reconnect.backoff.max.ms=1000 sensitive=false synonyms={} auto.create.mirror.topics.filters= sensitive=false synonyms={} ssl.engine.factory.class=null sensitive=false synonyms={} sasl.kerberos.ticket.renew.window.factor=0.8 sensitive=false synonyms={} reconnect.backoff.ms=50 sensitive=false synonyms={} consumer.offset.sync.ms=30000 sensitive=false synonyms={} ... link.mode=DESTINATION sensitive=false synonyms={} security.protocol=SASL_SSL sensitive=false synonyms={} acl.sync.ms=5000 sensitive=false synonyms={} ssl.keymanager.algorithm=SunX509 sensitive=false synonyms={} sasl.login.callback.handler.class=null sensitive=false synonyms={} replica.fetch.max.bytes=5242880 sensitive=false synonyms={} availability.check.consecutive.failure.threshold=5 sensitive=false synonyms={} sasl.login.refresh.window.jitter=0.05 sensitive=false synonyms={}
Teardown
Stop consumers and producers
Stop consumers and producers with Ctl-C in their respective command windows.
Promote mirror topics
Promote the mirror topics to normal topics.
On Confluent Cloud promote the mirror topic called
from-on-prem:confluent kafka mirror promote from-on-prem --link from-on-prem-link --cluster $CC_CLUSTER_ID
Your output will resemble:
Mirror Topic Name | Partition | Partition Mirror Lag | Error Message | Error Code | Last Source Fetch Offset +-------------------+-----------+----------------------+---------------+------------+--------------------------+ from-on-prem | 0 | 0 | | | 9
If you want to verify that the mirroring stopped, you can re-run the above command. You should get a message in the Error Message column that
Topic 'from-on-prem' has already stopped its mirror from 'from-on-prem-link'.On Confluent Platform, promote the mirror topic called
cloud-topic:kafka-mirrors --promote --topics cloud-topic --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
Your output should resemble:
Calculating max offset and ms lag for mirror topics: [cloud-topic] Finished calculating max offset lag and max lag ms for mirror topics: [cloud-topic] Request for stopping topic cloud-topics mirror was successfully scheduled. Please use the describe command with the --pending-stopped-only option to monitor progress.
If you retry this command, you will get an error indicating that the
Topic 'cloud-topic' has already stopped its mirror 'from-cloud-link'.
Delete the source and mirror topics
Tip
To list the topics on Confluent Cloud:
confluent kafka topic listTo list the topics on Confluent Platform:
kafka-topics --list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
Delete the topics on Confluent Cloud.
confluent kafka topic delete cloud-topic
confluent kafka topic delete from-on-prem
Delete the topics from Confluent Platform.
kafka-topics --delete --topic cloud-topic --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
kafka-topics --delete --topic from-on-prem --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
Delete the cluster links
Delete the cluster links on Confluent Platform.
List the cluster links on Confluent Platform.
kafka-cluster-links --list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
There will be two because one was required for the source initiated link and the other to act as the destination for Confluent Cloud data:
Link name: 'from-on-prem-link', link ID: '7eb4304e-b513-41d2-903e-147dea62a01c', remote cluster ID: 'lkc-1vgo6' local cluster ID: ', local cluster ID: 'G1pnOMOxSjWYIX8xuR2cfQ'' remote cluster available: 'true' Link name: 'from-cloud-link', link ID: 'b1a56076-4d6f-45e0-9013-ff305abd0e54', remote cluster ID: 'lkc-1vgo6' local cluster ID: ', local cluster ID: 'G1pnOMOxSjWYIX8xuR2cfQ'' remote cluster available: 'true'
Delete the cluster links on Confluent Platform, using
kafka-cluster-links --delete <link-name>.kafka-cluster-links --delete --link from-on-prem-link --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
kafka-cluster-links --delete --link from-cloud-link --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config $CONFLUENT_CONFIG/CP-command.config
You will get confirmation that the links were deleted as output for each command.
Delete the cluster links on Confluent Cloud.
List the cluster links on Confluent Cloud.
confluent kafka link list
Your output will resemble:
Link Name | Source Cluster Id +-------------------+------------------------+ from-on-prem-link | G1pnOMOxSjWYIX8xuR2cfQ
Delete the cluster link on Confluent Cloud, using
confluent kafka link delete <link-name>.confluent kafka link delete from-on-prem-link
You will get confirmation that the link was deleted.
Stop Confluent Platform and ZooKeeper
Stop all of the other components with Ctl-C in their respective command windows, in reverse order in which you started them.
Stop the Kafka broker first. If you used KRaft mode, teardown is complete.
If you used ZooKeeper mode, when the Kafka broker has fully shut down and your prompt has returned, then go to the other window and stop the associated ZooKeeper. Teardown is complete.
Configuration summary
The following environment variables must be configured across all terminal windows for the tutorial to run properly. These are described in Install Confluent Platform and configure environment variables.
CONFLUENT_HOME=<CP installation directory>
Use one of these: - KRaft: CONFLUENT_CONFIG=$CONFLUENT_HOME/etc/kafka/kraft - ZooKeeper mode: export CONFLUENT_CONFIG=$CONFLUENT_HOME/etc/kafka
File | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Configuration file used for ZooKeeper startup, as described in Configure Kafka brokers, controllers, and ZooKeeper files |
| Configuration file used for the Confluent Platform cluster startup, as described in Configure Kafka brokers, controllers, and ZooKeeper files |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A step-by-step guide for configuring all server properties is shown in Configure Kafka brokers, controllers, and ZooKeeper files.
Here is a quick summary of new configurations you add to the Kafka server properties file.
inter.broker.listener.name=SASL_PLAINTEXTsasl.enabled.mechanisms=SCRAM-SHA-512sasl.mechanism.inter.broker.protocol=SCRAM-SHA-512listener.name.sasl_plaintext.scram-sha-512.sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="kafka" password="kafka-secret";confluent.reporters.telemetry.auto.enable=falseconfluent.cluster.link.enable=truepassword.encoder.secret=encoder-secretconfluent.cluster.link.metadata.topic.replication.factor=1(This explicit config is only needed in KRaft mode. In ZooKeeper mode, using $CONFLUENT_HOME/etc/kafka this is the default.)
And here are the configurations you modify from their defaults in the Kafka server:
listeners=SASL_PLAINTEXT://:9092advertised.listeners=SASL_PLAINTEXT://:9092log.dirs=/tmp/kafka-logs-1