Configure RBAC for Confluent Platform Using Confluent for Kubernetes
Confluent for Kubernetes (CFK) supports role-based access control (RBAC). RBAC is powered by Confluent’s Metadata Service (MDS), which acts as the central authority for authorization and authentication data. RBAC leverages role bindings to determine which users and groups can access specific resources and what actions the users can perform on those resources.
Confluent provides audit logs, that record the runtime decisions of the permission checks that occur as users/applications attempt to take actions that are protected by ACLs and RBAC.
There are a set of principals and role bindings required for the Confluent components to function, and those are automatically generated when CFK is deployed.
When you deploy Confluent Platform with RBAC enabled, CFK automates the security setup. Here’s the end-state ZooKeeper-based Confluent Platform configured with LDAP:
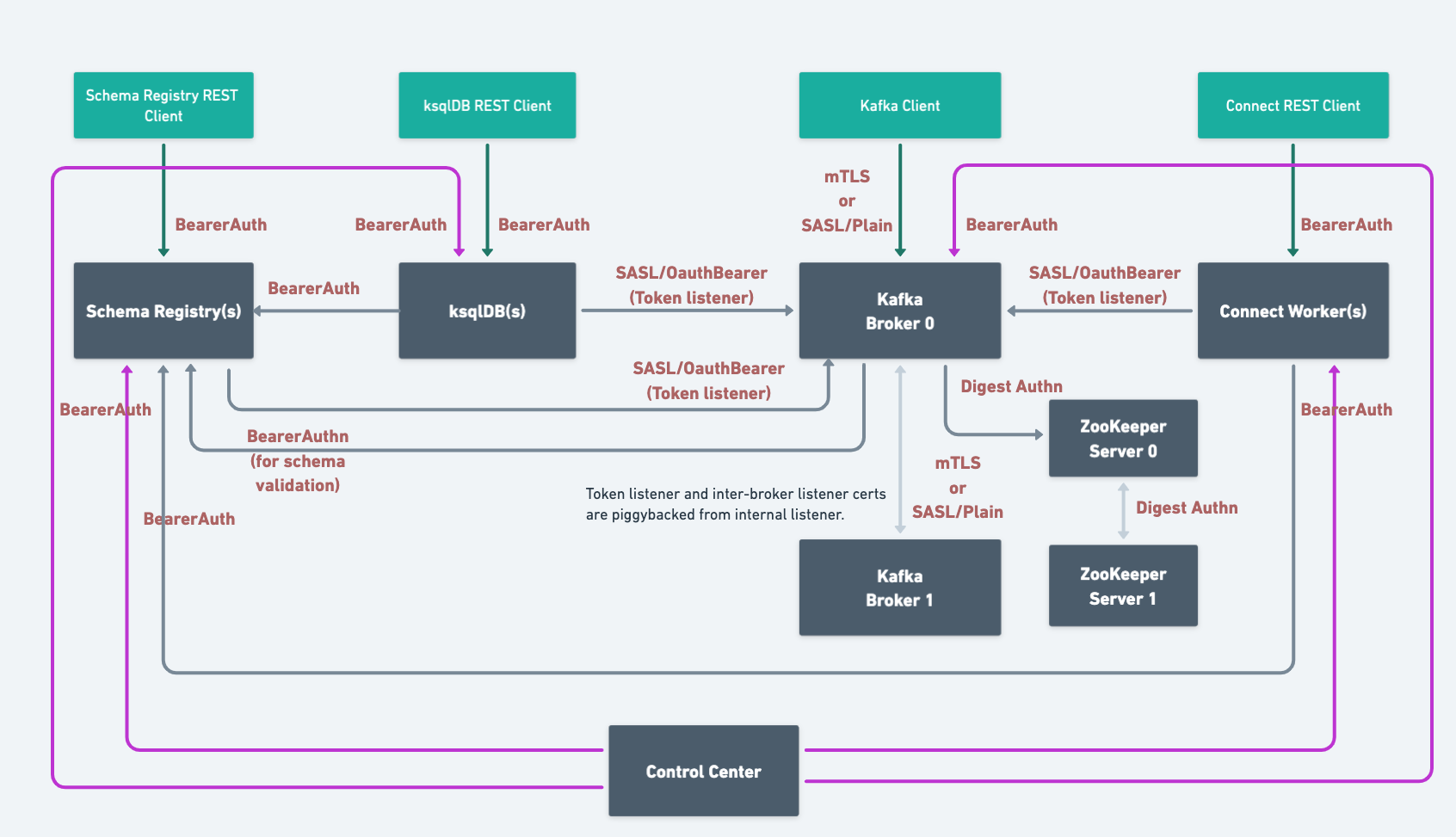
Based on the components and features you use, you need to configure the following additional role bindings:
Requirements and considerations
The following are the requirements and considerations for enabling and using RBAC with CFK:
Confluent REST service is automatically enabled for RBAC and cannot be disabled when RBAC is enabled.
Use the Kafka bootstrap endpoint (same as the MDS endpoint) to access Confluent REST API.
When RBAC is enabled, CFK always uses the internal MDS endpoint. Even when you configure the external MDS listener endpoint and TLS settings, CFK does not use those settings.
Listener authentication with RBAC
When RBAC is enabled with LDAP or OAuth, CFK adds a token listener with the authentication based upon MDS. Other Confluent Platform components connect to Kafka using the token listener authentication, ignoring the authentication defined in the component custom resource (CR) in
spec.dependencies.kafka.authentication.When RBAC is enabled with mTLS, the internal listener is not overridden. And Confluent Platform components connect to Kafka using the internal listener authentication as defined in the component CR under
spec.dependencies.kafka.authentication.When RBAC is enabled with mTLS only, CFK adds a tokenSasl listener, which is used by REST Proxy to authenticate with MDS.
When you use the custom listener instead of internal listener for internal communication, the custom listener authentication setting is not overridden and is used in place of token listener. The custom listener must support MDS authentication method for this setup to work.
Requirements and considerations for RBAC with LDAP
The following are the requirements and considerations for enabling and using RBAC using LDAP:
You must have an LDAP server that Confluent Platform can use for authentication.
Currently, CFK only supports the
GROUPSLDAP search mode. The search mode indicates if the user-to-group mapping is retrieved by searching for group or user entries. If you need to use theUSERSsearch mode, specify using theconfigOverridessetting in the Kafka CR as below:spec: configOverrides: server: - ldap.search.mode=USERS
See Sample Configuration for User-Based Search for more information.
You must create the user principals in LDAP that will be used by Confluent Platform components. These are the default user principals:
Kafka:
kafka/kafka-secretConfluent REST API:
erp/erp-secretControl Center:
c3/c3-secretksqlDB:
ksql/ksql-secretSchema Registry:
sr/sr-secretReplicator:
replicator/replicator-secretConnect:
connect/connect-secret
Create the LDAP user/password for a user who has a minimum of LDAP read-only permissions to allow Metadata Service (MDS) to query LDAP about other users. For example, you’d create a user
mdswith passwordDeveloper!Create a user for the Admin REST service in LDAP and provide the username and password.
Configure RBAC with CFK
The high-level workflow to configure RBAC with CFK is:
Enable RBAC for KRaft controller for the KRaft-based deployments
Grant roles to a Control Center user to administer Confluent Platform
The comprehensive security tutorial walks you through an end-to-end setup of role-based access control (RBAC) for Confluent with CFK. We recommend you take the CustomResource spec and the steps outlined in the scenario as a starting point and customize for your environment.
Configure MDS for RBAC
To enable RBAC in CFK, first, configure the MDS and its provider settings in your Kafka custom resource (CR):
kind: Kafka
spec:
services:
mds: --- [1]
tokenKeyPair: --- [2]
provider: --- [3]
impersonation:
admins: --- [4]
protectedUsers: --- [5]
[1] Required.
[2] Required. The token key pair to authenticate to MDS.
For details, see MDS authentication token keys.
[3] The identity provider settings. Specify
oauth,ldap,file, ormtls.For the full list of supported settings for each type of provider, see Configure authentication to access MDS.
To use mTLS only as the identity provider, set
provider.mtlsandprovider.file(only for Confluent CLI and Control Center). See mTLS authentication and File-based authentication.To use mTLS and LDAP as the identity providers, set
provider.mtlsandprovider.ldap. See mTLS authentication.To use mTLS and OAuth as the identity providers, set
provider.mtlsandprovider.oauth. See mTLS authentication and OAuth/OIDC authentication.
[4] User principals that are allowed to be impersonated by the REST Proxy for the purpose of authorization. For example:
admins: - User:kafka - User:krp # kafkarestproxy principal should always be added as impersonation admin - User:connect
[5] Principals which are not allowed to be impersonated. For example,
superadmin, mds.
Enable RBAC for Kafka
To configure and deploy Kafka with the Confluent RBAC:
Specify the RBAC settings in your Kafka Custom Resource (CR):
kind: Kafka spec: authorization: type: rbac --- [1] superUsers: --- [2] dependencies: kafkaRest: --- [3] authentication:
[1] Required.
[2] Required. The super users to be given the admin privilege on the Kafka cluster.
These users have no access to resources in other Confluent Platform clusters unless they are also configured with specific role bindings on the clusters.
This list is in the
User:<user-name>format. For example:superUsers: - User:kafka - User:testadmin
[3] Required. The REST client configuration for MDS. For the configuration of the Kafka client authentication you want to use, see Configure authentication to access Kafka and KRaft.
If enabling the Confluent RBAC for a KRaft-based deployment, configure the KraftController CR as described in Enable RBAC for KRaft controller.
MDS authentication token keys
When using the Bearer authentication for RBAC, to sign the token generated by the MDS server, you can use the PKCS#1 or PKCS#8 PEM key format. When using PKCS#8, the private key can be unencrypted or encrypted with a passphrase.
To provide the MDS token keys:
Create a PEM key pair as described in Create a PEM key pair for MDS.
If using an encrypted private key:
Create a passphrase file with the name,
mdsTokenKeyPassphrase.txt.In the
mdsTokenKeyPassphrase.txtfile, add the key-value pair with themdsTokenKeyPassphrasekey and the passphrase that the private key was encrypted with:
mdsTokenKeyPassphrase=<passphrase>
Add the public key and the token key pair to a secret or inject it in a directory path in the container using Vault.
To use an encrypted private key, add the passphrase value to the secret or the directory path in the container, as well.
An example command to create a secret with an unencrypted private key:
kubectl create secret generic mds-token \ --from-file=mdsPublicKey.pem=mds-publickey.txt \ --from-file=mdsTokenKeyPair.pem=mds-tokenkeypair.txt \ --namespace confluent
An example command to create a secret with an encrypted private key:
kubectl create secret generic mds-token \ --from-file=mdsPublicKey.pem=mds-publickey.txt \ --from-file=mdsTokenKeyPair.pem=mds-tokenkeypair.txt \ --from-file=mdsTokenKeyPassphrase.txt=mdsTokenKeyPassphrase.txt \ --namespace confluent
In the Kafka CR, specify the token key pair to authenticate to MDS:
kind: Kafka spec: services: mds: tokenKeyPair: secretRef: --- [1] directoryPathInContainer: --- [2] encryptedTokenKey: --- [3]
[1] The name of the Kubernetes secret that contains the public key and the token key pair to sign the token generated by the MDS server.
[2] The directory path in the container where the required public key and the token key pair are injected by Vault.
[3] Optional. Set to
trueto use an encrypted private key. The default value isfalse.
Enable RBAC for KRaft controller
To enable the Confluent RBAC for a KRaft-based deployment, after configuring MDS and Kafka as shown above in Enable RBAC for Kafka, you must enable RBAC in the KraftController CR.
kind: KRaftController
spec:
authorization:
type: rbac --- [1]
superUsers: --- [2]
dependencies:
mdsKafkaCluster: --- [3]
bootstrapEndpoint: --- [4]
authentication: --- [5]
type: --- [6]
jaasConfig: --- [7]
jaasConfigPassThrough: --- [8]
oauthSettings: --- [9]
sslClientAuthentication: --- [10]
tls: --- [11]
enabled: --- [12]
[1] Required.
[2] Required. The super users to be given the admin privilege on the KRaft cluster.
These users have no access to resources in other Confluent Platform clusters unless they are also configured with specific role bindings on the clusters.
This list is in the
User:<user-name>format. For example:superUsers: - User:kafka - User:testadmin
[3] Required.
[4] Required. Specify the MDS Kafka bootstrap endpoint.
[5] Specify the client-side authentication for the MDS Kafka cluster.
[6] Required. Specify the client-side authentication type for the MDS Kafka. Valid options are
plain,mtls, andoauth.For detail about the authentication type you want to use, see Configure authentication to access MDS. Note that Bearer authentication is not supported for KRaft to authenticate with MDS.
[7] When the authentication type (
type) is set toplain, specify the credential using JAAS configuration. For details, see Create client-side SASL/PLAIN credentials using JAAS config.[8] When the authentication type (
type) is set toplain, specify the credential usingjaasConfigPassThrough. For details, see Create client-side SASL/PLAIN credentials using JAAS config pass-through.[9] Required for the
oauthauthentication type.For the full list of the OAuth settings, see OAuth configuration.
[10] Set to
trueto enable the client-side mTLS for the MDS Kafka cluster. This is required for mTLS authentication when using RBAC (tls.enabled: truein [12]).[11] The client-side TLS setting for the MDS Kafka cluster. For details, see Client-side mTLS authentication for Kafka and KRaft.
[12] Required for mTLS authentication. Set to
true. When using mTLS, you must also setsslClientAuthentication: truein [10].
Configure Kafka REST Class for RBAC
Configure the Admin REST Class CR as following:
kind: KafkaRestClass
spec:
kafkaRest:
authentication:
type: --- [1]
bearer: --- [2]
secretRef: --- [3]
directoryPathInContainer: --- [4]
oauth: --- [5]
secretRef: --- [6]
directoryPathInContainer: --- [7]
configuration: --- [8]
tokenEndpointUri:
sslClientAuthentication: --- [9]
[1] Required. Set to
oauth,mtls, orbearerfor RBAC.[2] Required for the
bearerauthentication type ([1]).[3] or [4] Specify only one setting.
[3] The username and password are loaded through secretRef.
The expected key is
bearer.txt.The value for the key is:
username=<username> password=<password>
[4] Provide the path where required credentials are injected by Vault. See [3] for the expected key and the value.
[5] Required for the
oauthauthentication type ([1]).[6] or [7] Specify only one of the two.
[6] The secret that contains the OIDC client ID and the client secret for authorization and token request to the identity provider.
Create the secret that contains two keys with their respective values, clientId and clientSecret as following:
clientId=<client-id> clientSecret=<client-secret
[7] The path where required OIDC client ID and the client secret are injected by Vault.
See Provide secrets for Confluent Platform component CR for providing the credential and required annotations when using Vault.
[8] OAuth settings. For the full list of the OAuth settings, see OAuth configuration.
[9] Set to
trueto enable the client-side mTLS for the REST API client.
For the rest of the configuration details for the Admin REST Class, see Manage Confluent Admin REST Class for Confluent Platform Using Confluent for Kubernetes.
Enable RBAC for other Confluent Platform components
To configure and deploy other non-Kafka components with the Confluent RBAC:
Specify the settings in the component CR:
kind: <Component> spec: authorization: type: rbac --- [1] kafkaRestClassRef: --- [2] dependencies: mds: endpoint: --- [3] tokenKeyPair: --- [4] secretRef: directoryPathInContainer authentication: --- [5]
[1] Required for RBAC.
[2] If
kafkaRestClassRefis not configured, the kafkaRestClass with the name,default, in the current namespace is used.[3] Required. MDS endpoint.
[4] Required. The token key pair and the public key to authenticate to the MDS. Use
secretRefordirectoryPathInContainerto specify.You need to add the public key and the token key pair to the secret or directoryPathInContainer. For details, see Create a PEM key pair for MDS.
An example command to create a secret is:
kubectl create secret generic mds-token \ --from-file=mdsPublicKey.pem=mds-publickey.txt \ --from-file=mdsTokenKeyPair.pem=mds-tokenkeypair.txt \ --namespace confluent
[5] Required. For configuring the client-side MDS authentication you want to use, see MDS with mTLS authentication.
Use an existing Admin REST Class or create a new Admin REST Class CR as described in the previous section.
Control Center RBAC and MDS with mTLS-only authentication
Starting with Confluent Platform 7.8.3+ (in 7.8.x), 7.9.2+ (in 7.9.x), 8.0.0+, you can configure Control Center for RBAC to use MDS with mTLS-only authentication.
After you configure the Control Center for RBAC as described in Enable RBAC for other Confluent Platform components, add the additional configuration overrides to the Control Center CR. The following is a snippet of the required settings with example values:
kind: ControlCenter
spec:
configOverrides:
server:
- bootstrap.servers=kafka.confluent.svc.cluster.local:9075
- confluent.controlcenter.streams.sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerLoginModule required metadataServerUrls="https://kafka.confluent.svc.cluster.local:8090";
- confluent.controlcenter.streams.sasl.login.callback.handler.class=io.confluent.kafka.clients.plugins.auth.token.TokenCertificateLoginCallbackHandler
- confluent.controlcenter.streams.sasl.mechanism=OAUTHBEARER
- confluent.controlcenter.streams.security.protocol=SASL_SSL
If the Control Center is monitoring multiple Kafka clusters, the Control Center client for each Kafka cluster also needs to be updated in similar way. The following is a snippet of the required settings with example values:
kind: ControlCenter
spec:
configOverrides:
server:
- confluent.controlcenter.kafka.<name>.bootstrap.servers=kafka.confluent.svc.cluster.local:9075
- confluent.controlcenter.kafka.<name>.security.protocol=SASL_SSL
- confluent.controlcenter.kafka.<name>.sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerLoginModule required metadataServerUrls="https://kafka.confluent.svc.cluster.local:8090";
- confluent.controlcenter.kafka.<name>.sasl.login.callback.handler.class=io.confluent.kafka.clients.plugins.auth.token.TokenCertificateLoginCallbackHandler
- confluent.controlcenter.kafka.<name>.sasl.mechanism=OAUTHBEARER
Migrate LDAP-based RBAC to OAuth-based RBAC
Migrate RBAC from using LDAP to using both LDAP and OAuth
This section describes the steps to upgrade a Confluent Platform deployment configured with LDAP-based RBAC to LDAP and OAuth-based RBAC.
To migrate your Confluent Platform deployment to use OAuth, the Confluent Platform version must be 7.7.
Upgrading the Confluent Platform version and migrating to OAuth simultaneously is not supported.
Even though this upgrade can be done in one step, as described in this section, we recommend the two-step migration, MDS first, and the rest of the components to reduce failed restarts of components.
To migrate an existing Confluent Platform deployment from LDAP to LDAP and OAuth:
Upgrade the MDS with the required OAuth settings as described in Enable RBAC for Kafka and apply the CR with the
kubectl applycommand.Following is a sample snippet of a Kafka CR with LDAP and OAuth:
kind:kafka spec: services: mds: provider: ldap: address: ldaps://ldap.operator.svc.cluster.local:636 authentication: type: simple simple: secretRef: credential tls: enabled: true configurations: oauth: configurations: dependencies: kafkaRest: authentication: type: oauth jaasConfig: secretRef: oauth-secret oauthSettings:
After the Kafka successfully restarts, upgrade the rest of the Confluent Platform components.
Add the following annotation to the Schema Registry, Connect, and Control Center CRs:
kind: <component> metadata: annotations: platform.confluent.io/disable-internal-rolebindings-creation: "true"
Add the OAuth settings to the rest of the Confluent Platform components as described in Enable RBAC for KRaft controller and Enable RBAC for other Confluent Platform components and apply the CRs with the
kubectl applycommand.The following are sample snippets of the relevant settings in the component CRs.
kind: KRaftController spec: dependencies: mdsKafkaCluster: bootstrapEndpoint: authentication: type: oauth jaasConfig: secretRef: oauthSettings: tokenEndpointUri:
kind: KafkaRestClass spec: kafkaRest: authentication: type: oauth oauth: secretRef: configuration:
kind: SchemaRegistry spec: dependencies: mds: authentication: type: oauth oauth: secretRef: configuration:
If you have existing connectors, add the following to the Connect CR to avoid possible down time.
kind: Connect spec: configOverrides: server: - producer.sasl.login.callback.handler.class=org.apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerLoginCallbackHandler - consumer.sasl.login.callback.handler.class=org.apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerLoginCallbackHandler - admin.sasl.login.callback.handler.class=org.apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerLoginCallbackHandler
Log into Control Center and check if you can see Kafka, Schema Registry, and Connect.
Migrate RBAC from using LDAP and OAuth to using OAuth
After you migrate from LDAP to LDAP and OAuth as described in Migrate RBAC from using LDAP to using both LDAP and OAuth and validate the result, you can remove LDAP from the RBAC configuration and only use OAuth in your deployment.
The followup steps to complete the migration are:
Migrate the clients using LDAP credentials to OAuth.
Remove the LDAP authentication settings. See Enable RBAC for Kafka for the LDAP settings you can remove.
Migrate to mTLS-based RBAC
This section describes the workflow for brownfield migration to mTLS-based RBAC.
The migration to mTLS-based RBAC is supported with Confluent Platform 7.8 and later versions and CFK 3.0 and later versions.
Note that dual authentications are already supported for OAuth and mTLS or LDAP and mTLS when you configure two providers for Kafka MDS.
The following types of migrations are supported for RBAC-enabled clusters:
Migration from OAuth to OAuth + mTLS, LDAP to LDAP + mTLS
Migration from OAuth + mTLS to mTLS only, LDAP + mTLS to mTLS only
For comprehensive coverage of the example migration scenarios, see the RBAC migration scenarios
Note that the snippets shown in this section are for examples only and should not be directly used in your environment.
Migrate RBAC from OAuth or LDAP-based to dual authentication with mTLS
This section describes how to migrate an OAuth or LDAP-based RBAC deployment to use mTLS as the one of the dual authentication methods.
Add a custom listener with dual OAuth or LDAP and mTLS authentications in Kafka.
This listener will be used for Confluent Platform components to Kafka communications while the internal listener gets updated during migration.
If migrating from LDAP to dual LDAP and mTLS, set the listener authentication type to
bearer.If migrating from OAuth to dual OAuth and mTLS, set the listener authentication type to
oauth.kind: Kafka spec: listeners: custom: - name: customoauth port: 9093 authentication: type: <oauth or bearer> oauthSettings : # If type: oauth above tokenEndpointUri: expectedIssuer: jwksEndpointUri: subClaimName: client_id mtls: sslClientAuthentication: "required" principalMappingRules: - "RULE:.*CN=([a-zA-Z0-9.-]*).*$/$1/" - "DEFAULT" tls: enabled: true
Update all the Confluent Platform components CRs (Schema Registry, Connect, REST Proxy, Control Center) and the admin KafkaRestClass CR, to enable
sslClientAuthenticationfrom the client-side, and to update their Kafka dependency endpoint to communicate on the custom listener created in Step 1.All these have to be done in the same step.
Note that the MDS authentication type and the Kafka authentication type should be the same since MDS exists on the Kafka cluster.
For OAuth-based RBAC,
oauthfor Kafka and MDSFor LDAP-based RBAC,
oauthbearerfor Kafka andbearerfor MDSUpdate the Confluent Platform components:
kind: <component> spec: dependencies: kafka: bootstrapEndpoint: kafka.confluent.svc.cluster.local:9093 authentication: type: <oauth or oauthbearer> <oauth or oauthbearer>: sslClientAuthentication: true tls: enabled: true mds: endpoint: https://kafka.confluent.svc.cluster.local:8090 tokenKeyPair: secretRef: mds-token authentication: type: <oauth or oauthbearer> <oauth or bearer>: sslClientAuthentication: true tls: enabled: true
Update the
kafkaRestdependency in the Kafka CR to enable the client-side mTLS in the embedded REST Proxy.kind: Kafka spec: dependencies: kafkaRest: authentication: type: <oauth or bearer> <oauthSettings or bearer>: sslClientAuthentication: true tls: enabled: true secretRef: tls-kafka
Update the KaftRestClass CR. It is required to create role bindings.
kind: KafkaRestClass spec: kafkaRest: endpoint: https://kafka.confluent.svc.cluster.local:8090 authentication: type: <oauth or bearer> <oauth or bearer>: sslClientAuthentication: true tls: secretRef: tls-kafka
Add the mTLS provider in the MDS service in parallel to the already existing OAuth or LDAP provider. This enables dual authentication with OAuth or LDAP and mTLS.
kind: kafka spec: services: mds: provider: mtls: sslClientAuthentication: <"required" or "requested"> principalMappingRules: <oauth or ldap>: configurations:
Add the mTLS authentication section in the Schema Registry, Connect, and REST Proxy CRs to support dual authentication.
kind: <component> spec: authentication: mtls: sslClientAuthentication: "required" principalMappingRules: oauth: # If migrating to OAuth+mTLS
Migrate RBAC from OAuth or LDAP-based to mTLS-only authentication
This section describes how to migrate an OAuth or LDAP-based RBAC deployment to use mTLS as the only authentication.
If OAuth or LDAP principals for Confluent Platform components do not match the principal extracted from their certificates, it is a prerequisite to add role bindings for mTLS principals before starting to migrate to mTLS only. If role bindings for mTLS principals are not added, it will lead to downtime of the cluster.
Add a custom listener with mTLS authentication in Kafka.
This listener will be used for Confluent Platform components to Kafka communication while the internal listener gets updated during migration.
kind: Kafka spec: listeners: custom: - name: custommtls port: 9094 authentication: type: mtls principalMappingRules: - "RULE:.*CN=([a-zA-Z0-9.-]*).*$/$1/" - "DEFAULT" tls: enabled: true
Add role bindings for the certificate principals and migrate all external clients to mTLS. For creating role bindings, see Create a rolebinding.
Update all Confluent Platform components’ dependencies to communicate with Kafka and MDS using the custom listener with mTLS authentication. Note that Kafka and MDS dependencies should always be updated in the same step.
dependencies: kafka: bootstrapEndpoint: kafka.confluent.svc.cluster.local:9094 authentication: type: mtls sslClientAuthentication: true tls: enabled: true mds: endpoint: https://kafka.confluent.svc.cluster.local:8090 tokenKeyPair: secretRef: mds-token authentication: type: mtls sslClientAuthentication: true tls: enabled: true
Migrate MDS and all Confluent Platform components to mTLS only authentication.
Remove LDAP or OAuth from the MDS provider section.
Since the REST-based Confluent Platform components depend on the LDAP provider in MDS for basic authentication, all the REST components are also automatically migrated to mTLS-only as soon as LDAP is removed from MDS.
kind: Kafka spec: services: mds: impersonation: admins: - User:kafka - User:krp - User:connect tls: enabled: true tokenKeyPair: secretRef: mds-token provider: mtls: sslClientAuthentication: "required" principalMappingRules: [ "RULE:.*CN=([a-zA-Z0-9.-]*).*$/$1/,DEFAULT" ]
At this stage, all the communications among Kafka and Confluent Platform components are through mTLS.
When migrating from OAuth and mTLS-based RBAC, client to non-Kafka (Schema Registry, REST Proxy, Connect) communications are through OAuth.
Before migrating all Confluent Platform components to mTLS-only authentication, migrate the external clients to mTLS.
To disable OAuth in Confluent Platform components, remove
oauthfrom the authentication section and set the authentication type tomtls.kind: <component> spec: authentication: type: mtls mtls: sslClientAuthentication: "required" principalMappingRules: [ "RULE:.*CN=([a-zA-Z0-9.-]*).*$/$1/" , "DEFAULT" ]
Enable RBAC in running Confluent Platform cluster
This section describes the workflow to enable RBAC in the following types of non-RBAC or ACL-based Confluent Platform deployments:
ACL-enabled deployments
ZooKeeper-based clusters for Confluent Platform 7.9 or earlier versions
KRaft-based clusters
As a requirement for non-RBAC to RBAC migration, your Confluent Platform cluster must have authentication already enabled. Clusters with no authentication configured are not supported for this migration workflow.
For comprehensive coverage of the following example migration scenarios, see the RBAC migration scenarios.
Non-RBAC with authentication | RBAC |
|---|---|
SASL/PLAIN Kafka | MDS LDAP + Kafka SASL/PLAIN |
SASL/PLAIN Kafka | MDS OAuth + Kafka SASL/PLAIN |
Kafka mTLS | MDS mTLS + Kafka mTLS |
Kafka mTLS | MDS LDAP + Kafka mTLS |
Kafka mTLS | MDS OAuth + Kafka mTLS |
To enable RBAC in a running Confluent Platform cluster:
If your clusters have an authorizer and all required ACLs, you can start at Step 4.
For clusters without an authorizer, Steps 1-3 are needed to first enable authorization. Then you can migrate to RBAC.
Configure ACL authorizer (
authorizer.class.name) and add super users (authorization.superUsers) for broker principals.If an ACL authorizer was already configured, then we don’t need to do a rolling restart.
For KRaft-based clusters, an authorizer must be added to both the KRaftcontroller and Kafka CRs:
spec: configOverrides: server: - authorizer.class.name=org.apache.kafka.metadata.authorizer.StandardAuthorizer - allow.everyone.if.no.acl.found=true authorization: superUsers: - User:kafka type: simple
allow.everyone.if.no.acl.found=trueis set for zero downtime when enabling the authorizer.Caution
If someone adds an ACL while
allow.everyone.if.no.acl.foundis set totrue, all the users who previously had access will lose that access.Perform a rolling restart of the KRaft controllers and Kafka brokers.
Create ACLs for the broker principals and the user principals of all applications, including Confluent Platform components.
When a new ACL is added, all the users who previously had access will lose access to that resource since it was previously set to allow all before the new ACL is added.
There might be downtime for clients here between adding an authorizer and adding ACLs.
Enable RBAC on Kafka brokers as described in Enable RBAC for Kafka with the following specifics that apply to this migration workflow.
Update the authorization type
simpleset in Step 1 torbac.Remove the following configuration overrides set in Step 1 from the KRaftcontroller and Kafka CRs:
allow.everyone.if.no.acl.found=trueauthorizer.class.name
Add MDS service configuration as described in Configure MDS for RBAC.
kind: kafka spec: authorization: type: rbac services: mds: <mds-configs>
Add the Kafka REST dependency.
kind: kafka spec: authorization: type: rbac dependencies: kafkaRest: authentication: <auth-configs>
Perform a rolling restart of the Kafka brokers.
Add the KafkaRestClass CR and create a KafkaRestClass service as described in Configure Kafka REST Class for RBAC. For example:
kind: KafkaRestClass metadata: name: default namespace: confluent spec: kafkaRest: authentication: <auth-configs>
Configure RBAC role bindings for resources of other components. This includes all the external Kafka clients and the clients of Confluent Platform components.
Enable RBAC in all Confluent Platform components as described in Enable RBAC for other Confluent Platform components.
Set authorization type to
rbac.Set MDS dependency configuration in the CRs.
Perform a rolling restart.
Review the automatically created role bindings.
The following are alternative ways to set up RBAC in a running cluster.
Cluster Linking
Use Cluster Linking to set up RBAC in a running cluster.
Create a new CFK-based Kafka cluster with the required RBAC configuration as you would do in a greenfield setup.
Setup Cluster Linking between the existing non-RBAC cluster to the new RBAC cluster.
Once the replication lag is 0 we can start migrating the clients to the newer cluster.
Decommission the old non-RBAC cluster once all clients have been migrated.
Centralized MDS
To set up RBAC in a running cluster, create an external (centralized) MDS cluster and use the non-RBAC cluster as the secondary cluster.
Create a new CFK-based Kafka cluster with the required RBAC configurations as described in the greenfield setup.
Enable authorization in the existing non-RBAC cluster and add ACLs for zero downtime.
Add MDS client specs in existing non-RBAC cluster to connect to external MDS cluster.
Automated creation of role bindings for Confluent Platform component principals
CFK automatically creates all required role bindings for Confluent Platform components as ConfluentRoleBinding custom resources (CRs).
Review the role bindings created by CFK:
kubectl get confluentrolebinding
Grant role to Kafka user to access Schema Registry
Use the following ConfluentRolebinding CR to create the required role binding to access Schema Registry:
apiVersion: platform.confluent.io/v1beta1
kind: ConfluentRolebinding
metadata:
name: internal-schemaregistry-schema-validation
namespace: <namespace>
spec:
principal:
name: <user-id>
type: user
clustersScopeByIds:
schemaRegistryClusterId: <schema-registry-group-id>
kafkaClusterId: <kafka-cluster-id>
resourcePatterns:
- name: "*"
patternType: LITERAL
resourceType: Subject
role: DeveloperRead
Grant roles to a Control Center user to administer Confluent Platform
Control Center users require separate roles for each Confluent Platform component and resource they wish to view and administer in the Control Center or Control Center (Legacy) UI. Grant explicit permissions to the users as shown below.
In the following example, the testadmin principal is used as a Control Center UI user.
Grant permission to view and administer Confluent Platform components
The rolebinding CRs in the examples GitHub repo specifies the permissions needed in CFK. Create the rolebindings with the following command:
kubectl apply -f \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/confluentinc/confluent-kubernetes-examples/master/security/production-secure-deploy/controlcenter-testadmin-rolebindings.yaml
Check the roles created:
kubectl get confluentrolebinding
Troubleshooting: Verify MDS configuration
Log into MDS to verify the correct configuration and to get the Kafka cluster ID. You need the Kafka cluster ID for component role bindings.
Replace https://<mds_endpoint> in the below commands with the value you set in the spec.dependencies.mds.endpoint in the Kafka CR.
Log into MDS as the Kafka super user as below:
confluent login \ --url https://<mds_endpoint> \ --ca-cert-path <path-to-cacerts.pem>
You need to pass the
--ca-cert-pathflag if:You have configured MDS to serve HTTPS traffic (
kafka.spec.dependencies.mds.tls.enabled: true).The CA used to issue the MDS certificates is not trusted by system where you are running these commands.
Provide the Kafka username and password when prompted, in this example,
kafkaandkafka-secret.You get a response to confirm a successful login.
Verify that the advertised listeners are correctly configured using the following command:
curl -ik \ -u '<kafka-user>:<kafka-user-password>' \ https://<mds_endpoint>/security/1.0/activenodes/https
Get the Kafka cluster ID using one of the following commands:
confluent cluster describe --url https://<mds_endpoint>
curl -ik \ https://<mds_endpoint>/v1/metadata/id