Important
You are viewing documentation for an older version of Confluent Platform. For the latest, click here.
Manage Schemas for Topics¶
Use the Schema Registry feature in Control Center to manage Confluent Platform topic schemas.
You can:
- create, edit, and view schemas
- compare schema versions
- download schemas
The Schema Registry performs validations and compatibility checks on schemas.
Tip
- Review the step-by-step tutorial for using Schema Registry.
- For comprehensive information on Schema Registry, see the Schema Registry documentation.
The Schema Registry feature in Control Center is enabled by default. Disabling the feature disables both viewing and editing of schemas.
Note
As of Confluent Platform version 5.2, schemas can be created and edited. Versions prior to 5.2 only have view access to schema information in Control Center, including comparing version history and downloading schemas.
Creating a topic schema in Control Center¶
Create key and value schemas. Value schemas are typically created more frequently than a key schema.
Best practices:
- Provide default values for fields to facilitate backward-compatibility if pertinent to your schema.
- Document at least the more obscure fields for human-readability of a schema.
To create a topic value schema:
Select a cluster from the navigation bar.
Click the Topics menu. The All Topics page appears.
Select a topic.
The topic overview page appears.
Click the Schema tab.
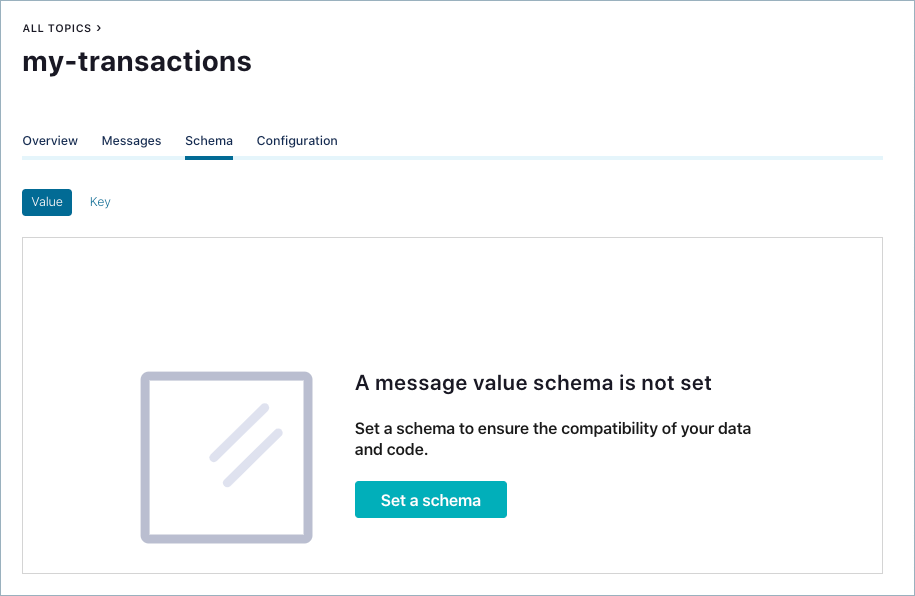
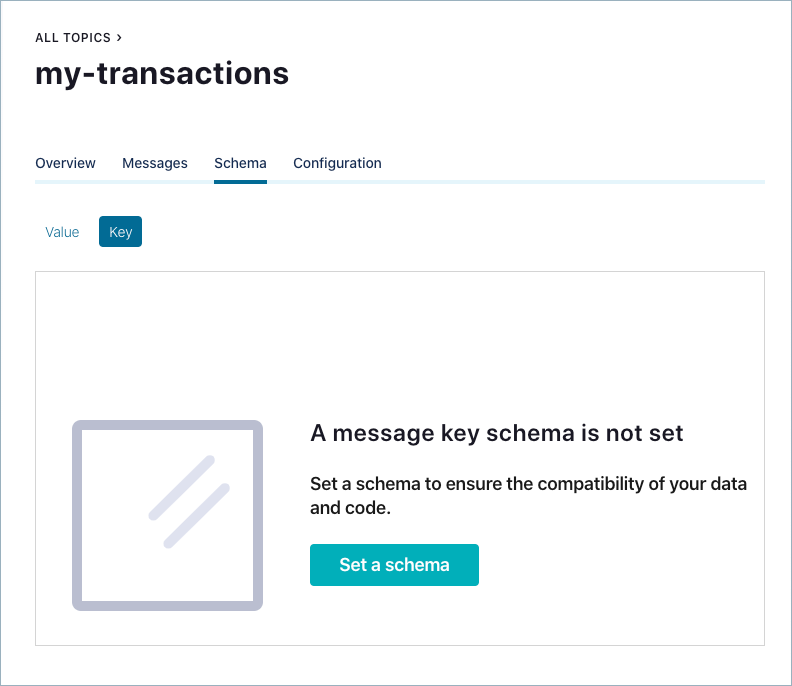
You are prompted to set a message value schema.
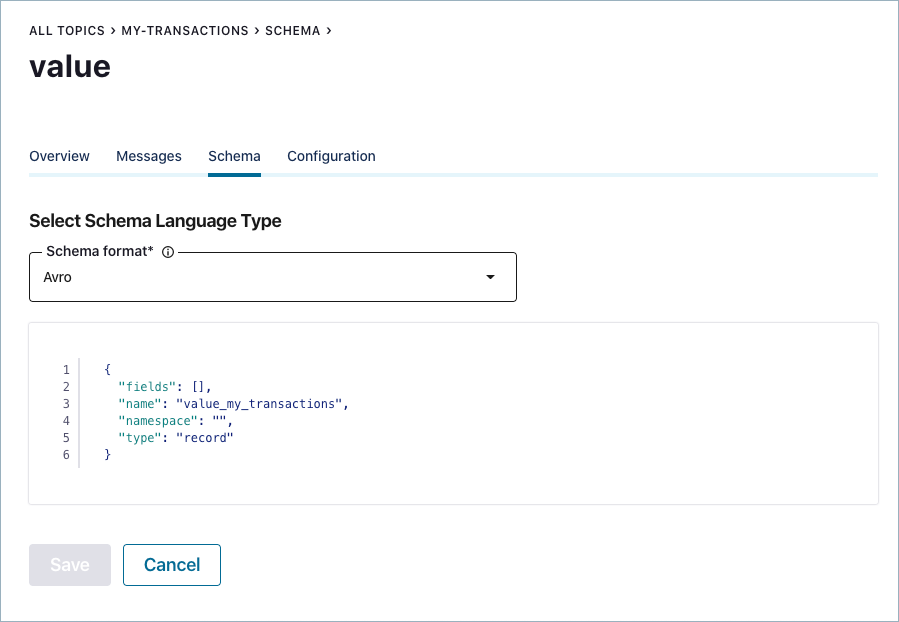
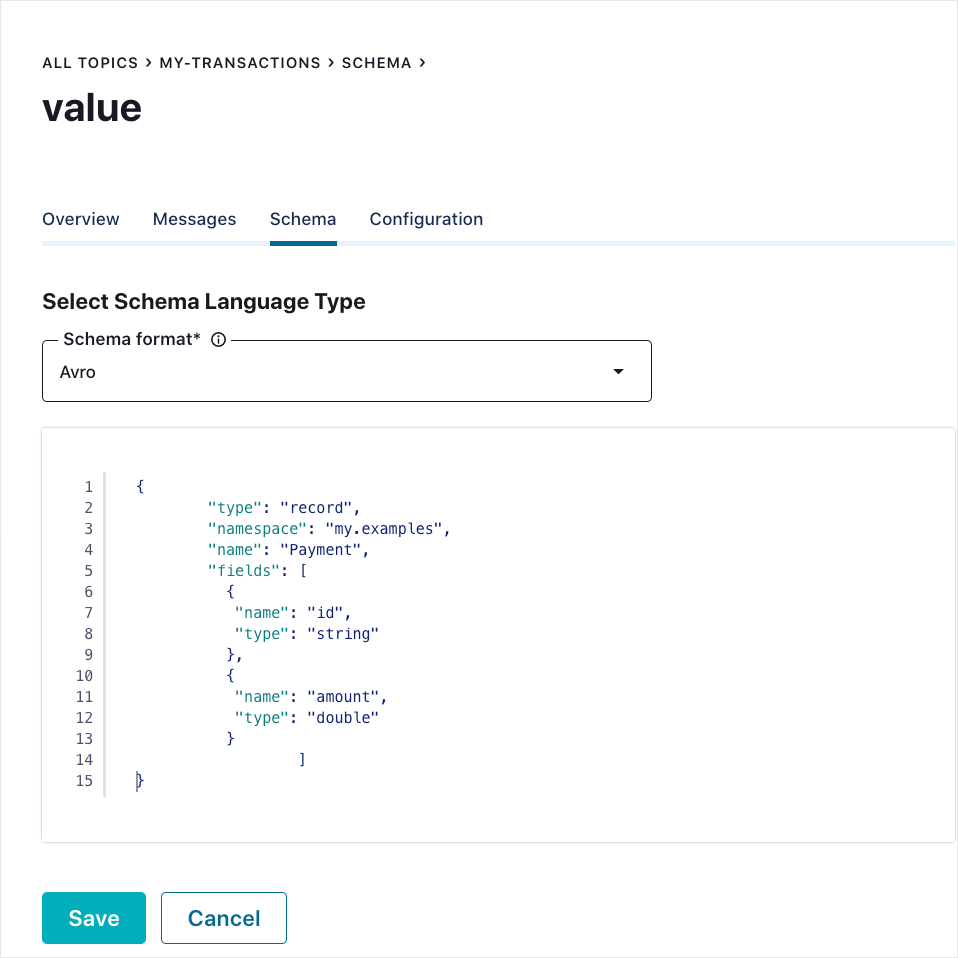
Click Set a schema. The Schema editor appears pre-populated with the basic structure of an Avro schema to use as a starting point, if desired.
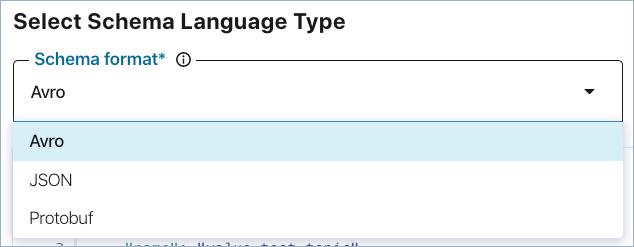
Select a schema format type:
- Avro
- JSON
- Protobuf
Choose Avro if you want to try out the code examples provided in the next steps.
Tip
To learn more about each of the schema types, see Supported Formats.
Enter the schema in the editor:
name: Enter a name for the schema if you do not want to accept the default, which is determined by the subject name strategy. The default isschema_type_topic_name. Required.type: Eitherrecord,enum,union,array,map, orfixed. Required.namespace: Fully-qualified name to prevent schema naming conflicts. String that qualifies the schemaname. Optional but recommended.fields: JSON array listing one or more fields for a record. Required.Each field can have the following attributes:
name: Name of the field. Required.doc: Field metadata. Optional but recommended.default: Default value for a field. Optional but recommended.order: Sorting order for a field. Valid values are ascending, descending, or ignore. Default: Ascending. Optional.aliases: Alternative names for a field. Optional.
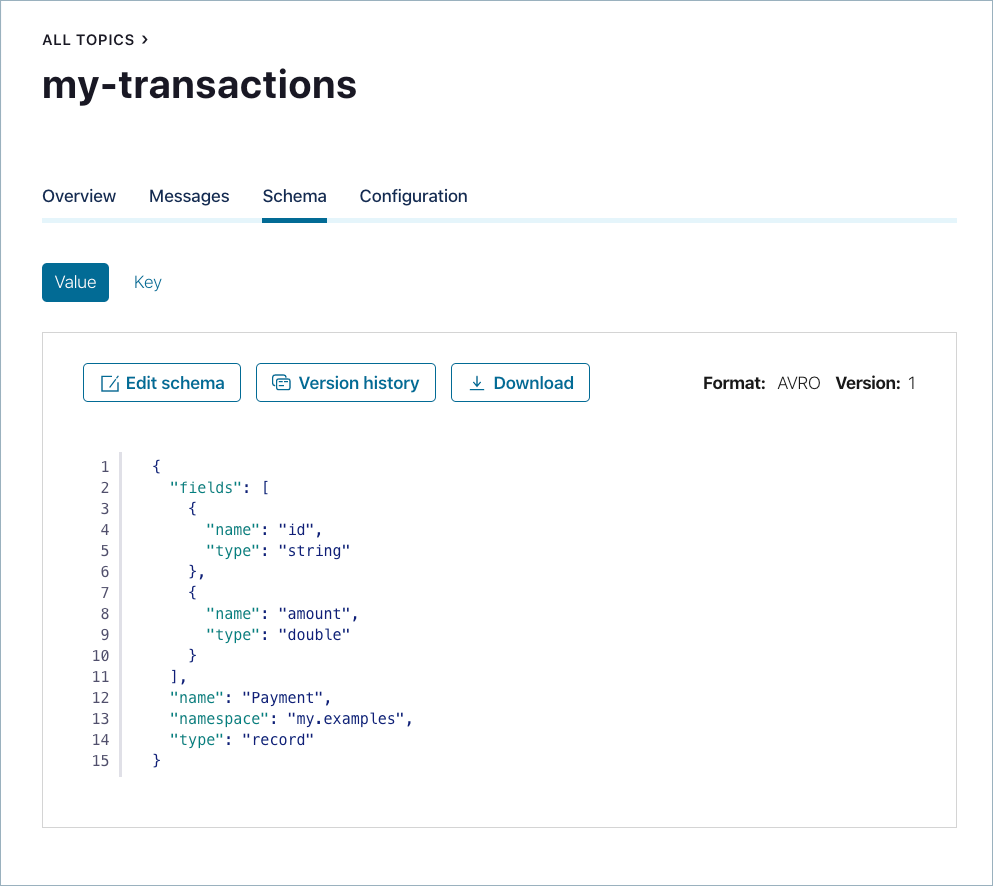
Copy and paste the following example schema.
{ "type": "record", "namespace": "my.examples", "name": "Payment", "fields": [ { "name": "id", "type": "string" }, { "name": "amount", "type": "double" } ] }
Click Save.
- If the entered schema is valid, the Schema updated message is briefly displayed in the banner area.
- If the entered schema is not valid, an Input schema is an invalid Avro schema error is displayed in the banner area.
If applicable, repeat the procedure as appropriate for the topic key schema.
To create a topic key schema:
Click the Key option. You are prompted to set a message key schema.
Click Set a schema.
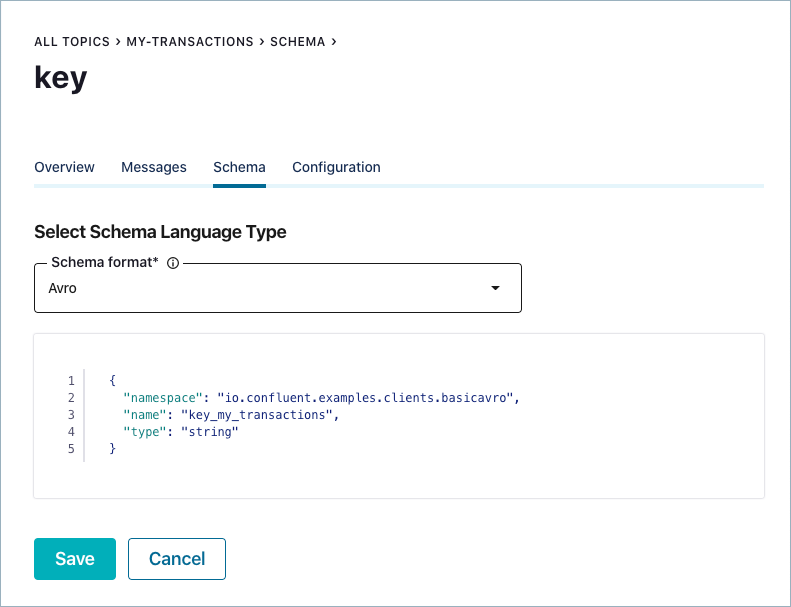
Enter the schema into the editor and click Save.
Copy and paste the following example schema, and save it.
{ "namespace": "io.confluent.examples.clients.basicavro", "name": "key_my_transactions", "type": "string" }
Tip
Kafka messages are key/value pairs. Message keys and message values can be
serialized independently. For example, the value may be using an
Avro record,
while the key may be a primitive (string, integer, and so forth).
Typically message keys, if used, are primitives, but they can be complex data types
as well (for example, record or array). How you set the key is up to you
and the requirements of your implementation. For detailed examples of key and value schemas,
see the discussion under Schema Formats, Serializers, and Deserializers in the Schema Registry documentation.
Viewing a schema in Control Center¶
View the schema details for a specific topic.
Select a cluster from the navigation bar.
Click the Topics menu. The All Topics page appears.
Select a topic.
The topic overview page appears.
Click the Schema tab.
The Value schema is displayed by default.
Tip
The Control Center schema display may re-order the placement of meta information about the schema. Comparing this view with the example provided in the previous section, note that schema name, namespace, and record type are shown below the field definitions. This is an artifact of the display in Control Center; the schema definition is the same.
Click the Key tab to view the key schema if present.
Editing a schema in Control Center¶
Edit an existing schema for a topic.
Select a cluster from the navigation bar.
Click the Topics menu. The All Topics page appears.
Select a topic.
Click the Schema tab.
Select the Value or Key tab for the schema.
Click Edit schema and make the changes in the schema editor.
For example, if you are following along with the example:
Select the topic
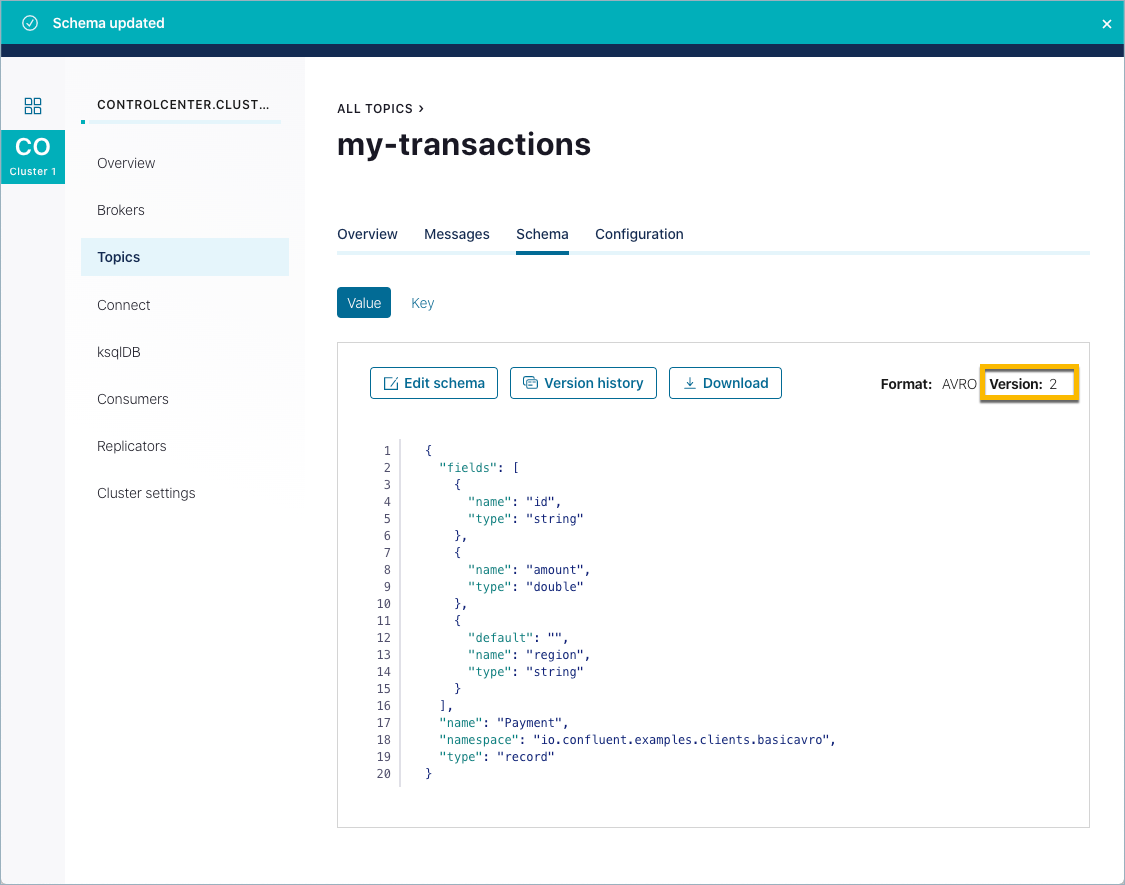
my-transactions, click Schema, and select the Value tab.Edit the schema by copy-pasting the following definition for a new
regionfield, after theidandamountfields. Precede your new definition with a comma, per the syntax.{ "name": "region", "type": "string", "default": "" }
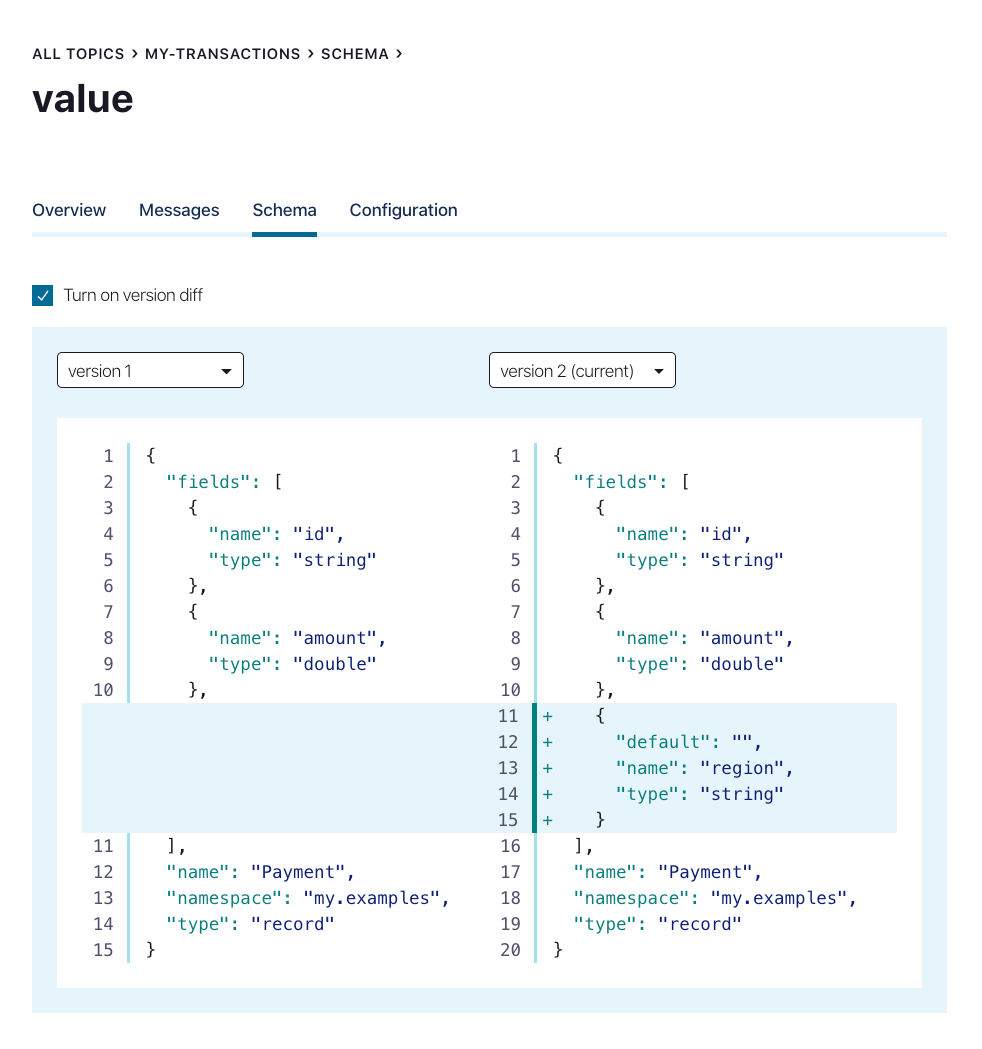
Note that the new
regionfield includes a default value, which makes it backward compatible. By plugging in the default value, consumers can use the new schema to read data submitted by producers that use the older schema (without theregionfield).Click Save.
If the schema update is valid and compatible with its prior versions (assuming a backward-compatible mode), the schema is updated and the version count is incremented. You can compare the different versions of a schema.
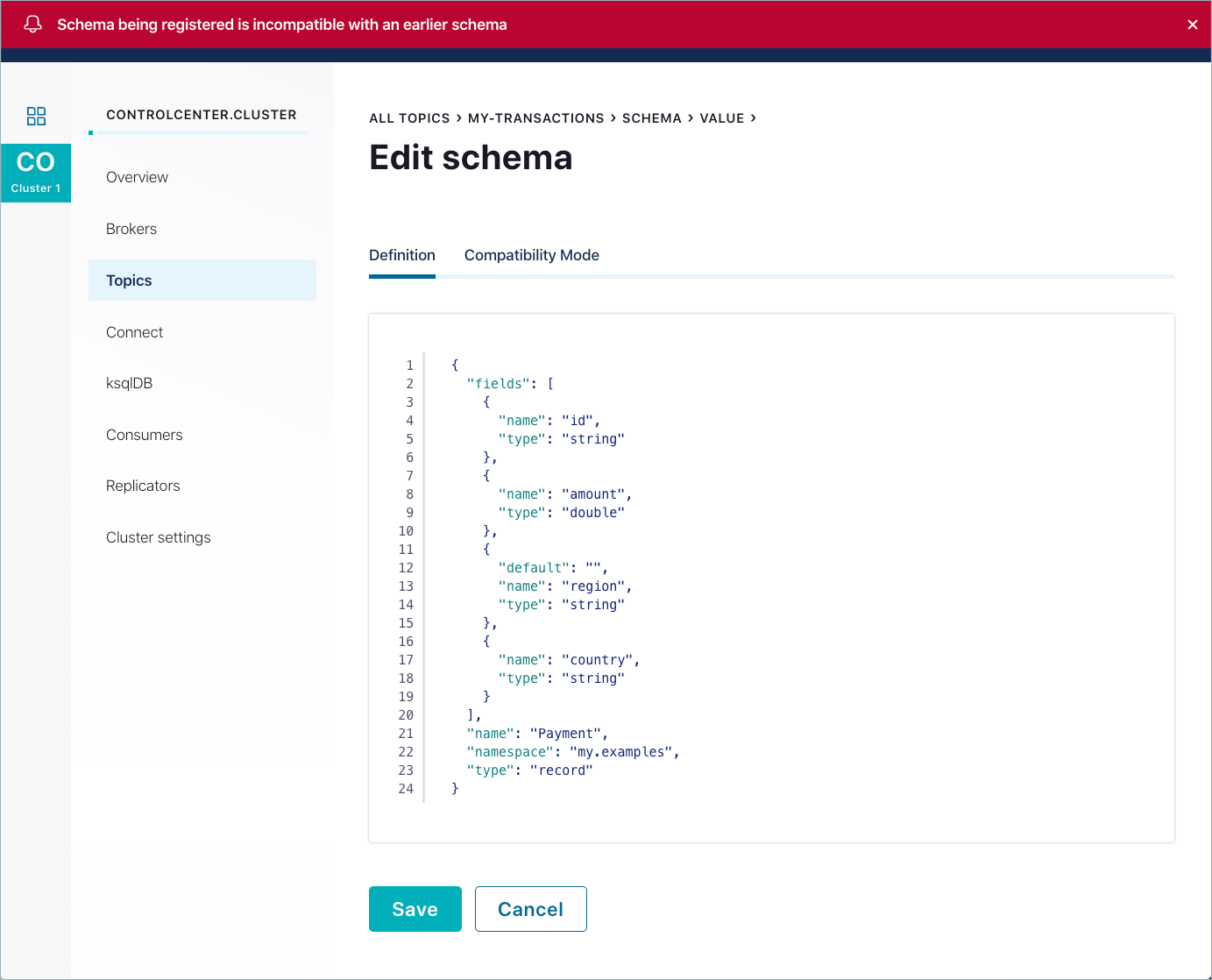
If the schema update is invalid or incompatible with an earlier schema version, an error is displayed.
The example below shows the addition of another new field,
country, with no default provided for backward compatibility.
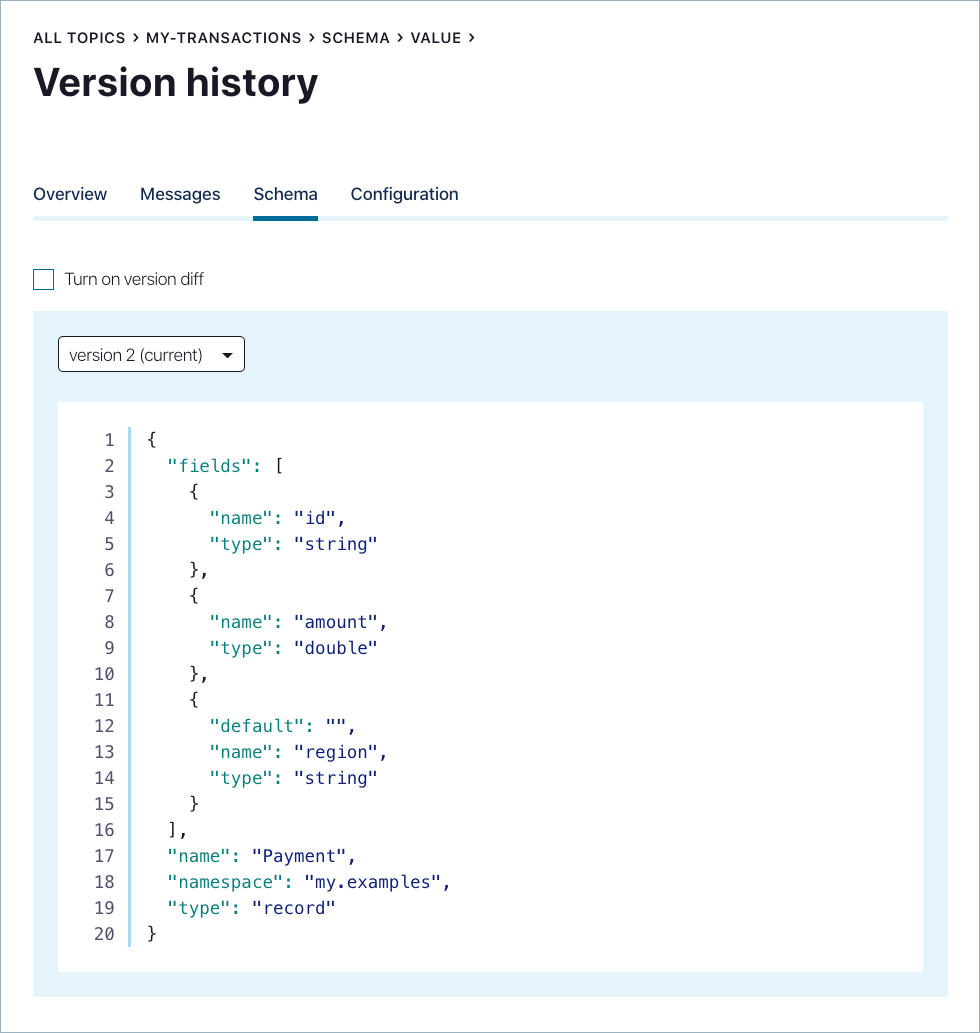
Comparing schema versions in Control Center¶
Compare versions of a schema to view its evolutionary differences.
Select a cluster from the navigation bar.
Click the Topics menu. The All Topics page appears.
Select a topic.
Click the Schema tab.
Select the Key or Value tab for the schema.
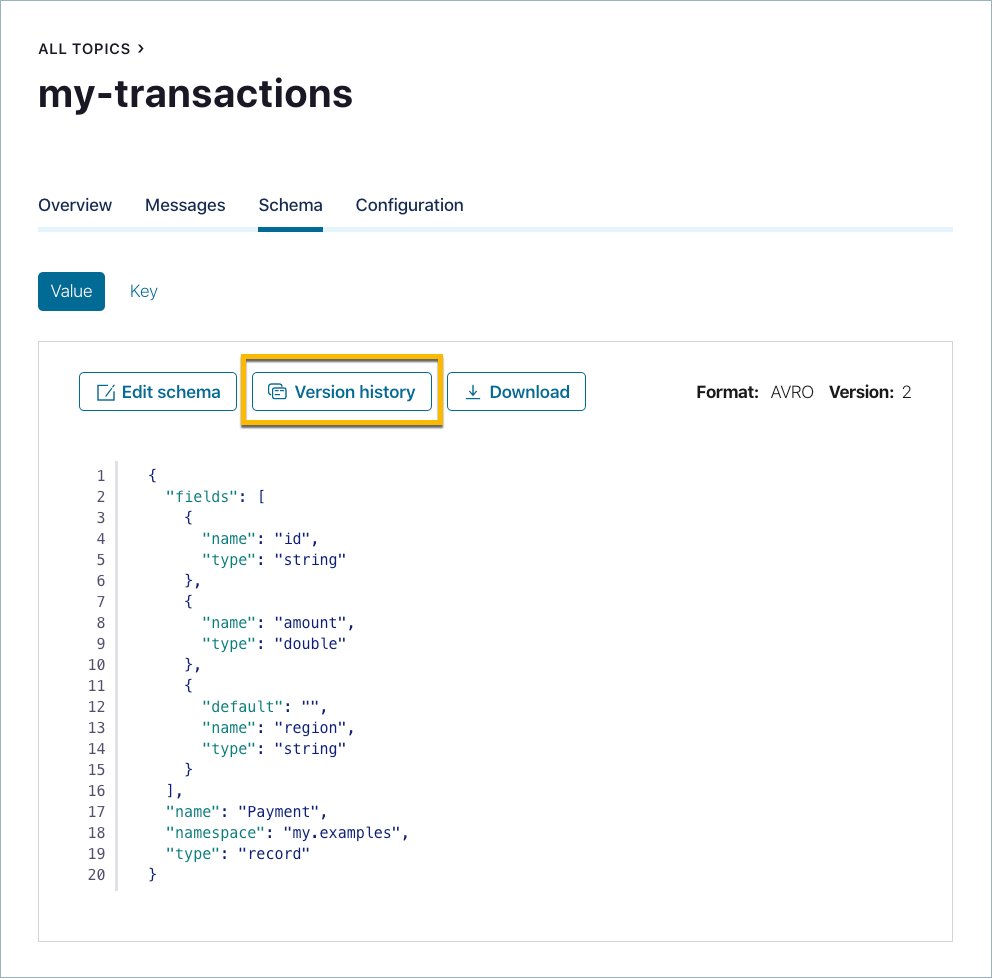
Click Version history.
The current version number of the schema is indicated on the version menu.
Select the Turn on version diff check box.
Select the versions to compare from each version menu. The differences are highlighted for comparison.
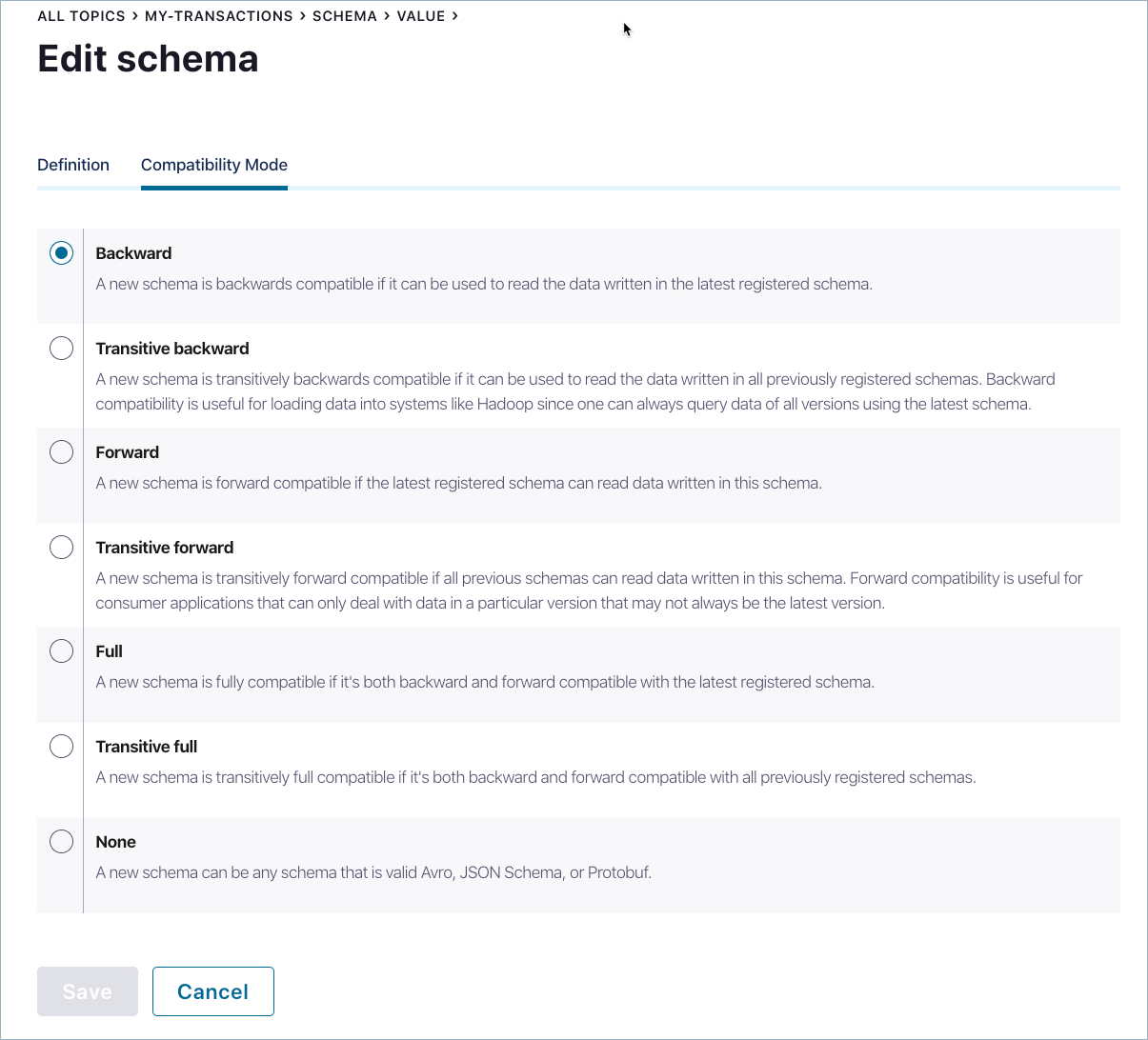
Changing the compatibility mode of a schema in Control Center¶
The default compatibility mode is Backward. The mode can be changed for the schema of any topic if necessary.
Caution
If you change the compatibility mode of an existing schema already in production use, be aware of any possible breaking changes to your applications.
Select a cluster from the navigation bar.
Click the Topics menu. The All Topics page appears.
Select a topic.
Click the Schema tab.
Select the Key or Value tab for the schema.
Click Edit Schema -> Compatibility Mode tab.
Select a mode option:
- Backward (Confluent Schema Registry default)
- Transitive backward
- Forward
- Transitive forward
- Full
- Transitive full
- None (not recommended)
Descriptions indicate the compatibility behavior for each option. For more information, including the changes allowed for each option, see Schema Evolution and Compatibility.
Click Save.
Downloading a schema from Control Center¶
Select a cluster from the navigation bar.
Click the Topics menu. The All Topics page appears.
Select a topic.
Click the Schema tab.
Select the Key or Value tab for the schema.
Click Download. A schema JSON file for the topic is downloaded into your Downloads directory.
Example filename:
schema-transactions-v1-Ry_XaOGvTxiZVZ5hbBhWRA.jsonExample contents:
{"subject":"transactions-value","version":1,"id":2,"schema":"{\"type\":\"record\",\"name\":\"Payment\", \"namespace\":\"io.confluent.examples.clients.basicavro\", \"fields\":[{\"name\":\"id\",\"type\":\"string\"},{\"name\":\"amount\",\"type\":\"double\"}, {\"name\":\"region\",\"type\":\"string\"}]}"}This is the first version of the schema, and it has an
idof 2. The schema is escaped JSON. A backslash precedes double-quotes.
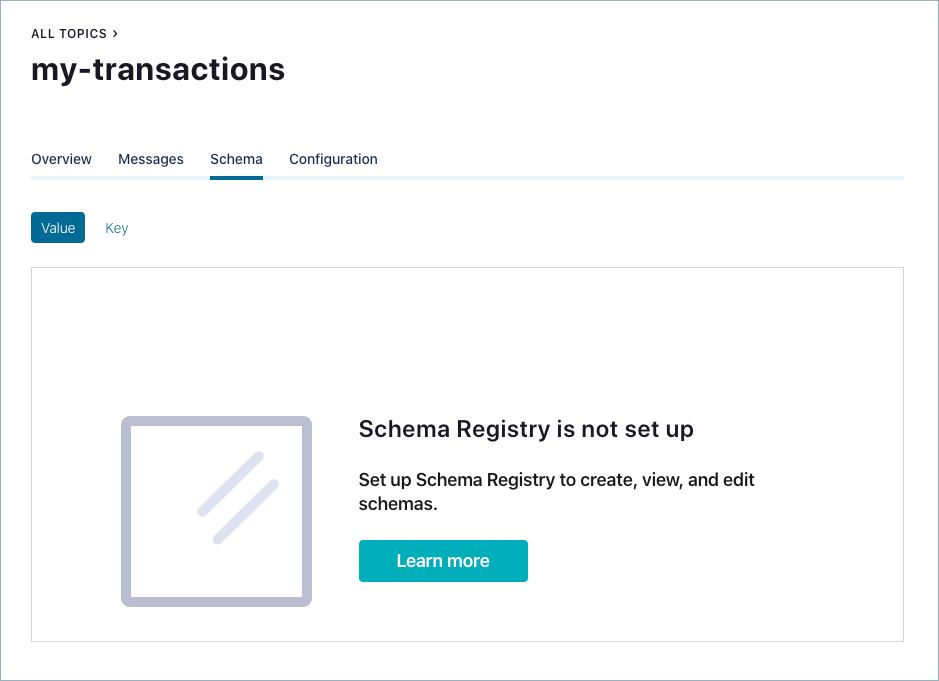
Troubleshoot error “Schema Registry is not set up”¶
If you get an error message on Control Center when you try to access a topic schema
(”Schema Registry is not set up”), first make sure that Schema Registry is running. Then verify that the
Schema Registry listeners configuration matches the Control Center confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.url
configuration. Also check the HTTPS configuration parameters.
For more information, see A schema for message values has not been set for this topic, and start-up procedures for Quick Start for Apache Kafka using Confluent Platform Community Components (Local), Quick Start for Apache Kafka using Confluent Platform Community Components (Docker), or On-Premises Deployments, depending on which one of these you are using to run Confluent Platform.
Enabling and disabling Schema Registry in Control Center¶
The feature that allows working with schemas in Control Center is enabled by default. The feature can be disabled if an organization does not want any users to access the feature. After disabling the feature, the Topics Schema menu and the Schema tab are no longer visible in the Control Center UI. The ability to view and edit schemas is disabled.
To disable the edit schema feature in Control Center:
Set the
confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.enableoption in yourcontrol-center.propertiesfile tofalse.confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.enable=false
Note
Make the change in the appropriate Control Center properties file or files configured for your environments, including
control-center-dev.propertiesorcontrol-center-production.properties. The properties files are located in/path-to-confluent/etc/confluent-control-center/.Restart Control Center and pass in the properties file for the configuration to take effect:
./bin/control-center-stop ./bin/control-center-start ../etc/confluent-control-center/control-center.propertiesTip
If you are using a Confluent Platform development environment with a confluent local, stop and start as follows:
./confluent local stop control-center ./confluent local start control-center ../etc/confluent-control-center/control-center-dev.properties
To enable the feature again, set the option back to true and restart Control Center with the updated properties file.
Enabling Multi-Cluster Schema Registry¶
Starting with version 5.4.1, Confluent Platform supports the ability to run multiple schema registries and associate a unique Schema Registry to each Kafka cluster in multi- cluster environments.
The ability to scale up schema registries in conjunction with Kafka clusters is useful for evolving businesses; and particularly supports data governance, organization, and management across departments in large enterprises.
When multi-cluster Schema Registry is configured and running, you can create and manage schemas per topics in Control Center as usual.
Configuration Properties and Files¶
Multiple Schema Registry clusters may be specified with confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.{name}.url
in the appropriate Control Center properties file. To use a Schema Registry cluster identified in this way, add or verify
the following broker and Control Center configurations.
A new endpoint /v1/metadata/schemaRegistryUrls has been exposed by Kafka to
return the confluent.schema.registry.url field from the Kafka broker
configurations. Control Center uses this field to look up the registries from Kafka
broker configurations. To use this, you must configure unique listener endpoints for
each cluster:
- In the broker
server.propertiesfiles (unique for each Kafka cluster), specify the REST endpoint with theconfluent.http.server.listenersfield, which defaults tohttp://0.0.0.0:8090. - In the appropriate Control Center properties file, use
confluent.controlcenter.streams.cprest.urlto define the REST endpoint forcontrolcenter.cluster. - For additional clusters, define REST endpoints using
confluent.controlcenter.kafka.{name}.cprest.url. This should be consistent with the Kafka cluster name used for other Kafka Control Center configurations; for example,confluent.controlcenter.kafka.{name}.bootstrap.servers.
A minimal viable configuration touches the following files, and includes settings for these properties (example names and ports are given):
Control Center properties file¶
The Control Center properties files file includes:
confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.url=http://localhost:8081confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.sr-1.url=http://localhost:8082confluent.controlcenter.streams.cprest.url=http://localhost:8090confluent.controlcenter.kafka.AK1.cprest.url=http://localhost:8091
See Control Center configuration reference for a full description of confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.url.
Broker configuration file for the Control Center cluster¶
The Kafka broker configuration file for controlcenter.cluster, such as server0.properties, includes:
confluent.http.server.listeners=http://localhost:8090confluent.schema.registry.url=http://localhost:8081
Broker configuration file for the Kafka cluster¶
The Kafka broker configuration file for AK1, server1.properties) includes:
confluent.http.server.listeners=http://localhost:8091confluent.schema.registry.url=http://localhost:8082
With these configurations, editing the schema through the Control Center UI
will connect to http://localhost:8081 for controlcenter.cluster and http://localhost:8082 for AK1.
Defaults and Fallback¶
If confluent.schema.registry.url fields are not specified for any brokers, the confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.url Schema Registry URL is applied.
For example, if the Schema Registry URL was not provided for AK1, AK1’s associated Schema Registry cluster would also be specified at http://localhost:8081.
If confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.url is not explicitly specified in the Control Center properties file, it defaults to http://localhost:8081.
Example¶
Following is a detailed example of a functional multi-cluster Schema Registry setup with two Kafka clusters connected to Control Center,
one the controlcenter.cluster, and the other named AK1, each with one broker.
The table below shows files and configurations in each for the two cluster example. These are not complete properties files, but rather excerpts from each file that define multi-cluster Schema Registry specifics, port numbers, and configurations that are important to the example setup or generally not found in default properties files.
To run the example, copy default Apache ZooKeeper™, Kafka (server.properties), Schema Registry,
and Control Center properties files to new files per the example filenames below,
add/modify properties as shown, and run the components as described in
Run the Example.
Key Configurations¶
| File | Properties |
| zookeeper0.properties |
|
| zookeeper1.properties |
|
| server0.properties |
|
| server1.properties |
|
| schema-registry0.properties |
|
| schema-registry1.properties |
|
| control-center-multi-sr.properties |
cpcrest.url, confluent.controlcenter.kafka.AK1.cprest.url, and
confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.SR-AK1.url are new properties, specific to multi-cluster Schema Registry.
|
Run the Example¶
To run the example:
- Start the ZooKeepers.
- Start the Kafka brokers
- Start the Schema Registry clusters.
- Start Confluent Control Center.
The following example start commands assume the
properties files are in the <path-to-confluent>/etc/ directories shown
below, and that you are running the commands from <path-to-confluent>.
Start ZooKeepers
./bin/zookeeper-server-start etc/kafka/zookeeper0.properties
./bin/zookeeper-server-start etc/kafka/zookeeper1.properties
Start the Kafka brokers
./bin/kafka-server-start etc/kafka/server0.properties
./bin/kafka-server-start etc/kafka/server1.properties
Start Schema Registry clusters
./bin/schema-registry-start etc/schema-registry/schema-registry0.properties
./bin/schema-registry-start etc/schema-registry/schema-registry1.properties
Start Control Center
./bin/control-center-start etc/confluent-control-center/control-center-multi-sr.properties
Manage Schemas for Both Clusters on Control Center¶
- When the example clusters are running and Control Center finishes initialization, open Control Center in your web browser. (Control Center runs at
http://localhost:9021/by default, as described in Control Center User Guide.) - Select a cluster from the navigation bar, click the Topics menu, and explore the schema management options for one or both clusters, starting with Creating a topic schema in Control Center.
Security¶
Any other configurations used to set up a Schema Registry client with Control Center can be
configured for an additional Schema Registry cluster by simply appending the Schema Registry cluster’s
name to the confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry prefix.
For example, for basic authentication with multi-cluster Schema Registry, specify the following in the Confluent Control Center configuration file:
- Use
confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.basic.auth.credentials.sourceandconfluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.basic.auth.user.infoto define authentication for theconfluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.urlcluster. - Use
confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.{name}.basic.auth.credentials.sourceandconfluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.{name}.basic.auth.user.infofor additional Schema Registry clusters (associated with the URL fields by{name}).
Some Schema Registry client configurations also include a schema.registry prefix. For SSL security settings, specify the following in the Confluent Control Center configuration file:
- Use
confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.schema.registry.ssl.truststore.locationandconfluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.schema.registry.ssl.truststore.passwordfor theconfluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.urlcluster. - Use
confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.{name}.schema.registry.ssl.truststore.locationandconfluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.{name}.schema.registry.ssl.truststore.passwordfor additional Schema Registry clusters (associated with the URL fields by{name}).
To learn more, see Schema Registry authentication properties in the Control Center Configuration Reference under Kafka Encryption, Authentication, Authorization Settings and the section on Schema Registry in HTTP Basic Auth. See also, How to configure clients to Schema Registry in the Schema Registry Security Overview.
Errors and Troubleshooting¶
If the brokers for the cluster have matching Schema Registry URLs, but these URLs were not defined in the Control Center properties file, an error message is displayed on the cluster overview page.

Version Compatibility¶
The confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.url configuration in
the Control Center properties file acts as a default if a
cluster’s broker configurations do not contain confluent.schema.registry.url
fields. Multiple Schema Registry clusters may be specified with
confluent.controlcenter.schema.registry.{name}.url fields.
Multi-cluster Schema Registry cannot be used with Kafka versions prior to Kafka 2.4.x, the version current with Confluent Platform 5.4.0. However, using a single cluster Schema Registry setup will work with earlier Kafka versions. To learn more, see Confluent Platform and Apache Kafka Compatibility.
Suggested Reading¶
- See Schema Registry Tutorials for hands-on examples of developing schemas, mapping to topics, and sending messages.
- See Schema Management for an overview of Schema Registry and schema management.
- Control Center Configuration Reference
- Control Center properties files
- A schema for message values has not been set for this topic in Troubleshooting Control Center
- Schema Validation
- Change the subject naming strategy for a topic