Confluent Platform Networking Overview
This section of documents describes the networking options you can configure in Confluent for Kubernetes (CFK) to expose Kafka and other Confluent Platform components to clients.
Confluent Platform networking interfaces
The following images show the networking interfaces available for Confluent Platform components.
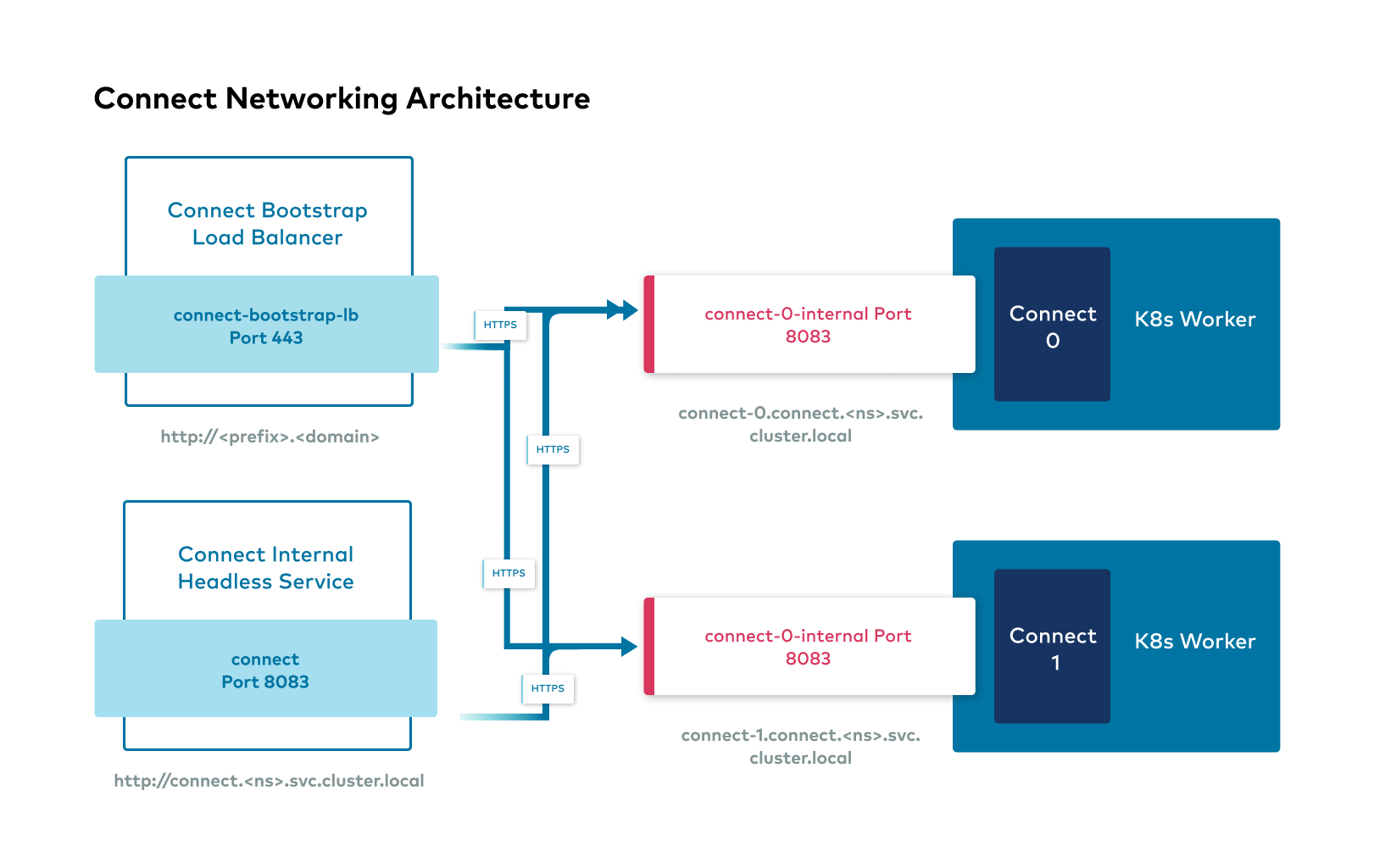
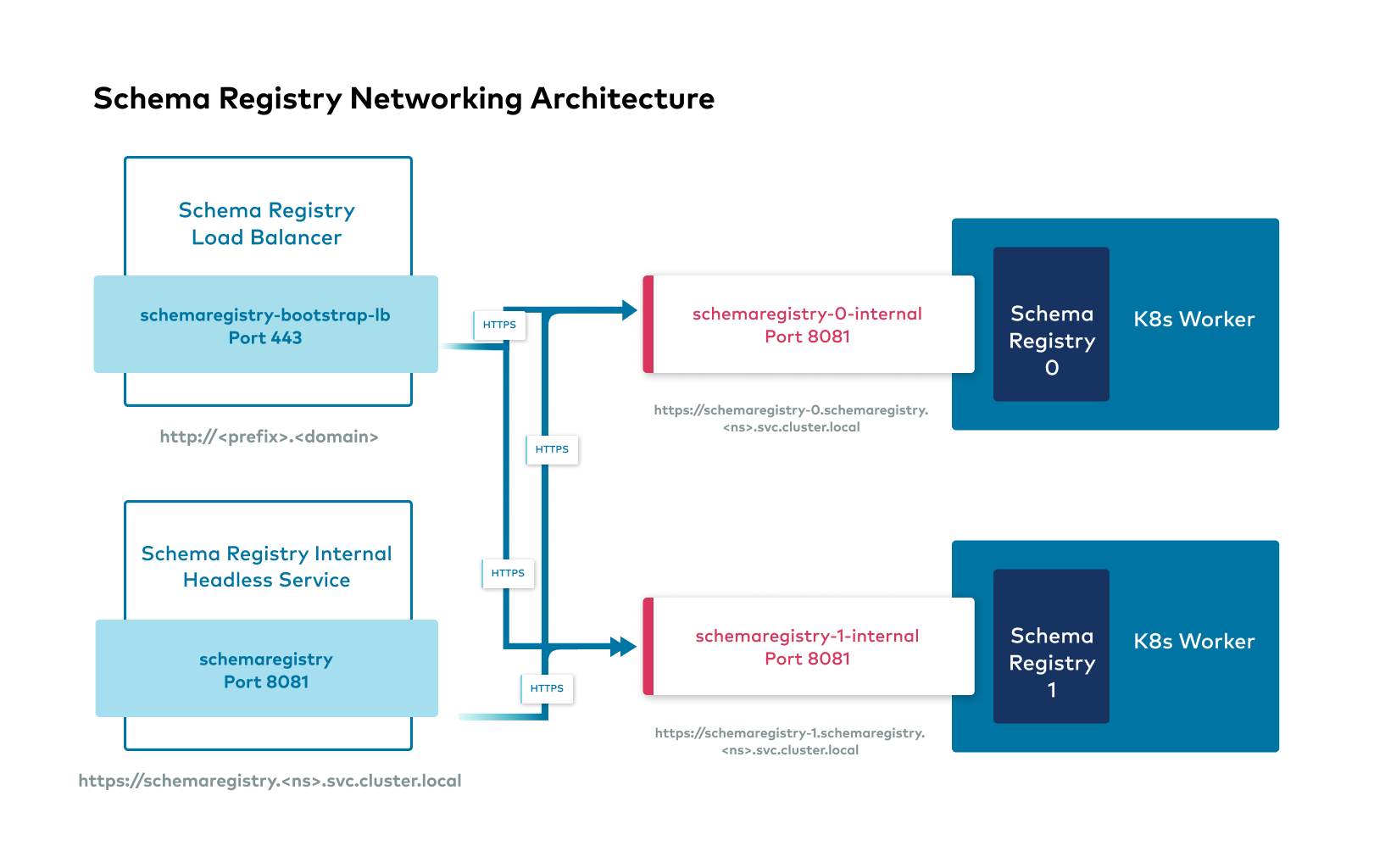
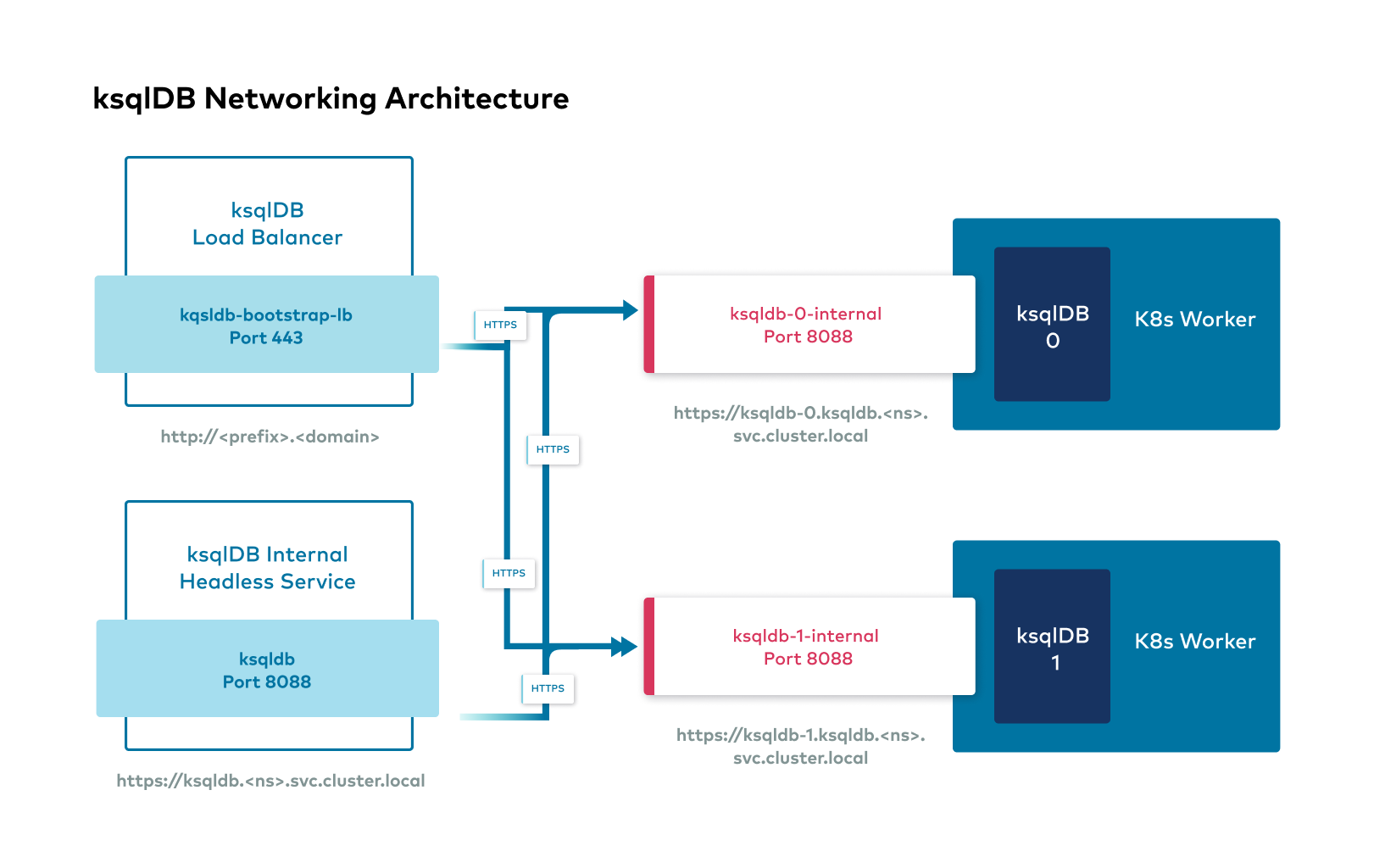
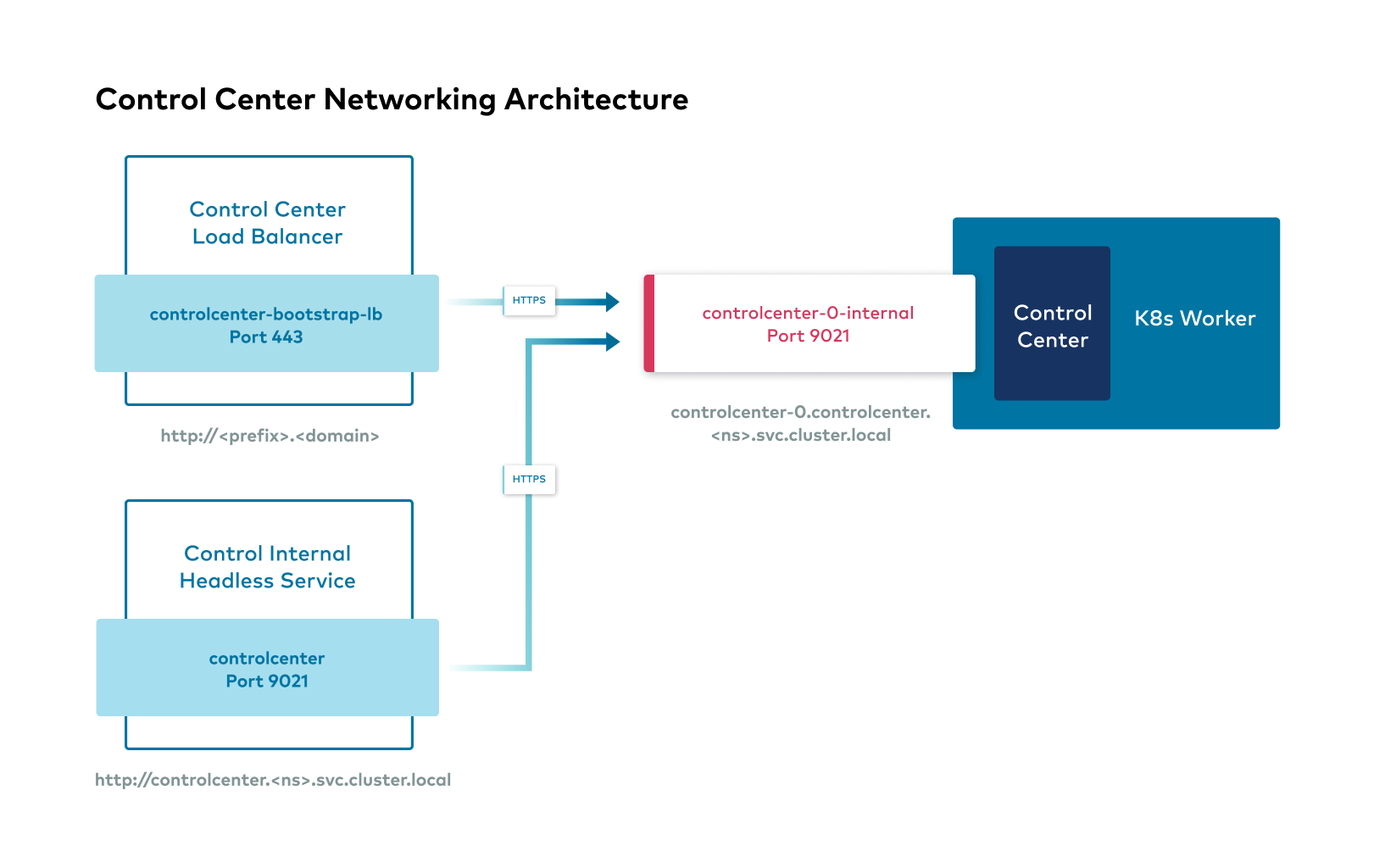
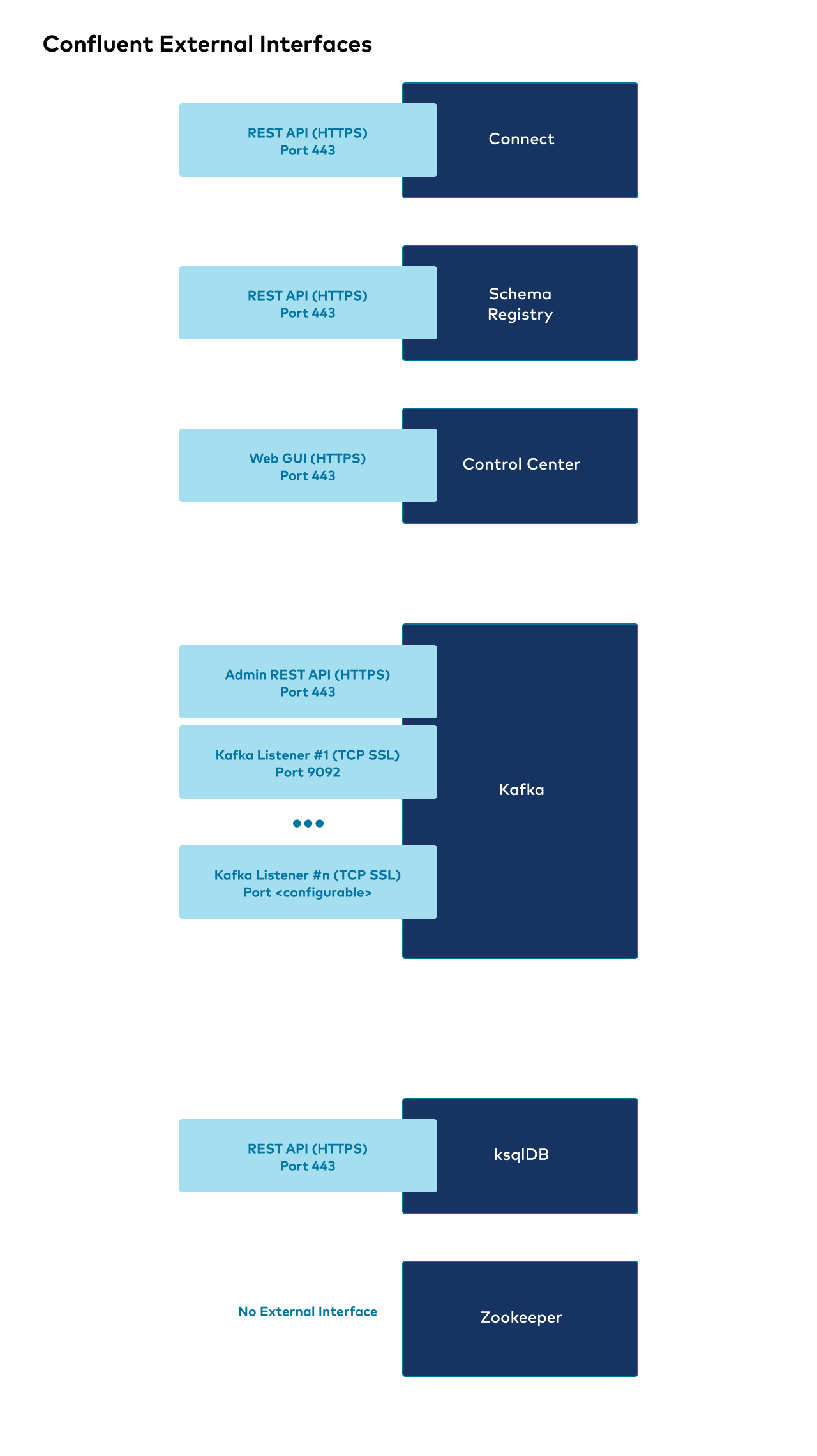
Confluent Platform external interfaces
The following shows the high level overview of external interfaces to connect to Confluent components from outside the Kubernetes cluster.
Kafka listeners
Listeners are the interfaces that Kafka binds to. Advertised listeners are how clients and components can connect to Kafka.
A Kafka listener is configured by providing a hostname, port, and security protocol.
CFK allows you to configure listeners in flexible ways while providing the same default configurations out of the box. To facilitate that, CFK organizes listeners into the following categories in Kafka custom resources (CRs):
- Internal listener
Within the same Kubernetes cluster, Confluent components deployed by CFK and client applications connect to Kafka over Kafka’s internal listener at the following addresses:
If Kafka cluster is deployed to the same namespace as this client / component:
<kafka-component-name>:9071If Kafka cluster is deployed to a different namespace as this client / component:
<kafka-component-name>.<kafka-namespace>.svc.cluster.local:9071
- External listener
Clients external to the Kubernetes network connect to Confluent Platform components using the external listener, with the default port
9092.The following are the external access methods CFK supports. You can configure each component with one method, and once you enable external access one method and deploy Confluent, you cannot change to another external access method.
Clients connect to Confluent Platform using the Kubernetes provider’s load balancer.
Clients connect to Confluent Platform at specified static ports (the NodePort) on the Kubernetes worker node (or via customer-managed networking infrastructure that can forward traffic to those ports).
A Kubernetes Ingress controller manages clients’ connection to Kafka using port-based routing.
A Kubernetes Ingress controller manages clients’ connection to Kafka using host-based routing.
Clients connect to Confluent Platform using OpenShift routes.
- Custom listeners
In addition to external and internal access listeners, you can configure additional custom listeners to access Kafka, for example, to have a separate networking channel for sets of clients.
You can specify a port number that is greater than
9092.9092and lower port numbers are reserved by CFK.The name of a custom listener is case-insensitive.
See Kafka custom listeners for a sample scenario for setting up custom Kafka listeners.
In CFK, you can configure the following for each Kafka listener:
Security
Networking
Name if custom listeners