Migrate Confluent Platform from ZooKeeper to KRaft using Confluent for Kubernetes
ZooKeeper has been deprecated and is no longer included in Confluent Platform 8.0 and later. This topic describes the process to migrate a ZooKeeper-based Confluent Platform 7.9 deployment to KRaft-based 7.9 deployment. After you migrate the Confluent Platform 7.9 to the KRaft-based deployment, upgrade Confluent Platform to 8.1.1 as described in Upgrade KRaft-based Confluent Platform.
Starting in the 2.8 release, Confluent for Kubernetes (CFK) supports migration from a ZooKeeper-based Confluent Platform deployment to a KRaft-based deployment.
To migrate a ZooKeeper-based Confluent Platform deployment to a KRaft-based deployment, use the KRaftMigrationJob custom resource (CR) and follow the steps below.
For an example tutorial of the migration process, see the CFK example GitHub repo.
The high-level workflow to migrate ZooKeeper to KRaft is:
Select to complete the migration or to roll back to Zookeeper.
When the migration job reaches the Dual-Write phase, the migration job waits for you to apply the annotation. You have the following options:
Move to the KRaft-only mode, and perform the post-migration tasks.
Roll back to Zookeeper mode if you encounter issues.
Migration time would be dependent on the following factors:
Time to take single Kafka roll multiplied by
3Time to migrate metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaftController
Time to take the KRaftController roll
If you encounter an issue, review the Troubleshooting tips and the known issues.
Requirements and considerations
Here are the requirements and considerations that you should review before migrating ZooKeeper to KRaft using CFK.
Use one of the following CFK versions:
2.8.4 or higher in the 2.8.x branch
2.9.2 or higher
CFK only supports migration over the same Confluent Platform version of 7.6 or later.
Migrating Confluent Platform 7.6.0 clusters is not recommended for production environments. Use Confluent Platform 7.6.1 or later version with CFK 2.8.1 or later for production environment migration.
The migration job, KRaftMigrationJob custom resource, does not support the Helm-based Confluent Platform. It only supports migrating the CFK-based Confluent Platform.
You need to upgrade Confluent Platform first before running the migration.
You cannot upgrade of Confluent Platform version and migrate ZooKeeper to KRaft at the same time.
Adding incorrect configurations that are not needed can lead to issues during migration. Carefully follow the steps in this document to set the required properties using the specified methods.
For example, if you set the Kafka inter broker protocol version using
configOverridesin the Kafka CR, it will be ignored during the migration process as it should take the annotation over it.To prevent unwanted modification to ZooKeeper, Kafka, and KRaft during and after migration, the migration job puts locks on ZooKeeper, Kafka, and KRaft resources.
This lock is only enforceable for the CFK deployments with webhooks enabled.
If you are migrating a deployment that does not have the webhooks enabled, make sure no other actor, for example, continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) tools such as gitOps, FluxCD, is updating/deleting ZooKeeper, Kafka, and KRaft resources while migration is in progress.
You need to manually remove the lock at the end of the migration after validating a successful migration. For details, see the following migration steps.
You can upgrade from ZooKeeper to KRaft in the isolated mode with separate KRaft controller nodes and broker nodes.
You cannot migrate to the combined mode where KRaft and brokers are on the same process (
role=controller, broker).ACL is migrated from ZooKeeper to KRaft.
CFK does not support rolling back to the ZooKeeper mode once migration to the KRaft mode is triggered.
CFK supports ZooKeeper migration of the brokers that use multiple log directories (JBOD). JBOD is in Early Access in Kafka 3.7 which is part of the Confluent Platform 7.7 release.
CFK does not automatically delete the ZooKeeper cluster after migration.
You can delete the ZooKeeper cluster when you verify that it is not used for any other Kafka cluster.
Migrate Confluent Platform from ZooKeeper to KRaft using CFK
Step 1: Configure Kafka for migration
If you are migrating a multi-region (MRC) deployment, follow the step below for each region and restart the Kafka brokers in each region.
Note
When you use CFK to migrate from ZooKeeper to KRaft, CFK automatically fetches the Kafka cluster id. You do not need to manually perform the step described in the manual Confluent Platform migration process.
Set the Kafka inter-broker protocol version if needed.
By default, CFK uses the inter-broker protocol (IBP) version of 3.6 in the ZooKeeper to KRaft migration workflow.
When migrating a Confluent Platform version higher than 7.6, set the corresponding IBP version in the Kafka CR. To get the IBP, refer to the table in Confluent Platform upgrade guide. For example, to migrate a Confluent Platform deployment of version 7.9 from ZooKeeper to KRaft, set the IBP version to the corresponding 3.9 as below.
Note that this annotation is ZooKeeper-to-KRaft migration specific and sets the IBP version only pertaining to the migration workflow.
kind: Kafka
metadata:
annotations:
"platform.confluent.io/kraft-migration-ibp-version": "3.9"
Using the incorrect IBP for the Confluent Platform version you are on can cause the migration process to fail. If you set an IBP in configOverrides section, the value is ignored during the migration process as it should take the annotation over it. Additionally, the migration process will set the IBP in the kRaftController CR, and you should not manually change that IBP setting.
Step 2: Configure and deploy KRaft controller
Create a KRaftController CR and apply the KRaftController CR to start the controller.
If you are migrating a multi-region (MRC) deployment, follow the step below for each region and restart the KRaft controllers in each region.
For more information on configuring KRaft in multi-region (MRC), see Configure KRaft in MRC.
For an example configuration of KRaftController CR, see the CFK example GitHub repository.
Important
Do not use configOverrides to add migration-related or ZooKeeper-related properties in the kRaftController CR.
Configure the KRaftController CR to reflect the desired state post migration.
The migration does not automatically inherit previous configurations present in ZooKeeper. For example:
If RBAC is enabled on the cluster before migration, create the KRaftController CR with RBAC configuration as shown in the following sample CR:
kind: KRaftController spec: authorization: superUsers: - User:kafka type: rbac dependencies: mdsKafkaCluster: authentication: jaasConfig: secretRef: kraftcontroller-credential type: plain bootstrapEndpoint: kafka.confluent.svc.cluster.local:9071 tls: enabled: true
For Cluster Linking, set the same password encoder secret in the KRaftController CR as set in the Kafka broker CR (in
spec.passwordEncoder) as shown in the example below:Using the
kubectl get secretcommand or the Vault location to get the content of thepassword-encoder.txtfile fromspec.passwordEncoder, and specify the encoder secret (encoder-secret) and old encoder secret (encoder-old-secretif the value is present in thepassword-encoder.txtfile) as shown below.kind: KRaftController spec: configOverrides: server: - password.encoder.secret=<encoder-secret> - password.encoder.old.secret=<encoder-old-secret>
Add the migration-related annotation.
This migration annotation indicates CFK to wait for KRaftMigrationJob to modify KRaftController CR with migration configurations and then create the KRaftController pods.
kind: KRaftController metadata: annotations: platform.confluent.io/kraft-migration-hold-krc-creation: "true"
When using CFK 3.0 or later, add the following annotation to use Log4j 1.
kind: KRaftController metadata: annotations: platform.confluent.io/use-log4j1: "true"
Step 3: Deploy migration job
If you are migrating a multi-region (MRC) deployment, follow the step below for each region and deploy the migration job in each region.
Create a KRaftMigrationJob CR and apply the CR to kick off the migration process.
kind: KRaftMigrationJob spec: dependencies: zookeeper: # provide ZK clusterRef kRaftController: # provide KRaftController clusterRef kafka: # provide Kafka clusterRef
For example:
kind: KRaftMigrationJob metadata: name: kraftmigrationjob namespace: confluent spec: dependencies: kafka: name: kafka namespace: confluent zookeeper: name: zookeeper namespace: confluent kRaftController: name: kraftcontroller namespace: confluent
Step 4: Monitor migration progress
To track the phases and the progress, run the following commands as soon as the migration is started. The commands will continuously print outputs to your terminal as they are generated, so run the commands in separate shell windows.
kubectl get kraftmigrationjob <migration job name> -n <namespace> -oyaml -w
Review the CFK log and look for the migration phases/subphases to understand which phase the migration job is in.
kubectl logs <CFK-pod-name> -f -n <namespace>
Note that Kubernetes does not keep the logs of restarted pods.
Step 5: Select to move to KRaft-only deployment
The migration job status shows a message:
KRaft migration workflow is in dual write mode.
At this point, Confluent Platform is in DUAL-WRITE phase (Metadata being copied to both ZooKeeper and KRaft controller), and the migration job waits for your input to move to the KRaft only mode or to roll back to ZooKeeper.
Take the following steps to proceed:
To move to KRaft only deployment, check the logs and validate that all data has been migrated without any loss. You can use the following command:
kubectl logs -f -c=kraftcontroller --selector app=kraftcontroller -n <namespace> | grep "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"
If validation passes and you wish to complete the migration process, apply the
platform.confluent.io/kraft-migration-trigger-finalize-to-kraftannotation to the migration job CR.kubectl annotate kraftmigrationjob <migration job name> \ platform.confluent.io/kraft-migration-trigger-finalize-to-kraft=true \ --namespace <namespace>
The migration job moves to the MoveToKRaftControllerOnly phase.
Alternatively, if validation fails, you can roll back to using Zookeeper cluster.
Important
Rollback can only be done when the cluster is in the Dual-Write mode. Since the data in ZooKeeper is still consistent with that of the KRaft metadata log, it is still possible to revert back to ZooKeeper. Once you take the KRaft controller out of the migration mode and restart Kafka in KRaft mode, you can no longer roll back to ZooKeeper mode.
Step 6: Perform post-migration tasks
After the migration job completes, you need to manually perform the following tasks:
Remove the lock that the migration job placed on the resources.
The migration job locks the Kafka, ZooKeeper, and KRaft resources on initialization of migration workflow.
When migration is completed, status message will prompt you to:
Remove the lock using the
platform.confluent.io/kraft-migration-release-cr-lockannotation.kubectl annotate kraftmigrationjob <migration job name> \ platform.confluent.io/kraft-migration-release-cr-lock=true \ --namespace <namespace>
The migration job modifies the
yamlrepresentation of Kafka and KRaft CRs. Download the modified Kafka and KRaft CRs to update your CI/CD as necessary.For example:
kubectl get kafka <Kafka CR name> -n <namespace> -oyaml > updated_kafka.yaml kubectl get kraftcontroller <KRaftcontroller CR name> -n <namespace> -oyaml > updated_kraftcontroller.yaml
After migration completes and after you verify that it is not used for any other Kafka cluster, remove the ZooKeeper cluster.
kubectl delete -f <Zookeeper CR>
Roll back to ZooKeeper
If the migration fails, you can roll back to the ZooKeeper cluster in the migration process prior to taking the KRaft controllers out of the migration mode. Up to that point, the controller makes dual writes to KRaft and ZooKeeper. Since the data in ZooKeeper is still consistent with that of the KRaft metadata log, it is still possible to revert back to ZooKeeper.
To roll back to ZooKeeper:
Apply the
platform.confluent.io/kraft-migration-trigger-rollback-to-zkannotation to the migration job.kubectl annotate kraftmigrationjob <migration job name> \ platform.confluent.io/kraft-migration-trigger-rollback-to-zk=true --overwrite \ --namespace <namespace>
Remove the
controllerandmigrationnodes.When you get the status message to delete the controller nodes from ZooKeeper, run the following commands:
zookeeper-shell <zkhost:zkport> deleteall <kafka-cr-name>-<kafka-cr-namespace>/controller
zookeeper-shell <zkhost:zkport> deleteall <kafka-cr-name>-<kafka-cr-namespace>/migration
Trigger node removal process.
kubectl annotate kraftmigrationjob <migration job name> \ platform.confluent.io/continue-kraft-migration-post-zk-node-removal=true \ --overwrite \ --namespace <namespace>
Migration phases and sub-phases
This section describes the phases and sub-phases in the ZooKeeper to KRaft migration. Use the information to follow the progress. In case of an error, you can use the information in the CFK log to troubleshoot at which phase, the migration job runs into an issue.
Review the CFK log and look for the migration phase/subphase to understand which phase the migration job is in.
The ZooKeeper to KRaft migration process includes the following phases:
SETUP
MIGRATE
DUAL-WRITE
MoveToKRaft or RollbackToZk
COMPLETE
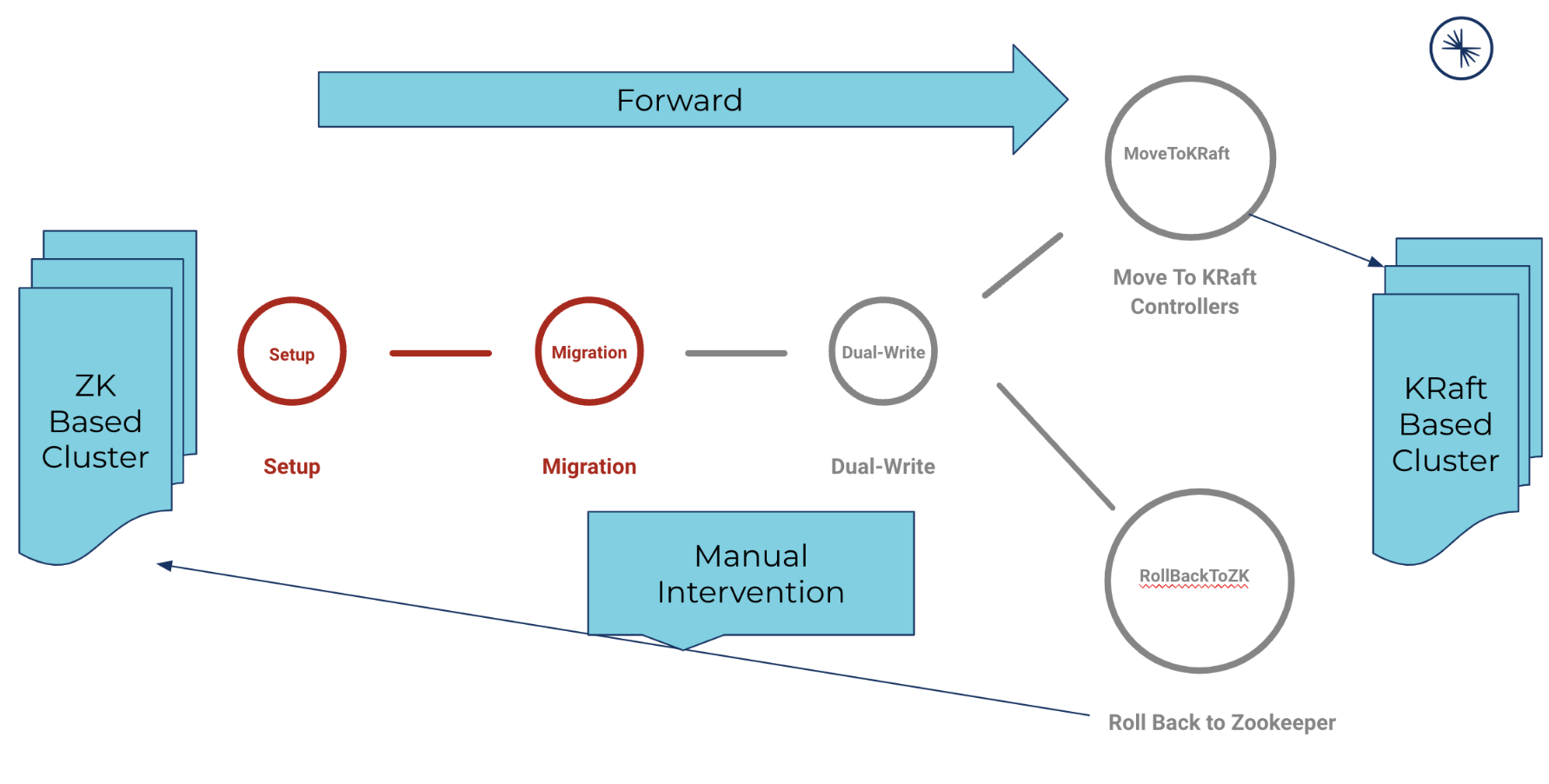
Migration phase: SETUP
When the migration job is in the SETUP phase, the log will have the status, Migration current status SETUP/<sub-phase>. For example:
Migration current status SETUP/SubPhaseSetupAddMigrationAnnotation:
CFK performs the following tasks at each sub-phase during the SETUP phase:
SubPhaseSetupAddMigrationAnnotation: Adds theplatform.confluent.io/kraft-migration-cr-lockannotation to the ZooKeeper, Kafka, and KRaft controller CRs.SubPhaseSetupCheckHealthyKafka: Ensures Kafka is running healthy.SubPhaseSetupCheckKafkaVersion: Ensures Kafka version is 7.6.0 or higher.SubPhaseSetupEnsureKRaftControllerExists: Ensure KRaftController is present in the hold state. KRaftController created with theplatform.confluent.io/kraft-migration-hold-krc-creationannotation does’t come alive until CFK removes the annotation later, atSubPhaseSetupMutateKRaftController.SubPhaseSetupTriggerIBPUpgrade: Upgradesinter.broker.protocol.versionto3.5.SubPhaseSetupEnsureIBPUpgradeComplete: Waits for Kafka roll to get complete afterinter.broker.protocol.versionwas upgraded in the previous sub-phase.SubPhaseSetupFetchKafkaClusterId: Fetches the Kafka Cluster ID from Jolokia Endpoint in Kafka Cluster.SubPhaseSetupFetchKafkaZookeeperEndpoint: Fetches the ZooKeeper endpoint from the Kafka CR Status.SubPhaseSetupMutateKRaftController:Removes the hold annotation,
platform.confluent.io/kraft-migration-hold-krc-creation.Supplies the Kafka Cluster ID from previous step, so that the bootstrapped cluster has the same cluster ID.
Adds migration configuration.
SubPhaseSetupKRaftControllerHealthy: Waits for KRaftController to become healthy.SubPhaseSetupCheckKraftControllerVersion: Validates if KRaftController version is 7.6 or higher.SubPhaseSetupComplete: Marks the completion of theSETUPphase.
Migration phase: MIGRATE
When the migration job is in the MIGRATE phase, the log will have the status, Migration current status MIGRATE/<sub-phase>. For example:
Migration current status MIGRATE/SubPhaseMigrateEnsureKafkaRollComplete:
CFK performs the following tasks at each sub-phase during the MIGRATE phase:
SubPhaseMigrateTriggerKafkaMigration: Following configs gets added at this phase.Migration configurations
KRaft reference
SubPhaseMigrateEnsureKafkaRollComplete: Wait for the Kafka roll to complete.SubPhaseMigrateMonitorMigrationProgress: Monitors the migration progress, and checks if it reaches DUAL-WRITE mode.SubPhaseMigrateDualWrite: Marks the completion of Migration phase.
Migration phase: DUAL-WRITE
The DUAL-WRITE phase doesn’t have any sub-phases.
The migration job status shows a message:
KRaft migration workflow is in dual write mode.
At this point, Confluent Platform is in DUAL-WRITE state (Metadata being copied to both ZooKeeper and KRaft controller), the migration job waits for your input to move to the KRaft only mode or to roll back to ZooKeeper.
When you apply the desired annotation, platform.confluent.io/kraft-migration-trigger-finalize-to-kraft or platform.confluent.io/kraft-migration-trigger-rollback-to-zk, the migration job moves to the MoveToKRaftControllerOnly or RollbackToZk phase phase.
Migration Phase: MoveToKRaftControllerOnly
When the migration job is in the MoveToKRaftControllerOnly phase, the log will have the status, Migration current status SETUP/<sub-phase>. For example:
Migration current status MoveToKRaftControllerOnly/SubPhaseMoveToKRaftControllerEnsureKafkaRollIsComplete:
The migration job performs the following tasks at each sub-phase during the MoveToKRaftControllerOnly phase:
SubPhaseMoveToKRaftControllerTriggerZkRemoval: Removes ZooKeeper dependency from Kafka.SubPhaseMoveToKRaftControllerEnsureKafkaRollIsComplete: Waits for Kafka roll to finish.SubPhaseMoveToKRaftControllerTriggerKRaftControllerMigrationModeRemoval: Triggers migration config removal from KRaftControllers.SubPhaseMoveToKRaftControllerEnsureKRaftControllerMigrationModeRemovalComplete: Waits for KRaftController roll to get completed.SubPhaseMoveToKRaftControllerComplete: Marks completion of the migration.
Migration Phase: RollbackToZk
To roll back to ZooKeeper, the migration job performs the following tasks at each sub-phase during the RollbackToZK phase:
SubPhaseRollbackToZkMakeProcessRoleEmpty: Removesprocess.rolesproperties from Kafka.SubPhaseRollbackToZkEnsureKafkaRollIsComplete: Ensures Kafka roll is complete.SubPhaseRollbackToZkWaitForManualNodeRemovalFromZk: Waits for a manual removal for ZooKeeper controller node.When you remove the
controllerandmigrationnodes and trigger node removal process as described in the second and third steps in Roll back to ZooKeeper, the migration moves to the next sub-phase.SubPhaseRollbackToZkRemoveKRaftControllerDepsInKafka: Removes KRaft dependency from Kafka.SubPhaseRollbackToZkEnsureKafkaRollIsComplete2: Ensures Kafka roll is complete.SubPhaseRollbackToZkAddClusterMetadataCleanUpAnnotationInKafka: Addsplatform.confluent.io/format-cluster-metadata-in-kafkaannotation which directs the init container to remove cluster_metadata directory/mnt/data/data0/logs/__cluster_metadatain Kafka.SubPhaseRollbackToZkEnsureKafkaRollIsComplete3: Ensures Kafka roll is complete.SubPhaseRollbackToZkRemoveClusterMetadataCleanUpAnnotationInKafka: Removesplatform.confluent.io/format-cluster-metadata-in-kafka.SubPhaseRollbackToZkEnsureKafkaRollIsComplete4: Ensures Kafka roll is complete.SubPhaseRollbackToZkComplete: Marks completion of rollback to ZooKeeper.
Migration phase: COMPLETE
The final phase of the ZooKeeper to KRaft migration has the one of the following status:
COMPLETEThis is the final phase and it doesn’t have any sub-phase associated with this phase.
FAILUREThis is the failure phase, if the migration sees a non recoverable error.
Troubleshoot ZooKeeper to KRaft migration issues
The following is a list of tasks you can perform to troubleshoot issues during a migration:
Collect the support bundle when the migration job is stuck.
Get the output of the command, if possible:
kubectl get kraftmigrationjob <migration job name> \ -n <namespace> \ -oyaml > kraftmigrationjob.yaml
Enable debug logging for CFK if there is not enough logs available in the CFK log to troubleshoot the migration issue.
Look in the CFK log that confirms when the migration job is started. For example:
2024-10-15T19:52:31.435Z INFO kraftmigrationjob log/log.go:31 Migration current status SETUP/SubPhaseSetupAddMigrationAnnotation: <nil>, requeuing ... {"name": "kraftmigrationjob", "namespace": "intellimine-otp"Understand the phase/subphase flow and the log message in the CFK log. For example:
2024-10-15T18:42:56.734Z INFO kraftmigrationjob log/log.go:31 Migration current status MIGRATE/SubPhaseMigrateEnsureKafkaRollComplete: <nil>, requeuing ...{"name": "kraftmigrationjob", "namespace": "intellimine-otp"} 2024-10-15T18:42:56.740Z INFO kraftmigrationjob log/log.go:31 Migration current status MIGRATE/SubPhaseMigrateEnsureKafkaRollComplete: kafka [kafka] in namespace [intellimine-otp] roll not complete yet, requeuing {"name": "kraftmigrationjob", "namespace": "intellimine-otp"}To help with debugging, enable TRACE level logging for metadata migration:
log4j.logger.org.apache.kafka.metadata.migration=TRACE, stdout
Check if you are running into a known issue.
Known issues in KRaft migration
Issue: Migration fails in FIPS mode in CFK 2.8.x
The migration job fails if FIPS is enabled in the Confluent Platform deployment.
Workaround: Disable FIPS, migrate to KRaft, and re-enable FIPS.
Fixed Version: This issue is fixed in CFK 2.9.0.
Issue: A Kafka pod is stuck during the rollback to ZooKeeper phase
In the rollback to ZooKeeper process, a Kafka pod is stuck on the first restart with an error message that a topic was not found.
Workaround: None.
Fixed Version: This issue is fixed in CFK 2.9.0.
Issue: During rollback to ZooKeeper, ZooKeeper nodes cannot be deleted
During the rollback to ZooKeeper phase, the KRaftMigrationJob is stuck with the error message that the ZooKeeper nodes cannot be deleted.
Failed to delete some node(s) in the subtree!
Solution: Provide the required TLS certificates using the zookeeper-shell or zkcli tool. After giving the right permission to the ZooKeeper, you will be able to complete the rollback process.
Fixed Version: This issue is fixed in CFK 2.9.0.
Issue: Kafka pods fail to restart in the initial rolling stage and the migration job gets stuck
If you have the inter-broker protocol version and the TRACE logger set as shown below, the Kafka pod will not be able to roll due to a known issue with deadlock.
inter.broker.protocol.version=3.8
log4j.logger.org.apache.kafka.metadata.migration=TRACE
Workaround: Remove one of the above configurations from the Kafka CR, and Kafka pods will roll as part of the migration step.
Fixed Version: This issue is fixed in CFK 2.9.5, 2.10.1, and 2.11.1.
Issue: KRaft cannot authenticate to ZooKeeper during migration
When ZooKeeper uses digest authentication and the Kafka CR has zookeeper.set.acl=true in the spec.configOverrides.server section, KRaft cannot correctly authenticate with ZooKeeper. The migration gets stuck in PhaseMigration, not reaching the dual write phase. And the KRaft log contains:
org.apache.kafka.metadata.migration.MigrationClientAuthException:
org.apache.zookeeper.KeeperException$NoAuthException: KeeperErrorCode = NoAuth
for /consumers.
Workaround: Explicitly specify an override in the KRaftController CR to add the JAAS configuration to KRaft as shown below:
kind: KRaftController
spec:
configOverrides:
jvm:
- -Djava.security.auth.login.config=/mnt/secrets/digest-jaas.conf