Configure Security for Confluent Private Cloud Gateway
This section provides details on the security configurations for Confluent Private Cloud Gateway (Confluent Gateway) using Docker Compose.
For the security configuration steps using Confluent for Kubernetes (CFK), see Configure Security for Confluent Gateway using CFK.
The top-level layout for the Confluent Gateway security configuration is as follows:
gateway:
secretStores:
streamingDomains:
kafkaCluster:
bootstrapServers:
- id:
endpoint:
ssl:
routes:
- name:
security:
auth:
ssl:
swapConfig:
For streamingDomains.kafkaCluster.bootstrapServers.ssl and routes.security.ssl, see the SSL configuration section.
Security best practices and recommendations
Use unique Gateway-to-Broker credentials per client
In Confluent Gateway deployments, there are typically two authentication layers in security configuration scenarios:
Client → Gateway (SASL/PLAIN)
Gateway → Broker (SASL/PLAIN or SASL/OAUTHBEARER), with secrets stored in AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault, Azure Key Vault, or local directory.
The following are best practice recommendations:
Do not map multiple client users to a single Gateway-to-Broker credential.
Each client should ideally have its own Gateway-to-Broker SASL credential.
Avoid static “shared” credentials across multiple clients.
Authentication configuration
Confluent Gateway supports two modes for authenticating clients and forwarding traffic to Kafka clusters: identity passthrough and authentication swapping.
Identity passthrough: Client credentials are forwarded directly to Kafka clusters without modification.
Use identity passthrough for environments where the authentication method is uniform and Confluent Gateway transparency is sufficient.
With identity passthrough, SASL authentication mechanisms, such as SASL/PLAIN or SASL/OAUTHBEARER, are supported.
Authentication swapping: Client credentials are transformed into different credentials before connecting to Kafka clusters.
When enabled, Confluent Gateway authenticates incoming clients, optionally using a different authentication mechanism than the backing Kafka cluster. Confluent Gateway then swaps the client identity and credentials as it forwards requests to brokers.
With authentication swapping, SASL/PLAIN or mTLS authentication is supported for client-to-Confluent Gateway authentication, and SASL/PLAIN or SASL/OAUTHBEARER authentication is supported for Confluent Gateway-to-Kafka cluster authentication.
Use authentication swapping when you need to:
Migrate clients between source and destination clusters that have different authentication requirements, without modifying client applications.
Share cluster access with external clients while maintaining your internal authentication standards, even when you cannot enforce those standards directly on the client side.
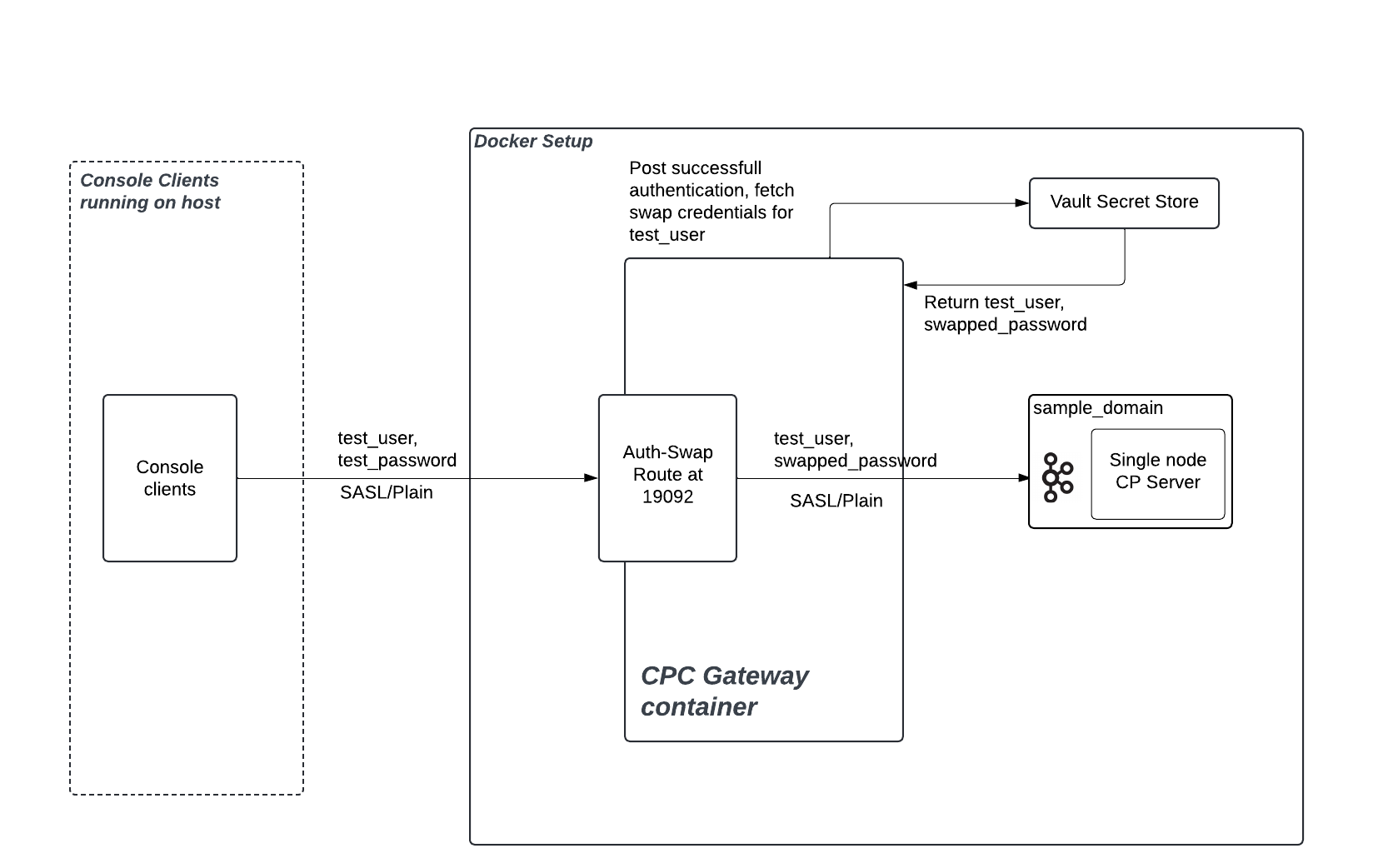
The following diagram shows a sample authentication flow for authentication swapping:
Some considerations when selecting the authentication mode in Confluent Gateway are:
You can configure either identity passthrough or authentication swapping for an individual route.
You cannot configure multiple authentication mechanisms for the same route while using authentication swapping.
Identity passthrough cannot be used for mTLS due to TLS termination at Confluent Gateway; currently, authentication swapping is mandatory for mTLS clients.
Swapping mandates more setup (identity stores, KMS, mappings) but adds flexibility and supports more complex enterprise scenarios.
Authentication swapping with multi-cluster streaming domains requires identical user identities and RBAC policies across all clusters. If clusters have different authentication systems or user permissions, use separate streaming domains instead.
Configure identity passthrough mode
When a Route is configured for identity passthrough, the Confluent Gateway forwards unaltered authentication information (no interception) directly to Kafka brokers, and it does not itself authenticate incoming clients. The brokers perform authentication and authorization checks.
Identity passthrough is supported for SASL authentication mechanisms, such as SASL/PLAIN or SASL/OAUTHBEARER.
To configure a Route for identity passthrough in Docker Compose:
gateway:
routes:
- name:
security:
auth: passthrough --- [1]
[1] The authentication mode for the route. Set to
passthroughto enable identity passthrough.
Configure authentication swapping mode
When a Route is configured for authentication swapping, Confluent Gateway authenticates incoming clients, optionally using a different authentication mechanism than the backing Kafka cluster. Confluent Gateway then swaps the client identity and credentials as it forwards requests to Kafka brokers.
authentication swapping requires configuration of identity mapping, potentially integration with external Key Management Systems (KMS) or secret stores, and audit policies.
The following secret stores are supported for fetching credentials:
HashiCorp Vault
AWS Secrets Manager
Azure Key Vault
To configure a Route for authentication swapping in Docker Compose:
gateway:
routes:
- name: --- [1]
security:
auth: swap --- [2]
swapConfig:
clientAuth: --- [3]
secretStore: --- [4]
clusterAuth: --- [5]
[1] The unique name for the route.
[2] The authentication mode for the route. Set to
swapto enable authentication swapping.[3] How clients authenticate to Confluent Gateway. See Client authentication for authentication swapping.
[4] Reference to a secret store for exchanging credentials. See Secret store configuration.
[5] How Confluent Gateway authenticates to the Kafka cluster after swapping. See Cluster authentication for authentication swapping.
Client authentication for authentication swapping
Configure how clients authenticate to Confluent Gateway for authentication swapping.
Exactly one of SASL (sasl) or mTLS (mtls) authentication should be defined.
SASL authentication
gateway:
routes:
- name:
security:
auth: swap
swapConfig:
clientAuth:
sasl:
mechanism: --- [1]
callbackHandlerClass: --- [2]
jaasConfig:
file: --- [3]
connectionsMaxReauthMs: --- [4]
[1] The SASL mechanism to use. Set to
PLAINfor SASL/PLAIN authentication.[2] The callback handler class to use. Set to
org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainServerCallbackHandlerfor SASL/PLAIN authentication.[3] The path to the JAAS configuration file. See below for the file format and content. See below for the JAAS configuration file content.
[4] The maximum re-authentication time in milliseconds.
JAAS configuration file content for SASL/PLAIN authentication
KafkaServer {
org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required
username="admin"
password="admin-secret"
user_admin="admin-secret";
};
The JAAS configuration file content is a KafkaServer block with the following properties:
org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule: The login module to use.username: The username to use.password: The password to use.user_<username>: The set of properties,user_<username>, defines the passwords for all users that connect to the brokers.
A sample JAAS configuration file content:
KafkaServer {
org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required
username="admin"
password="admin-secret"
user_admin="admin-secret"
user_additional-user="additionaluser-secret";
};
mTLS Authentication
gateway:
routes:
- name:
security:
auth: swap
swapConfig:
clientAuth:
mtls:
ssl:
principalMappingRules: --- [1]
[1] Required only for authentication swapping with mTLS authentication. The pattern to read principal name from the certificates. For example:
"OU=.*$/$1/,RULE:^UID=([a-zA-Z0-9._-]+),.*$/$1/,DEFAULT
Cluster authentication for authentication swapping
Configure how Confluent Gateway authenticates to the Kafka cluster for authentication swapping.
SASL authentication
gateway:
routes:
- name:
security:
auth: swap
swapConfig:
clusterAuth:
sasl:
mechanism: --- [1]
callbackHandlerClass: --- [2]
jaasConfig:
file: --- [3]
oauth:
tokenEndpointUri: --- [4]
connectionsMaxReauthMs: --- [5]
[1] The SASL mechanism to use. Set to
PLAINfor SASL/PLAIN authentication, or set toOAUTHBEARERfor SASL/OAUTHBEARER authentication.[2] The callback handler class to use. Set to
org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainServerCallbackHandlerfor SASL/PLAIN authentication.[3] The path to the JAAS configuration file.
[4] The URI for the OAuth token endpoint.
[5] The maximum re-authentication time in milliseconds.
JAAS configuration file content for SASL/PLAIN authentication
org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username="%s" password="%s";
JAAS configuration file content for SASL/OAUTHBEARER authentication
org.apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerLoginModule required clientId="%s" clientSecret="%s";
Sample configurations for authentication swapping
SASL/PLAIN to SASL/OAUTHBEARER example:
gateway:
routes:
- name: gateway
security:
auth: swap
ssl:
ignoreTrust: false
truststore:
type: PKCS12
location: /opt/ssl/client-truststore.p12
password:
file: /opt/secrets/client-truststore.password
keystore:
type: PKCS12
location: /opt/ssl/gw-keystore.p12
password:
file: /opt/secrets/gw-keystore.password
keyPassword:
value: inline-password
clientAuth: required
swapConfig:
clientAuth:
sasl:
mechanism: PLAIN
callbackHandlerClass: "org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainServerCallbackHandler" # (Optional if mechanism=SSL)
jaasConfig: # (required if SASL/PLAIN)
file: /opt/gateway/gw-users.conf
connectionsMaxReauthMs: 0 # optional. link: https://docs.confluent.io/platform/current/installation/configuration/broker-configs.html#connections-max-reauth-ms
secretstore: s1
clusterAuth:
sasl:
mechanism: OAUTHBEARER
jaasConfig:
file: /opt/gateway/cluster-login.tmpl.conf
oauth: # required only if clusterAuth.sasl.mechanism=oauth
tokenEndpointUri: "https://idp.mycompany.io:8080/realms/cp/protocol/openid-connect/token"
mTLS to SASL/OAUTHBEARER example:
gateway:
routes:
- name: gateway
security:
auth: swap
ssl:
ignoreTrust: false
truststore:
type: PKCS12
location: /opt/ssl/client-truststore.p12
password:
file: /opt/secrets/client-truststore.password
keystore:
type: PKCS12
location: /opt/ssl/gw-keystore.p12
password:
file: /opt/secrets/gw-keystore.password
keyPassword:
value: inline-password
clientAuth: required
swapConfig:
clientAuth:
ssl:
principalMappingRules: "RULE:^CN=([a-zA-Z0-9._-]+),OU=.*$/$1/,RULE:^UID=([a-zA-Z0-9._-]+),.*$/$1/,DEFAULT"
secretStore: "oauth-secrets"
clusterAuth:
sasl:
mechanism: OAUTHBEARER
callbackHandlerClass: "org.apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerValidatorCallbackHandler"
jaasConfig:
file: "/etc/gateway/cluster-jaas.tmpl.conf"
oauth:
tokenEndpointUri: "https://idp.mycompany.io:8080/realms/cp/protocol/openid-connect/token"
SSL configuration
The following SSL configuration is supported for Streaming Domain configuration (streamingDomains.kafkaCluster.bootstrapServers.ssl) and Route configuration (routes.security.ssl) using Docker Compose.
ssl:
ignoreTrust: --- [1]
truststore: --- [2]
type: --- [3]
location: --- [4]
password: --- [5]
keystore: --- [6]
type: --- [7]
location: --- [8]
password: --- [9]
keyPassword: --- [10]
value:
file:
[1] Skip certificate validation (not recommended for production). Essentially, setting this to
truetrusts all certificates.Important
Ensure that
ignoreTrust: falseis set in all production configurations. Setting this totruedisables TLS certificate validation, introducing critical security risks, such as:Exposure to man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks
Possibility of certificate spoofing
Compromise of encrypted traffic
Risk to data confidentiality
[2] Truststore configuration.
[3] Truststore certificate type. The supported values are
JKS,PKCS12, andPEM.[4] The path to the truststore file.
[5] The password for the truststore file. See Password configuration.
[6] Keystore configuration (gateway identity).
[7] The keystore certificate type. The supported values are
JKS,PKCS12, andPEM.[8] The path to the keystore file.
[9] The password for the keystore file. See Password configuration.
[10] The password for the private key inside the keystore. Can be defined either inline or file-based.
An example SSL configuration for Confluent Gateway using Docker Compose:
ssl:
ignoreTrust: false
truststore:
type: PKCS12 # optional, default=JKS
location: /opt/ssl/client-truststore.p12
password:
file: /opt/secrets/client-truststore.password # or inline password
keystore:
type: PKCS12 # optional, default=JKS
location: /opt/ssl/gw-keystore.p12
password:
file: /opt/secrets/gw-keystore.password # or inline password
keyPassword:
value: inline-password
Password configuration
Confluent Gateway supports the file-based and inline password configurations. Only one of the two should be provided.
password:
file: --- [1]
value: --- [2]
[1] The path to the password file.
[2] The inline password value.
Secret store configuration
Confluent Gateway uses secret stores, such as AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, Vault, HashiCorp Vault, or a file, to securely manage authentication credentials and sensitive information. This setup is critical for several key operations:
Storing Confluent Gateway to Kafka broker credentials
Supporting authentication swapping scenarios
In cases where Confluent Gateway translates or “swaps” authentication (such as from mTLS clients to OAuthbearer brokers, or vice versa), secret stores are needed to store and fetch the credentials used in the swap. This allows each client connection to use its mapped broker credential, enhancing security and enabling fine-grained access control.
Interaction with these secret stores should always occur over TLS for confidentiality and integrity.
As a security best practice, configure Confluent Gateway to assume an IAM roles with the least privilege principle. Avoid using static IAM user credentials to avoid sensitive credential exposure.
Ensure proper role trust policies are in place and limit permissions to only what the Confluent Gateway needs. For example in AWS:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"secretsmanager:GetSecretValue"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:123456789012:secret:gateway/*",
"arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:123456789012:secret:confluent/*"
],
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"aws:RequestTag/Environment": "production"
}
}
}
]
}
HashiCorp Vault
To use HashiCorp Vault as a secret store, provide the following configurations.
Connect using an authentication token
gateway:
secretStores:
- name: --- [1]
provider:
type: --- [2]
config:
address: --- [3]
authMethod: --- [4]
authToken: --- [5]
path: --- [6]
prefixPath: --- [7]
separator: --- [8]
[1] A unique name for the secret store.
[2] The type of the secret store. Set to
Vaultto use HashiCorp Vault.[3] The address of the Vault server.
[4] The authentication method to use. You can set to
Token(the default value) or leave it empty.[5] The authentication token for the Vault server to connect using the
authTokenmethod.[6] The path to the secret store.
[7] Optional. The prefix path to the secret store.
[8] Optional. The separator for the secret store. The default value is
:.
Connect using AppRole
gateway:
secretStores:
- name: --- [1]
provider:
type: --- [2]
config:
address: --- [3]
authMethod: --- [4]
role: --- [5]
secret: --- [6]
path: --- [7]
prefixPath: --- [8]
separator: --- [9]
[1] A unique name for the secret store.
[2] The type of the secret store. Set to
Vaultto use HashiCorp Vault.[3] The address of the Vault server.
[4] The authentication method to use. Set to
AppRole.[5] The role to use to connect to the Vault server.
[6] The secret to use to connect to the Vault server.
[7] The path to the secret store.
[8] Optional. The prefix path to the secret store.
[9] Optional. The separator for the secret store. The default value is
:.
Connect using Username and Password
gateway:
secretStores:
- name: --- [1]
provider:
type: --- [2]
config:
address: --- [3]
authMethod: --- [4]
username: --- [5]
password: --- [6]
path: --- [7]
prefixPath: --- [8]
separator: --- [9]
[1] A unique name for the secret store.
[2] The type of the secret store. Set to
Vaultto use HashiCorp Vault.[3] The address of the Vault server.
[4] The authentication method to use. Set to
UserPass.[5] The username to use to connect to the Vault server.
[6] The password to use to connect to the Vault server.
[7] The path to the secret store.
[8] Optional. The prefix path to the secret store.
[9] Optional. The separator for the secret store. The default value is
:.
Note that connecting to HashiCorp Vault using a certificate is not supported.
AWS Secrets Manager
To use AWS Secrets Manager as a secret store, provide the following configurations. You can connect to the Secrets Manager using IAM Role or using Access Key and Secret Key.
If the environment (EC2 for instance) has an IAM Role attached with sufficient permissions, you do not need to specify accessKey or secretKey. The provider will automatically assume the attached IAM role via the default AWS credential provider chain.
gateway:
secretStores:
- name: --- [1]
provider:
type: --- [2]
config:
region: --- [3]
accessKey: --- [4]
secretKey: --- [5]
endpointOverride: --- [6]
prefixPath: --- [7]
separator: --- [8]
useJson: --- [9]
[1] A unique name for the secret store.
[2] The type of the secret store. Set to
AWS.[3] The region of the AWS Secrets Manager.
[4] AWS IAM Access Key ID. Only required when authenticating with IAM user credentials.
[5] AWS IAM Secret Key corresponding to the
accessKey. Only required when authenticating with IAM user credentials.[6] Optional. A custom endpoint URL to use instead of the default AWS endpoint. Defaults to the AWS region endpoint.
[7] Optional. A string prefix that will be added to all secret paths. Useful for environment separation (e.g., staging, production). Defaults to an empty string.
[8] Optional. The character/string used to split authentication data within the retrieved secret. Defaults to
:.[9] If set to
true, the provider will attempt to parse the secret value as a JSON object. Iffalse(the default value), the raw string value will be returned.
An example IAM role configuration for AWS Secrets Manager:
gateway:
secretStores:
- name: aws-secrets
provider:
type: AWS
config:
region: us-west-2
endpointOverride: https://secretsmanager.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
prefixPath: confluent-
separator: ":"
useJson: true
Azure Key Vault
To use Azure Key Vault as a secret store, provide the following configurations.
Connect using Client ID and Secret
gateway:
secretStores:
- name: --- [1]
provider:
type: --- [2]
config:
vaultUrl: --- [3]
credentialType: --- [4]
tenantId: --- [5]
clientId: --- [6]
clientSecret: --- [7]
prefixPath: --- [8]
separator: --- [9]
[1] A unique name for the secret store.
[2] The type of the secret store. Set to
Azure.[3] The URL of the Azure Key Vault to connect to.
[4] The credential type to use. Set to
ClientSecret.[5] The tenant ID of the Azure Key Vault.
[6] The client ID of the Azure Key Vault.
[7] The client secret of the Azure Key Vault for the authentication.
[8] Optional. The prefix path to the secret store. Defaults to an empty string.
[9] Optional. The character or string used to split authentication data within the retrieved secret. Defaults to
:.
An example configuration for Azure Key Vault using Client ID and Secret:
gateway:
secretStores:
- name: azure-keyvault
provider:
type: Azure
config:
vaultUrl: https://authswap.vault.azure.net/
credentialType: ClientSecret
tenantId: xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxx
clientId: xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxx
clientSecret: client-secret
prefixPath: ""
separator: ":"
Connect using Username and Password
gateway:
secretStores:
- name: --- [1]
provider:
type: --- [2]
config:
vaultUrl: --- [3]
credentialType: --- [4]
tenantId: --- [5]
clientId: --- [6]
username: --- [7]
password: --- [8]
prefixPath: --- [9]
separator: --- [10]
[1] A unique name for the secret store.
[2] The type of the secret store. Set to
Azure.[3] The URL of the Azure Key Vault to connect to.
[4] The credential type to use. Set to
UsernamePassword.[5] The tenant ID of the Azure Key Vault.
[6] The client ID of the Azure Key Vault.
[7] The username to authenticate with.
[8] The password to authenticate with.
[9] Optional. The prefix path to the secret store. Defaults to an empty string.
[10] Optional. The character or string used to split authentication data within the retrieved secret. Defaults to
:.
An example configuration for Azure Key Vault using Username and Password:
gateway:
secretStores:
- name: azure-keyvault
provider:
type: Azure
config:
vaultUrl: https://authswap.vault.azure.net/
credentialType: UsernamePassword
tenantId: xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxx
clientId: xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxx
username: username
password: password
prefixPath: ""
separator: ":"
Connect using Client Certificate
You can connect to Azure Key Vault using the Privacy-Enhanced Mail (PEM) or Personal Information Exchange (PFX) format certificates.
gateway:
secretStores:
- name: --- [1]
provider:
type: --- [2]
config:
vaultUrl: --- [3]
credentialType: --- [4]
tenantId: --- [5]
clientId: --- [6]
certificateType: --- [7]
certificatePath: --- [8]
certificatePfxPassword: --- [9]
certificateSendChain: --- [10]
prefixPath: --- [11]
separator: --- [12]
[1] A unique name for the secret store.
[2] The type of the secret store. Set to
Azure.[3] The URL of the Azure Key Vault to connect to.
[4] The credential type to use. Set to
ClientCertificate.[5] The tenant ID of the Azure Key Vault.
[6] The client ID of the Azure Key Vault.
[7] The type of encoding used on the file specified in certificatePath.
Set to
PEMfor PEM certificates orPFXfor PFX certificates.[8] The path to the client certificate file.
[9] Required for the PFX certificates. The password protecting the PFX file.
[10] Optional. The flag to indicate if certificate chain should be sent as part of authentication request. Defaults to
false.[11] Optional. The prefix path to the secret store. Defaults to an empty string.
[12] Optional. The character or string used to split authentication data within the retrieved secret. Defaults to
:.
An example configuration for Azure Key Vault using PEM certificate:
gateway:
secretStores:
- name: azure-keyvault
provider:
type: Azure
config:
vaultUrl: https://authswap.vault.azure.net/
credentialType: ClientCertificate
tenantId: xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxx
clientId: xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxx
certificatePath: /opt/ssl/client-cert.pem
prefixPath: ""
separator: ":"
An example configuration for Azure Key Vault using PFX certificate:
gateway:
secretStores:
- name: azure-keyvault
provider:
type: Azure
config:
vaultUrl: https://authswap.vault.azure.net/
credentialType: ClientCertificate
tenantId: xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxx
clientId: xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxx
certificateType: PFX
certificatePath: /opt/ssl/client-cert.pfx
certificatePfxPassword: <pfx-password>
prefixPath: ""
separator: ":"