Confluent Private Cloud Gateway Overview
Confluent Private Cloud Gateway (Confluent Gateway) is a cloud-native Kafka proxy solution designed to simplify client connectivity, secure access, and cluster management across distributed Kafka environments. It provides a stable, protocol-aware entry point for Kafka clients—abstracting away complex broker lists, inconsistent security settings, and the operational overhead of managing direct client-to-cluster connections.
When deployed between clients and Kafka clusters, Confluent Gateway acts as an intelligent routing layer. As a self-managed solution, it gives you full control over deployment, configuration, and operations, while integrating seamlessly with your existing streaming infrastructure.
Confluent Gateway abstracts the complexity of Kafka connectivity, making modern, secure, and highly available Kafka operations possible for enterprise environments.
Confluent Gateway enables the following use cases:
Future migrations of on-premises clients to Confluent Cloud without client changes.
On-premises disaster recovery switchover from one unhealthy cluster to another healthy cluster without client changes, achieving a significant reduction in recovery time.
Secure external partner access for a private cluster.
Custom domains for your Kafka listeners.
Blue-green upgrades from an earlier Kafka version to the latest Kafka version.
You deploy Confluent Gateway using Confluent for Kubernetes (CFK).
For example configuration scenarios, see Confluent Gateway GitHub repository.
High-level architecture
When Kafka client applications connect to the Confluent Gateway using the Kafka protocol, the Confluent Gateway intercepts and routes these protocol messages securely to the appropriate upstream Kafka clusters. The Confluent Gateway rewrites Kafka responses (including metadata and broker addresses) to present only virtualized endpoints to clients, ensuring that cluster changes remain seamless and transparent to applications.
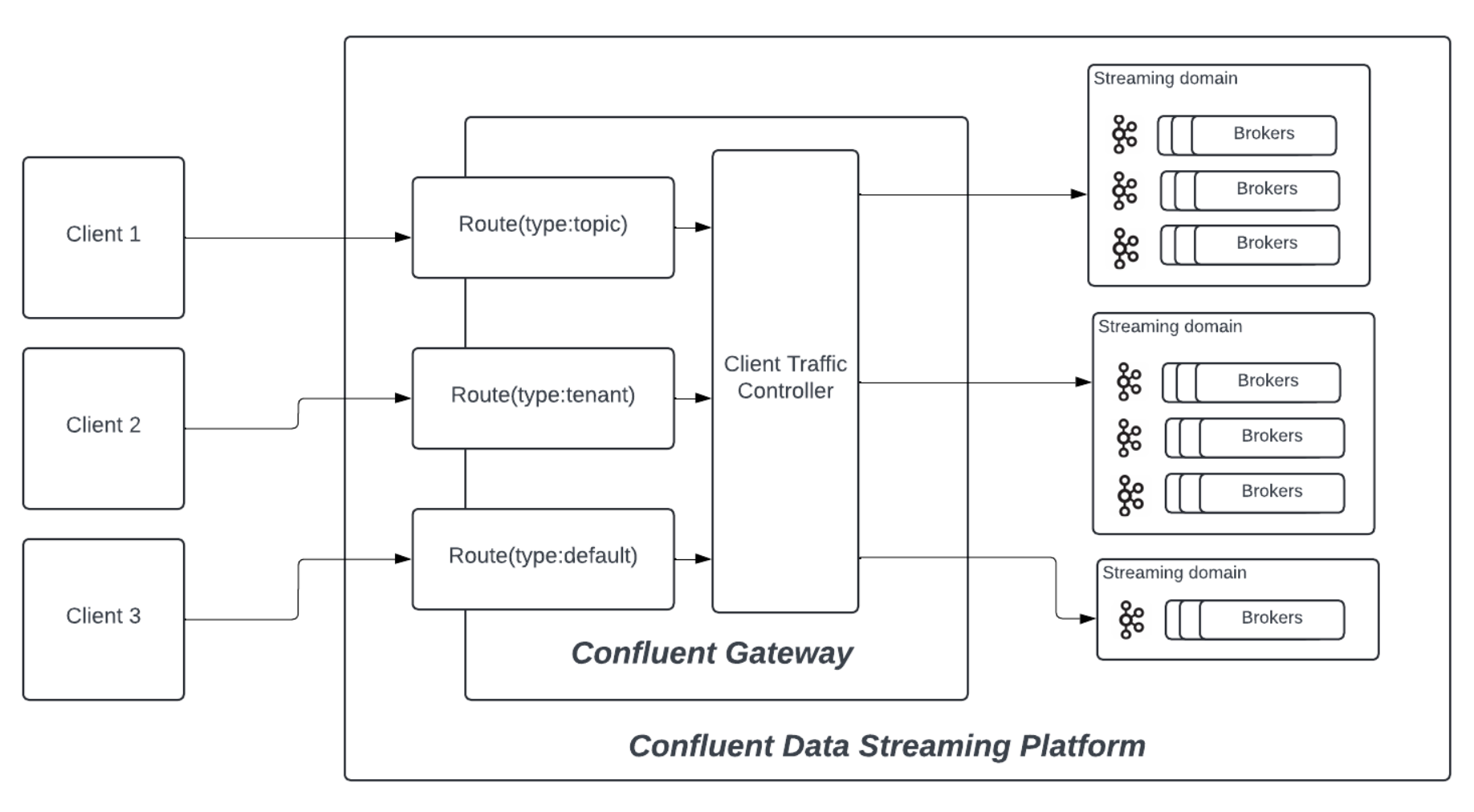
Routes: Confluent Gateway endpoints where client applications connect to stream data.
Confluent Gateway uses Routes to create an abstraction layer between client applications and Kafka clusters. These routing abstractions help decouple the client applications and Kafka brokers.
Streaming Domains: Logical representations of your Kafka clusters at the Confluent Gateway.
With Confluent Gateway, you need to configure each Route with a Streaming Domain. Client applications then connect to Routes instead of directly connecting to brokers’ listener endpoints. For every payload request addressed to a particular Route, Confluent Gateway will automatically forward the request to a Kafka cluster based on the Route’s associated Streaming Domain.
You can create multiple Routes and associate multiple Streaming Domains with the Confluent Gateway. By changing the mapping of a Route to a different Streaming Domain, central platform teams can independently and centrally change the backing Kafka cluster infrastructure for migrations, upgrades, and disaster recovery.
Supported features
The following features are supported in the current release of Confluent Gateway:
Virtual bootstrap and broker endpoints for simplified client setup
Transparent protocol proxying (no client-side changes required)
Multiple authentication methods, Identity Pass-through, and Authentication Swapping
Secure credential storage and retrieval
Metrics, tracing, and simplified troubleshooting
Compatibility with Kafka protocol versions 3.x and 4.x
No support for legacy protocol versions, sidecar deployment, or Schema Registry in the current release
System resource requirements
The recommended system resources for Confluent Gateway are:
CPU and memory:
Minimum: 2 vCPUs, 4 GB RAM
Recommended: 4 vCPUs, 8 GB RAM
Network throughput: 45 MB/sec of sustained workload for a 1-Gigabit link (1 Gbps)
Storage: 10 GB of disk space
Get started
To provision and configure Confluent Gateway, refer to the detailed guides available for both Docker and Confluent for Kubernetes (CFK) deployments. The documentation includes step-by-step installation, configuration for streaming domains and routes, and security recommendations.