Important
You are viewing documentation for an older version of Confluent Platform. For the latest, click here.
Writing Streaming Queries Against Apache Kafka® Using KSQL (Local)¶
This tutorial demonstrates a simple workflow using KSQL to write streaming queries against messages in Kafka.
To get started, you must start a Kafka cluster, including ZooKeeper and a Kafka broker. KSQL will then query messages from this Kafka cluster. KSQL is installed in the Confluent Platform by default.
Prerequisites:
- Confluent Platform is installed and running. This installation includes a Kafka broker, KSQL, Control Center, ZooKeeper, Schema Registry, REST Proxy, and Kafka Connect.
- If you installed Confluent Platform via TAR or ZIP, navigate into the installation directory. The paths and commands used throughout this tutorial assume that your are in this installation directory.
- Java: Minimum version 1.8. Install Oracle Java JRE or JDK >= 1.8 on your local machine
Create Topics and Produce Data¶
Create and produce data to the Kafka topics pageviews and users. These steps use the KSQL datagen that is included
Confluent Platform.
Create the
pageviewstopic and produce data using the data generator. The following example continuously generates data with a value in DELIMITED format.$ <path-to-confluent>/bin/ksql-datagen quickstart=pageviews format=delimited topic=pageviews maxInterval=500
Produce Kafka data to the
userstopic using the data generator. The following example continuously generates data with a value in JSON format.$ <path-to-confluent>/bin/ksql-datagen quickstart=users format=json topic=users maxInterval=100
Tip
You can also produce Kafka data using the kafka-console-producer CLI provided with Confluent Platform.
Launch the KSQL CLI¶
To launch the CLI, run the following command. It will route the CLI logs to the ./ksql_logs directory, relative to
your current directory. By default, the CLI will look for a KSQL Server running at http://localhost:8088.
$ LOG_DIR=./ksql_logs <path-to-confluent>/bin/ksql
Important
By default KSQL attempts to store its logs in a directory called logs that is relative to the location
of the ksql executable. For example, if ksql is installed at /usr/local/bin/ksql, then it would
attempt to store its logs in /usr/local/logs. If you are running ksql from the default Confluent Platform
location, <path-to-confluent>/bin, you must override this default behavior by using the LOG_DIR variable.
After KSQL is started, your terminal should resemble this.
===========================================
= _ __ _____ ____ _ =
= | |/ // ____|/ __ \| | =
= | ' /| (___ | | | | | =
= | < \___ \| | | | | =
= | . \ ____) | |__| | |____ =
= |_|\_\_____/ \___\_\______| =
= =
= Streaming SQL Engine for Apache Kafka® =
===========================================
Copyright 2018 Confluent Inc.
CLI v4.1.3, Server v4.1.3 located at http://localhost:8088
Having trouble? Type 'help' (case-insensitive) for a rundown of how things work!
ksql>
Create a Stream and Table¶
These examples query messages from Kafka topics called pageviews and users using the following schemas:
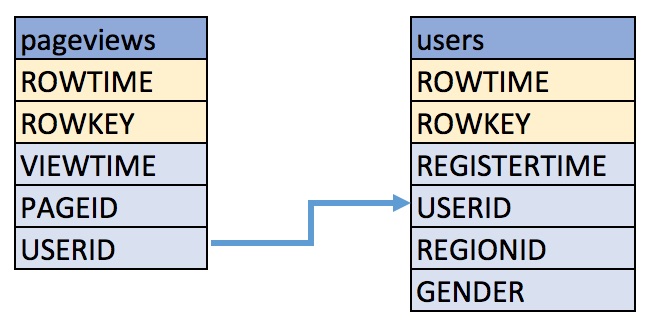
Create a stream
pageviews_originalfrom the Kafka topicpageviews, specifying thevalue_formatofDELIMITED.Describe the new STREAM. Notice that KSQL created additional columns called
ROWTIME, which corresponds to the Kafka message timestamp, andROWKEY, which corresponds to the Kafka message key.CREATE STREAM pageviews_original (viewtime bigint, userid varchar, pageid varchar) WITH \ (kafka_topic='pageviews', value_format='DELIMITED');
Your output should resemble:
Message --------------- Stream created ---------------
Tip
You can run
DESCRIBE pageviews_original;to describe the stream.Create a table
users_originalfrom the Kafka topicusers, specifying thevalue_formatofJSON.CREATE TABLE users_original (registertime BIGINT, gender VARCHAR, regionid VARCHAR, userid VARCHAR) WITH \ (kafka_topic='users', value_format='JSON', key = 'userid');
Your output should resemble:
Message --------------- Table created ---------------
Tip
You can run
DESCRIBE users_original;to describe the table.Optional: Show all streams and tables.
ksql> SHOW STREAMS; Stream Name | Kafka Topic | Format ----------------------------------------------------------------- PAGEVIEWS_ORIGINAL | pageviews | DELIMITED ksql> SHOW TABLES; Table Name | Kafka Topic | Format | Windowed -------------------------------------------------------------- USERS_ORIGINAL | users | JSON | false
Write Queries¶
These examples write queries using KSQL.
Note: By default KSQL reads the topics for streams and tables from the latest offset.
Use
SELECTto create a query that returns data from a STREAM. This query includes theLIMITkeyword to limit the number of rows returned in the query result. Note that exact data output may vary because of the randomness of the data generation.SELECT pageid FROM pageviews_original LIMIT 3;
Your output should resemble:
Page_24 Page_73 Page_78 LIMIT reached for the partition. Query terminated
Create a persistent query by using the
CREATE STREAMkeywords to precede theSELECTstatement. The results from this query are written to thePAGEVIEWS_ENRICHEDKafka topic. The following query enriches thepageviews_originalSTREAM by doing aLEFT JOINwith theusers_originalTABLE on the user ID.CREATE STREAM pageviews_enriched AS SELECT users_original.userid AS userid, pageid, regionid, gender \ FROM pageviews_original LEFT JOIN users_original ON pageviews_original.userid = users_original.userid;
Your output should resemble:
Message ---------------------------- Stream created and running ----------------------------
Tip
You can run
DESCRIBE pageviews_enriched;to describe the stream.Use
SELECTto view query results as they come in. To stop viewing the query results, press<ctrl-c>. This stops printing to the console but it does not terminate the actual query. The query continues to run in the underlying KSQL application.SELECT * FROM pageviews_enriched;
Your output should resemble:
1519746861328 | User_4 | User_4 | Page_58 | Region_5 | OTHER 1519746861794 | User_9 | User_9 | Page_94 | Region_9 | MALE 1519746862164 | User_1 | User_1 | Page_90 | Region_7 | FEMALE ^CQuery terminated
Create a new persistent query where a condition limits the streams content, using
WHERE. Results from this query are written to a Kafka topic calledPAGEVIEWS_FEMALE.CREATE STREAM pageviews_female AS SELECT * FROM pageviews_enriched WHERE gender = 'FEMALE';
Your output should resemble:
Message ---------------------------- Stream created and running ----------------------------
Tip
You can run
DESCRIBE pageviews_female;to describe the stream.Create a new persistent query where another condition is met, using
LIKE. Results from this query are written to thepageviews_enriched_r8_r9Kafka topic.CREATE STREAM pageviews_female_like_89 WITH (kafka_topic='pageviews_enriched_r8_r9', \ value_format='DELIMITED') AS SELECT * FROM pageviews_female WHERE regionid LIKE '%_8' OR regionid LIKE '%_9';
Your output should resemble:
Message ---------------------------- Stream created and running ----------------------------
Create a new persistent query that counts the pageviews for each region and gender combination in a tumbling window of 30 seconds when the count is greater than 1. Results from this query are written to the
PAGEVIEWS_REGIONSKafka topic in the Avro format. KSQL will register the Avro schema with the configured Schema Registry when it writes the first message to thePAGEVIEWS_REGIONStopic.CREATE TABLE pageviews_regions WITH (value_format='avro') AS SELECT gender, regionid , COUNT(*) AS numusers \ FROM pageviews_enriched WINDOW TUMBLING (size 30 second) GROUP BY gender, regionid HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;
Your output should resemble:
Message --------------------------- Table created and running ---------------------------
Tip
You can run
DESCRIBE pageviews_regions;to describe the table.Optional: View results from the above queries using
SELECT.SELECT gender, regionid, numusers FROM pageviews_regions LIMIT 5;
Your output should resemble:
FEMALE | Region_6 | 3 FEMALE | Region_1 | 4 FEMALE | Region_9 | 6 MALE | Region_8 | 2 OTHER | Region_5 | 4 LIMIT reached for the partition. Query terminated ksql>
Optional: Show all persistent queries.
SHOW QUERIES;
Your output should resemble:
Query ID | Kafka Topic | Query String ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- CTAS_PAGEVIEWS_REGIONS | PAGEVIEWS_REGIONS | CREATE TABLE pageviews_regions WITH (value_format='avro') AS SELECT gender, regionid , COUNT(*) AS numusers FROM pageviews_female WINDOW TUMBLING (size 30 second) GROUP BY gender, regionid HAVING COUNT(*) > 1; CSAS_PAGEVIEWS_FEMALE | PAGEVIEWS_FEMALE | CREATE STREAM pageviews_female AS SELECT users_original.userid AS userid, pageid, regionid, gender FROM pageviews_original LEFT JOIN users_original ON pageviews_original.userid = users_original.userid WHERE gender = 'FEMALE'; CSAS_PAGEVIEWS_FEMALE_LIKE_89 | pageviews_enriched_r8_r9 | CREATE STREAM pageviews_female_like_89 WITH (kafka_topic='pageviews_enriched_r8_r9', value_format='DELIMITED') AS SELECT * FROM pageviews_female WHERE regionid LIKE '%_8' OR regionid LIKE '%_9'; ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Terminate and Exit¶
KSQL¶
Important: Queries will continuously run as KSQL applications until they are manually terminated. Exiting KSQL does not terminate persistent queries.
From the output of
SHOW QUERIES;identify a query ID you would like to terminate. For example, if you wish to terminate query IDCTAS_PAGEVIEWS_REGIONS:TERMINATE CTAS_PAGEVIEWS_REGIONS;
Run the
exitcommand to leave the KSQL CLI.ksql> exit Exiting KSQL.
Confluent Platform¶
If you are running the Confluent Platform, you can stop it with this command.
$ <path-to-confluent>/bin/confluent stop
