Important
You are viewing documentation for an older version of Confluent Platform. For the latest, click here.
Kubernetes Helm Charts¶
You can use the Helm charts to deploy Confluent Platform services on Kubernetes for development, test, and proof of concept environments.
Important
The Confluent Platform Helm charts are in developer preview and are not supported for production use.
Introduction¶
Helm is an open-source packaging tool that helps you install applications and services on Kubernetes.
Helm uses a packaging format called charts. Charts are a collection of YAML templates that describe a related set of Kubernetes resources.
This repository provides Helm charts for the following Confluent Platform services:
- Kafka brokers
- ZooKeeper
- Kafka Connect
- Confluent Schema Registry
- Confluent REST Proxy
Environment Preparation¶
You must have a Kubernetes cluster that has Helm configured.
Tested Software¶
These Helm charts have been tested with the following software versions:
- Kubernetes 1.9.2+
- Helm 2.8.2+
- Confluent Platform Open Source Docker Images 4.1.3
For local Kubernetes installation with Minikube, see Appendix: Create a Local Kubernetes Cluster.
Install Helm on Kubernetes¶
Follow the directions to install and deploy Helm to the Kubernetes cluster.
View a list of all deployed releases in releases in the local installation.
helm init
helm repo update
helm list
Important
For Helm versions prior to 2.9.1, you may see "connect: connection refused", and will need to fix up
the deployment before proceeding.
kubectl delete --namespace kube-system svc tiller-deploy
kubectl delete --namespace kube-system deploy tiller-deploy
kubectl create serviceaccount --namespace kube-system tiller
kubectl create clusterrolebinding tiller-cluster-rule --clusterrole=cluster-admin --serviceaccount=kube-system:tiller
kubectl patch deploy --namespace kube-system tiller-deploy -p '{"spec":{"template":{"spec":{"serviceAccount":"tiller"}}}}'
helm init --service-account tiller --upgrade
Run Confluent Platform¶
Follow these steps to run Confluent Platform.
Persistence¶
The ZooKeeper and Kafka cluster are deployed with StatefulSets that have a volumeClaimTemplate which provides the persistent volume for each replica. You can define the size of the volumes by changing dataDirSize and dataLogDirSize under cp-zookeeper and size under cp-kafka in values.yaml.
You also could use the cloud provider’s volumes by specifying StorageClass.. For example, if you are on AWS your storage class will look like this:
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: ssd
provisioner: kubernetes.io/aws-ebs
parameters:
type: gp2
Tip
To adapt this example to your needs, read the Kubernetes StorageClass documentation.
The StorageClass that was created can be specified in dataLogDirStorageClass and dataDirStorageClass under cp-zookeeper and in storageClass under cp-kafka in values.yaml.
To deploy non-persistent Kafka and ZooKeeper clusters, you must change the value of persistence.enabled under cp-kafka and cp-zookeeper in values.yaml . These type of clusters are suitable for development and testing purposes. The StatefulSets are going to use emptyDir volumes, this means that its content is strictly related to the pod life cycle and is deleted when the pod goes down.
Install cp-helm-charts¶
Clone the Confluent Helm Chart repo
> helm repo add confluentinc https://confluentinc.github.io/cp-helm-charts/
"confluentinc" has been added to your repositories
> helm repo update
Hang tight while we grab the latest from your chart repositories...
...Skip local chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "confluentinc" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "stable" chart repository
Update Complete. ⎈ Happy Helming!⎈
Install a 3 node ZooKeeper ensemble, a Kafka cluster of 3 brokers, 1
Confluent Schema Registry instance, 1 REST Proxy instance, and 1 Kafka
Connect worker in your Kubernetes environment. Naming the chart
--name my-confluent-oss is optional, but we assume this is the name
in the remainder of the documentation.
helm install confluentinc/cp-helm-charts --name my-confluent-oss
If you want to install without the Confluent Schema Registry instance, the REST Proxy instance, and the Kafka Connect worker:
helm install --set cp-schema-registry.enabled=false,cp-kafka-rest.enabled=false,cp-kafka-connect.enabled=false confluentinc/cp-helm-charts
View the installed Helm releases:
helm list
NAME REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART NAMESPACE
my-confluent-oss 1 Tue Jun 12 16:56:39 2018 DEPLOYED cp-helm-charts-0.1.0 default
Verify Installation¶
Helm¶
This step is optional: run the embedded test pod in each sub-chart to verify installation:
helm test my-confluent-oss
Kafka cluster¶
This step is optional: to verify that Kafka is working as expected, connect to one of the Kafka pods and produce some messages to a Kafka topic.
List your pods and wait until they are all in
Runningstate.kubectl get pods
Connect to the container
cp-kafka-brokerin a Kafka broker pod to produce messages to a Kafka topic. If you specified a different release name, substitutemy-confluent-osswith whatever you named your release.kubectl exec -c cp-kafka-broker -it my-confluent-oss-cp-kafka-0 -- /bin/bash /usr/bin/kafka-console-producer --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic test
Wait for a
>prompt, and enter some text.m1 m2
Press Control-d to close the producer session.
Consume the messages from the same Kafka topic as above.
kubectl exec -c cp-kafka-broker -it my-confluent-oss-cp-kafka-0 -- /bin/bash /usr/bin/kafka-console-consumer --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic test --from-beginning
You should see the messages which were published from the console producer. Press Control-c to stop consuming.
Manual Test¶
ZooKeeper¶
Clone Helm Chars git repository
git clone https://github.com/confluentinc/cp-helm-charts.git
Deploy a ZooKeeper client pod.
kubectl apply -f cp-helm-charts/examples/zookeeper-client.yaml
Connect to the ZooKeeper client pod and use the
zookeeper-shellcommand to explore brokers, topics, etc:kubectl exec -it zookeeper-client -- /bin/bash zookeeper-shell <zookeeper service>:<port> ls /brokers/ids kubectl exec -it zookeeper-client -- /bin/bash zookeeper-shell <zookeeper service>:<port> get /brokers/ids/0 kubectl exec -it zookeeper-client -- /bin/bash zookeeper-shell <zookeeper service>:<port> ls /brokers/topics
Kafka¶
Deploy a Kafka client pod.
kubectl apply -f cp-helm-charts/examples/kafka-client.yaml
Log into the Pod
kubectl exec -it kafka-client -- /bin/bash
From within the kafka-client pod, explore with kafka commands:
## Setup export RELEASE_NAME=<release name> export ZOOKEEPERS=${RELEASE_NAME}-cp-zookeeper:2181 export KAFKAS=${RELEASE_NAME}-cp-kafka-headless:9092 ## Create Topic kafka-topics --zookeeper $ZOOKEEPERS --create --topic test-rep-one --partitions 6 --replication-factor 1 ## Producer kafka-run-class org.apache.kafka.tools.ProducerPerformance --print-metrics --topic test-rep-one --num-records 6000000 --throughput 100000 --record-size 100 --producer-props bootstrap.servers=$KAFKAS buffer.memory=67108864 batch.size=8196 ## Consumer kafka-consumer-perf-test --broker-list $KAFKAS --messages 6000000 --threads 1 --topic test-rep-one --print-metrics
Run A Streams Application¶
Now that you have Confluent Platform running in your Kubernetes cluster, you may run a KSQL example. KSQL is the streaming SQL engine that enables real-time data processing against Apache Kafka.
Operations¶
Scaling¶
Tip
All scaling operations should be done offline with no producer or consumer connection.
Tip
The number of nodes should always be odd number.
ZooKeeper¶
Install cp-helm-charts with default 3 node ZooKeeper ensemble
helm install cp-helm-charts
Scale ZooKeeper nodes up to 5, change servers under cp-zookeeper
to 5 in values.yaml
helm upgrade <release name> cp-helm-charts
Scale ZooKeeper nodes down to 3, change servers under
cp-zookeeper to 3 in values.yaml
helm upgrade <release name> cp-helm-charts
Kafka¶
Important
Scaling Kafka brokers without doing Partition Reassignment will cause data loss. You must reassign partitions correctly before scaling the Kafka cluster.
Install cp-helm-charts with default 3 brokers kafka cluster
helm install cp-helm-charts
Scale kafka brokers up to 5, change brokers under cp-kafka to 5
in values.yaml
helm upgrade <release name> cp-helm-charts
Scale kafka brokers down to 3, change brokers under cp-kafka to
3 in values.yaml
helm upgrade <release name> cp-helm-charts
Monitoring¶
JMX Metrics are enabled by default for all components, Prometheus JMX Exporter is installed as a sidecar container along with all Pods.
Install Prometheus and Grafana in same Kubernetes cluster using helm
helm install stable/prometheus helm install stable/grafana
Add Prometheus as Data Source in Grafana, url should be something like:
http://illmannered-marmot-prometheus-server:9090Import dashboard under grafana-dashboard into Grafana
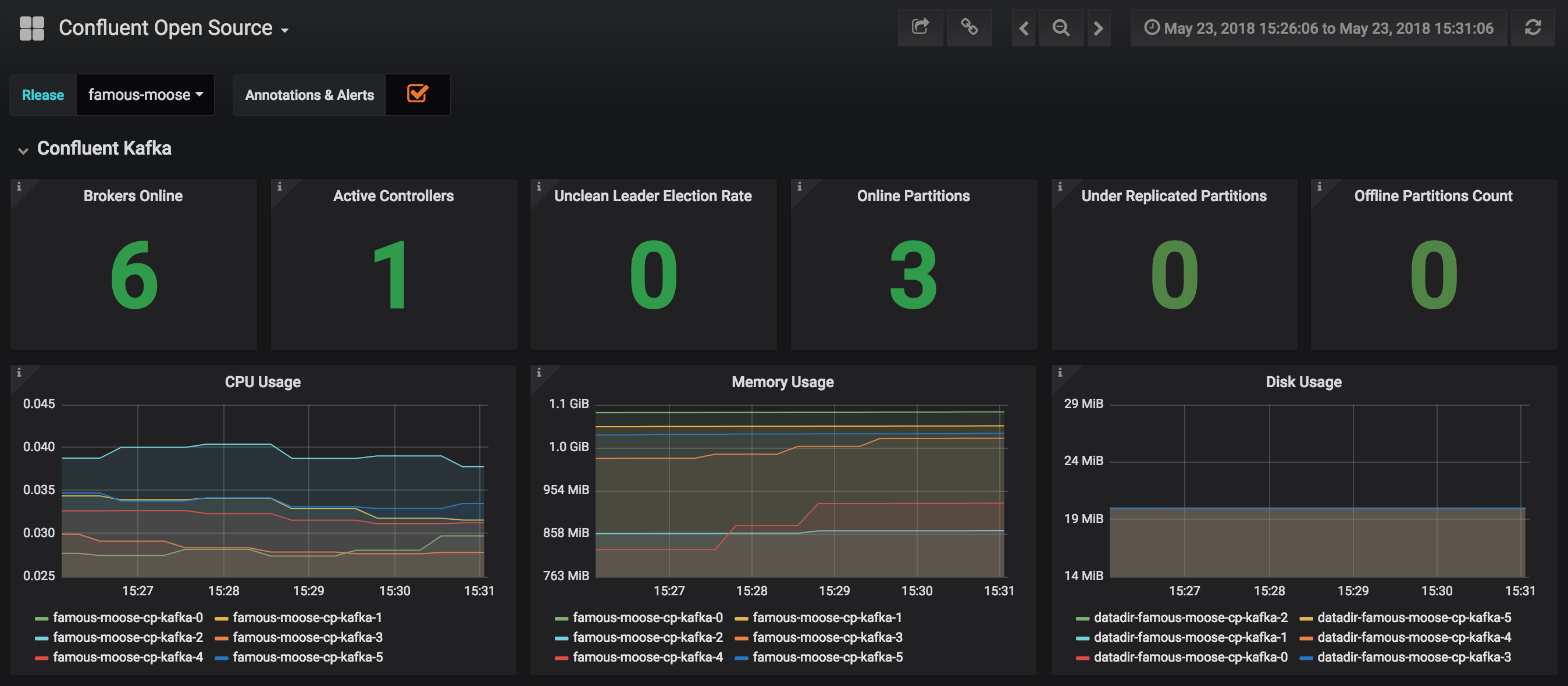
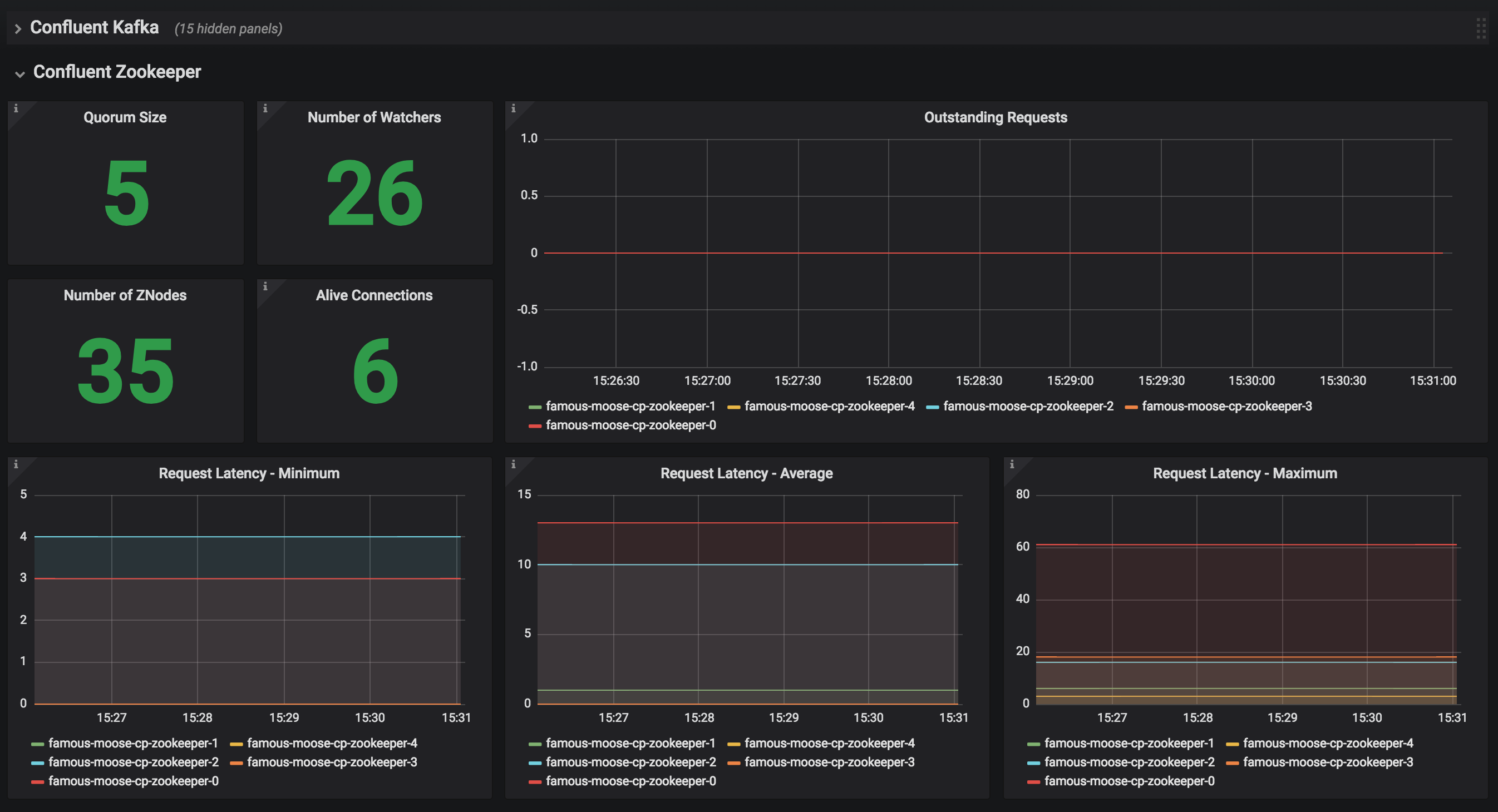
ZooKeeper Dashboard
Teardown¶
To remove the pods, list the pods with kubectl get pods and then
delete the pods by name.
kubectl get pods
kubectl delete pod <podname>
To delete the Helm release, find the Helm release name with
helm list and delete it with helm delete. You may also need to
clean up leftover StatefulSets, since helm delete can leave them
behind. Finally, clean up all persisted volume claims (pvc) created by
this release.
helm list
helm delete <release name>
kubectl delete statefulset <release name>-cp-kafka <release name>-cp-zookeeper
kubectl delete pvc --selector=release=<release name>
To stop or delete Minikube:
minikube stop
minikube delete
Appendix: Create a Local Kubernetes Cluster¶
There are many deployment options to get set up with a Kubernetes cluster, and this document provides instructions for using Minikube to set up a local Kubernetes cluster. Minikube runs a single-node Kubernetes cluster inside a VM on your laptop.
You may alternatively set up a Kubernetes cluster in the cloud using other providers such as Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).
Install Minikube and Drivers¶
Minikube version 0.23.0 or higher is required for docker server
https://github.com/moby/moby/pull/31352[17.05], which adds support for
using ARG in FROM in your Dockerfile.
First follow the basic Minikube installation instructions.
Then install the Minikube
drivers.
Minikube uses Docker Machine to manage the Kubernetes VM so it benefits
from the driver plugin architecture that Docker Machine uses to provide
a consistent way to manage various VM providers. Minikube embeds
VirtualBox and VMware Fusion drivers so there are no additional steps to
use them. However, other drivers require an extra binary to be present
in the host PATH.
If you are running on macOS, in particular make sure to install the
xhyve drivers for the native OS X hypervisor:
brew install docker-machine-driver-xhyve
sudo chown root:wheel $(brew --prefix)/opt/docker-machine-driver-xhyve/bin/docker-machine-driver-xhyve
sudo chmod u+s $(brew --prefix)/opt/docker-machine-driver-xhyve/bin/docker-machine-driver-xhyve
Start Minikube¶
Tip
The following command increases the memory to 6096 MB and uses the xhyve driver for the native macOS Hypervisor.
Start Minikube. The following command increases the memory to 6096 MB and uses the
xhyvedriver for the native macOS Hypervisor.minikube start --kubernetes-version v1.9.4 --cpus 4 --memory 6096 --vm-driver=xhyve --v=8
Continue to check status of your local Kubernetes cluster until both minikube and cluster are in Running state
minikube status minikube: Running cluster: Running kubectl: Correctly Configured: pointing to minikube-vm at 192.168.99.106
Work around Minikube issue #1568.
minikube ssh -- sudo ip link set docker0 promisc on
Set the context.
eval $(minikube docker-env) kubectl config set-context minikube.internal --cluster=minikube --user=minikube Context "minikube.internal" modified. kubectl config use-context minikube.internal Switched to context "minikube.internal".
Verify Minikube Local Kubernetes Environment¶
kubectl config current-context
minikube.internal
kubectl cluster-info
Kubernetes master is running at https://192.168.99.106:8443
KubeDNS is running at https://192.168.99.106:8443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
