KRaft Overview for Confluent Platform
Starting with Confluent Platform version 8.0, KRaft (pronounced craft) mode is how metadata is managed in Apache Kafka®.
Kafka Raft (KRaft) is the consensus protocol that greatly simplifies Kafka’s architecture by consolidating responsibility for metadata into Kafka itself.
The following image provides a simple illustration of Kafka running with KRaft managing metadata for the cluster. Each KRaft controller is a node in a Raft quorum, and each node is a broker that can handle client requests.
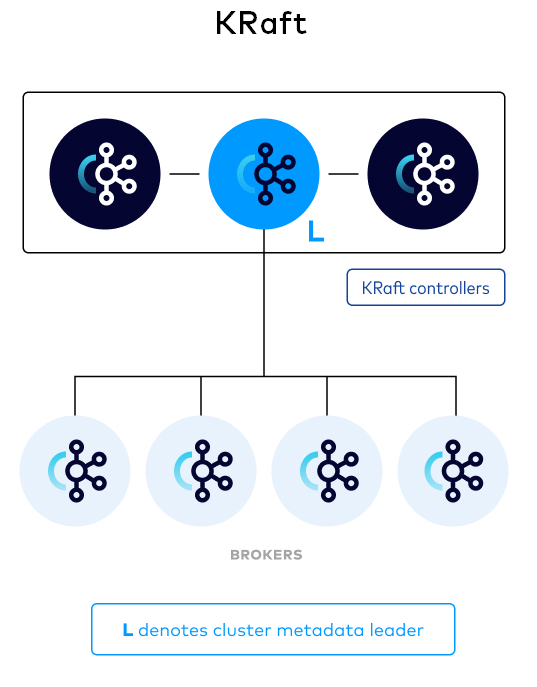
The controller quorum
The KRaft controller nodes comprise a Raft quorum which manages the Kafka metadata log. This log contains information about each change to the cluster metadata. Metadata about topics, partitions, ISRs, configurations, and so on, is stored in this log.
Using the Raft consensus protocol, the controller nodes maintain consistency and leader election without relying on any external system. The leader of the metadata log is called the active controller. The active controller handles all RPCs made from the brokers. The follower controllers replicate the data which is written to the active controller, and serve as hot standbys if the active controller should fail. With the concept of a metadata log, brokers use offsets to keep track of the latest metadata stored in the KRaft controllers, which results in more efficient propagation of metadata and faster recovery from controller failovers.
KRaft requires a majority of nodes to be running. For example, a three-node controller cluster can survive one failure. A five-node controller cluster can survive two failures, and so on.
Periodically, the controllers will write out a snapshot of the metadata to disk. This is conceptually similar to compaction, but state is read from memory rather than re-reading the log from disk.
Scaling Kafka with KRaft
There are two properties that determine the number of partitions an Kafka cluster can support: the per-node partition count limit and cluster-wide partition limit.
KRaft mode is designed to handle a large number of partitions per cluster, however Kafka’s scalability still primarily depends on adding nodes to get more capacity, so the cluster-wide limit still defines the upper bounds of scalability within the system.
In KRaft, the quorum controller reduces the time taken to move critical metadata in a controller failover scenario. The result of this change is a near-instantaneous controller failover. The following image shows the results of a Confluent lab experiment on a Kafka cluster running 2 million partitions, which is 10 times the maximum number of partitions for a cluster running ZooKeeper. The experiment shows that controlled shutdown time and recovery time after uncontrolled shutdown are greatly improved with a quorum controller versus ZooKeeper.
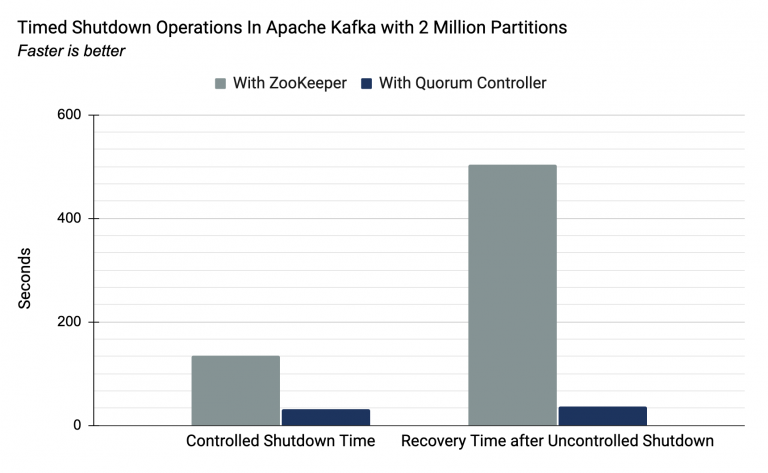
Configure Confluent Platform with KRaft
For details on how to configure Confluent Platform with KRaft, see KRaft Configuration for Confluent Platform.
Client configurations are not impacted by Confluent Platform moving to KRaft to manage metadata.
Migrate from ZooKeeper to KRaft
If you haven’t already migrated to KRaft, see Migrate from ZooKeeper to KRaft on Confluent Platform. You must do this before you upgrade to Confluent Platform 8.0.
Manage topic assignment to offline brokers
You can assign new topics to offline brokers. This behavior enables you to roll clusters when the cluster size equals the replication factor. For example, you can roll a cluster by shrinking it from 4 brokers to 3 brokers.
To prevent new topics from being assigned to offline brokers that are no longer considered part of the Confluent Platform cluster, unregister the broker using the kafka-cluster command. This command calls the UnregisterBroker API and removes all traces of the broker from the cluster metadata.
To unregister a broker, run the following command:
kafka-cluster unregister --bootstrap-controller <controller-host:port> --id <broker-id>
To list brokers you may need to unregister, run the following command:
kafka-cluster list-endpoints --bootstrap-controller <controller-host:port>
Limitations and known issues
Combined mode, where a Kafka node acts as both a broker and a KRaft controller, is not currently supported by Confluent. You can start a new KRaft cluster in combined mode for testing purposes in development or testing environments. However, Confluent does not support migration to KRaft in combined mode or direct deployment in combined mode, even for development or test clusters. There are key security and feature gaps between combined mode and isolated mode in Confluent Platform.
Confluent Platform versions older than 7.9 do not support dynamic controllers, so you cannot add or remove KRaft controllers while the cluster is running. Confluent Platform 7.9 adds this feature, but only for clusters that were bootstrapped to use dynamic controllers. For more information, see KIP-853. Confluent recommends three or five controllers for production. For hardware requirements, see Hardware.
For information about upgrading from static controllers to dynamic controllers, and for the full KRaft server compatibility matrix showing static and dynamic controller support across Confluent Platform versions, see KRaft server compatibility.
You cannot currently use Schema Registry Topic ACL Authorizer for Confluent Platform for Schema Registry with Confluent Platform in KRaft mode. As an alternative, you can use Schema Registry ACL Authorizer for Confluent Platform or Configure Role-Based Access Control for Schema Registry in Confluent Platform.
Currently, Health+ reports KRaft controllers as brokers and as a result, alerts may not function as expected.
Broker behavior during controller failures
To operate a production cluster, you need to understand how KRaft behaves during failure scenarios. The following sections describe what happens when brokers lose connectivity to the controller quorum, or when the controller quorum itself cannot achieve consensus.
Broker partition from the active controller
When one or more brokers are partitioned from the active controller (that is, they can’t successfully heartbeat to the active controller), the brokers continue to accept produce and consume requests from clients. However, brokers continuously attempt to reconnect to the active quorum controller.
Important
While brokers continue to serve client requests in this state, this state is not sustainable for an extended period. You should resolve the network partition or connectivity issue as soon as possible.
The following operations continue to work when brokers are partitioned from the active controller:
Produce requests: Brokers can continue to accept and process produce requests from clients for existing partitions. However, if the network partition also prevents data replication, producer requests requiring acknowledgments from other replicas (for example,
acks=all) might time out.Consume requests: Brokers can continue to serve consume requests from clients for existing partitions.
The following operations do not continue to work when brokers are partitioned from the active controller:
ISR (In-Sync Replicas) changes: The controller cannot update the ISR list for partitions, which means replicas cannot be added or removed from the ISR.
Partition changes: Partitions cannot be added to or removed from topics.
Leadership re-elections: Partition leadership cannot be reassigned, even if the current leader fails.
Admin operations: Topic configuration changes, topic creation and deletion, and other administrative operations do not succeed.
Consumer group rebalancing: Consumer groups cannot rebalance, which means new consumers cannot join groups and existing consumers cannot leave.
Metadata updates: Brokers cannot receive metadata updates from the controller, so they operate with stale metadata. This can lead to clients making decisions based on outdated information (for example, trying to produce to a stale leader).
Loss of controller quorum
When the controller quorum cannot achieve quorum (for example, when 2 out of 3 controller nodes are down), the active controller cannot be elected or maintained. In this scenario, the controller quorum is unable to process metadata changes, and brokers cannot successfully heartbeat to an active controller.
Similar to the broker partition scenario, brokers continue to accept produce and consume requests from clients while continuously attempting to reconnect to the controller quorum.
The following operations continue to work when the controller quorum is lost:
Produce requests: Brokers can continue to accept and process produce requests from clients for existing partitions. However, as the control plane is down, any failure requiring leader re-election or ISR changes will not be serviceable, and producers using
acks=allmight time out.Consume requests: Brokers can continue to serve consume requests from clients for existing partitions.
However, the same limitations apply: ISR changes, partition changes, leadership re-elections, admin operations, consumer group rebalancing, and metadata updates do not work.
Important
This is a critical failure state that requires immediate attention. You should restore the controller quorum to a healthy state (where a majority of controllers are available) as soon as possible.
To prevent quorum loss, ensure you have an adequate number of controller nodes. As mentioned in the controller quorum section, a three-node controller cluster can survive one failure, and a five-node controller cluster can survive two failures. For production environments, always run at least three controllers, with three or five controllers is the recommended configuration.