Kafka Streams Code Examples for Confluent Platform
If you’re new to Kafka Streams, here is a curated list of resources to get you started.
Confluent for VS Code
Use the Confluent for VS Code extension to generate a new Kafka Streams application that reads messages from a Kafka topic, performs a simple transformation, and writes the transformed data to another topic. This option is ideal if you’re learning about Kafka Streams.
For more information, see Confluent for VS Code with Confluent Platform.
Getting started examples
There are numerous Kafka Streams examples on Confluent Developer that provide full code examples with step–by-step instructions.
The code repository for the Kafka Streams examples is available on GitHub.
Routing
Transforming
Aggregations
Joins
Windowing and time operations
Miscellaneous
Interactive Queries examples
Since Confluent Platform 3.1+ and Kafka 0.10.1+, it is possible to query state stores created via the Kafka Streams DSL and the Processor API. For further information, see Kafka Streams Interactive Queries for Confluent Platform.
Java
With lambda expressions for Java 8+:
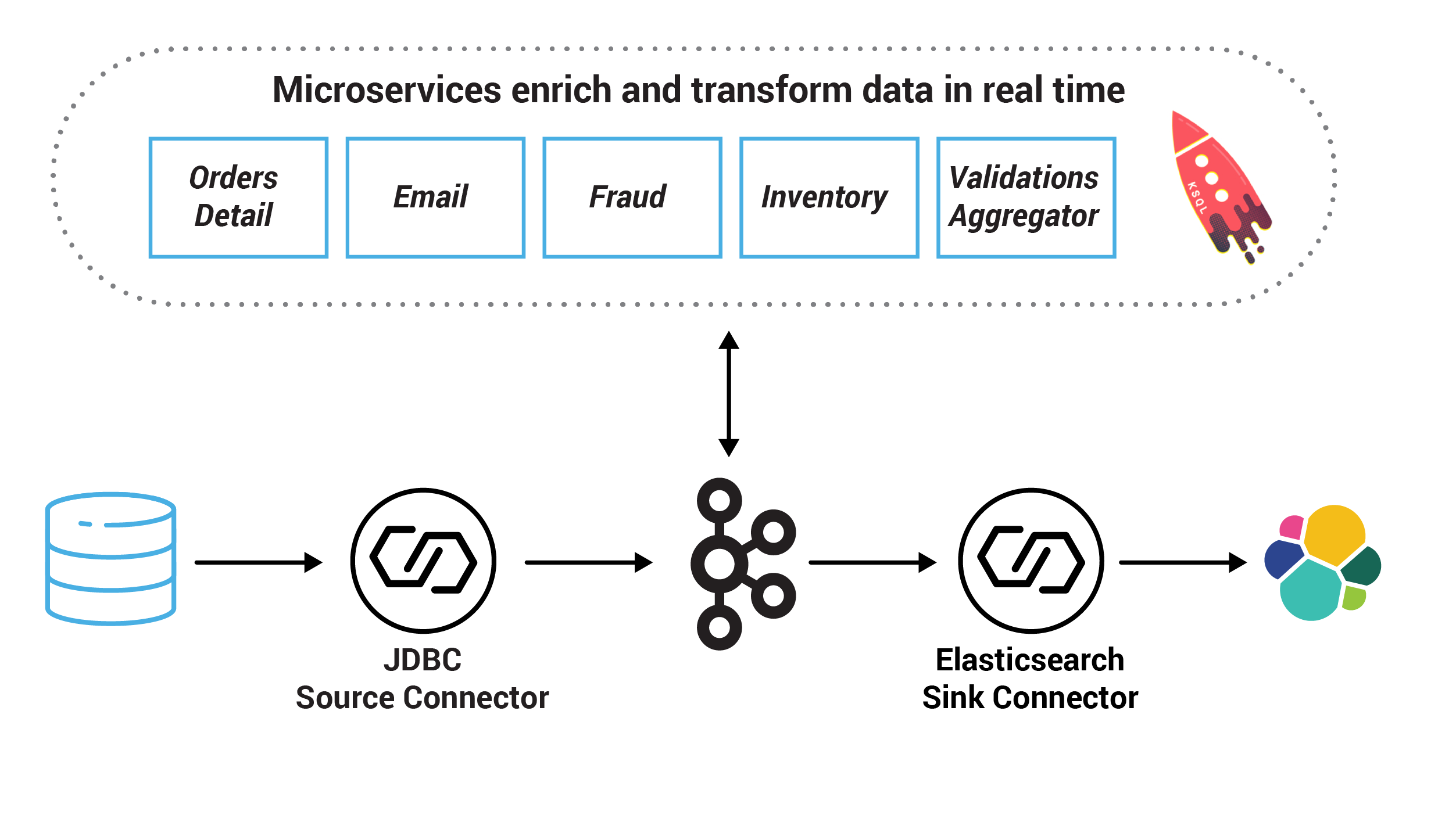
Event-Driven Microservice example
Java
The Event-Driven Microservice example implements an Order Service that provides a REST interface to POST and GET orders. Posting an order creates an event in Kafka, which is picked up by three different validation engines: a Fraud Service, an Inventory Service, and an Order Details Service. These services validate the order in parallel, emitting a PASS or FAIL based on whether each validation succeeds.
Self-paced Kafka Streams tutorial based on the microservices example above: deployed in an event streaming platform with all the services in Confluent Platform and interconnecting other end systems