Use Azure Private Link for Serverless Products on Confluent Cloud
Confluent Cloud supports private connectivity for serverless Confluent Cloud products, such as Enterprise Kafka clusters and Confluent Cloud for Apache Flink®. When you use Private Link Attachment, your Enterprise cluster or Flink resources are only accessible from tenant-specific private endpoints. Public access is blocked with Private Link Attachment.
Note
The Private Link Attachment enables you to access the Flink API with private networking, allowing you to issue Flink SQL queries and retrieve results through the associated Private Link connection. All data movement between Flink queries and Kafka clusters configured with private networking occurs over a secure private path within Confluent Cloud.
Confluent Cloud uses the following private networking resources for Enterprise clusters. These resources are regional and do not have a mapping to specific availability zones.
- Private Link Attachment
The Private Link Attachment (
PrivateLinkAttachment) resource represents a reservation to establish a Private Link connection from your Virtual Network (VNet) regional services in a Confluent Cloud environment.A Private Link Attachment belongs to an Environment in the Confluent resource hierarchy.
This resource is referred to as gateways in the Confluent Cloud Console.
- Private Link Attachment Connection
A Private Link Attachment Connection (
PrivateLinkAttachmentConnection) is a registration of VNet private endpoints that are allowed to connect to Confluent Cloud. A Private Link Attachment Connection belongs to a specific Private Link Attachment.This resource is referred as access points in the Confluent Cloud Console.
You can use the Confluent Cloud Console, Confluent REST API, Confluent CLI, or Terraform to establish a Private Link connectivity for serverless products, such as Enterprise Kafka clusters or Flink.
The high-level workflow is:
In Azure, create a private endpoint to be associated with the Private Link Attachment service.
If you are using the Confluent Cloud Console for configuration, this step is merged into the next step and shows up as the first step in connection creation.
In Confluent Cloud, create a Private Link Attachment Connection.
Create a Kafka client in your VNet using the bootstrap endpoint of your Enterprise Kafka cluster. This Kafka client can live in Virtual Machine or similar compute infrastructure.
Validate produce/consume traffic is successful.
Once you create a Private Link Attachment resource and establish a Private Link, you can securely send and receive traffic through the Private Link between your VNet and Confluent Cloud.
Requirements and considerations
You can connect to only one Confluent Cloud environment from a single VNet or from an on-premises network unless multiple DNS servers are used. Multiple connections utilizing a centralized DNS resolver does not work due to the overlap in domain names between Confluent Cloud environments.
For the workaround to configure cross-environment queries in Flink, see Configure cross-environment queries.
You can connect to only one region in a specific environment from a single VNet or from an on-premises network.
For the regions supported for Private Link Attachment on Azure, see Cloud Providers and Regions for Confluent Cloud.
PrivateLink Attachments and their associated connections can only be used to access Confluent Cloud resources belonging to the same environment.
Confluent Cloud Console components, like topic management and Flink workspaces, require additional configuration to function as they use cluster endpoints.
For information about using Flink with Azure Private Link, see Private Networking with Confluent Cloud for Apache Flink.
To use all features of the Confluent Cloud Console with Azure Private Link, see Use the Confluent Cloud Console with Private Networking.
Create a Private Link Attachment
The Private Link Attachment resource, referred as the gateway in the Confluent Cloud Console, represents a reservation to establish a Private Link connection from Virtual Network (VNet) regional services in a Confluent Cloud environment.
When you create a Private Link Attachment in an environment and in a region, the Private Link Attachment resource provides connectivity to all Enterprise Kafka clusters within the environment for the specific cloud region.
In the Confluent Cloud Console, the Private Link Attachment resources are labeled and referred as gateways.
In the Confluent Cloud Console, select an environment for the Private Link Attachment.
In the Network management tab in the environment, click For serverless products.
Click + Add gateway configuration.
Select the PrivateLink card to select the type of gateway configuration.
On the From your VPC or VNet to Confluent Cloud pane, click + Create configuration.
On the Configure gateway sliding panel, enter the following information.
Gateway name
Cloud provider: Click Microsoft Azure.
Region
Click Submit.
You can continue to create an access point for the Ingress Private Link connection.
Alternatively, you can create an access point at a later time by navigating to this gateway in the Network management tab.
The Private Link Attachment will be provisioned and move to the Waiting forconnection state.
A Private Link Attachment can be in one of the following states:
WAITING FOR CONNECTION: The Private Link Attachment is waiting for a connection to be created.READY: Azure Private Link connectivity is ready to be used.EXPIRED: A valid connection has not been provisioned within the allotted time. A new Private Link Attachment must be provisioned.
Send a request to create a Private Link Attachment resource:
REST request
POST https://api.confluent.cloud/networking/v1/private-link-attachments
REST request body
{ "spec": { "display_name": "<name of this resource>", "cloud": "<provider type>", "region": "<region>", "environment": { "id": "<environement id>" } } }
In the REST response,
status.phaseshould be set toPROVISIONING.Check the status of the new Private Link Attachment:
REST request
GET https://api.confluent.cloud/networking/v1/private-link-attachments/<platt-id>
REST response example
{ "status": { "phase": "WAITING_FOR_CONNECTIONS", "error_code": "", "error_message": "", "cloud": { "kind": "AzurePrivateLinkAttachmentStatus", "private_link_service":{ "private_link_service_alias": "<pls-plt-abcdef-az1.f5aedb5a-5830-4ca6-9285-e5c81ffca2cb.centralus.azure.privatelinkservice>", "private_link_service_resource_id": "</subscriptions/12345678-9012-3456-7890-123456789012/resourceGroups/rg-abcdef/providers/Microsoft.Network/privateLinkServices/pls-plt-abcdef>" } } } }
status.phaseisWAITING_FOR_CONNECTIONSbecause no Private Link Attachment Connection has not been associated with this Private Link Attachment resource yet.The
status.cloudobject has information about theprivate_link_service_aliasandprivate_link_service_resource_idthat you must connect your Private Link Attachment endpoint to.
Use the confluent network private-link attachment create Confluent CLI command to create an Azure private link attachment:
confluent network private-link attachment create <attachment-name> <flags>
The following command-specific flags are supported:
--cloud: Required. Cloud provider type. Specifyazure.--region: Required. Azure region where the resources to be accessed using the private link attachment.
You can specify additional optional CLI flags described in the Confluent CLI command reference, such as --environment.
The following is an example Confluent CLI command to create a private link attachment:
confluent network private-link attachment create my-private-link-attachment \
--cloud azure \
--region us-west-2
Use the confluent_private_link_attachment Confluent Terraform Provider resource to create a Private Link Attachment.
An example snippet of Terraform configuration for a Private Link Attachment:
resource "confluent_private_link_attachment" "main" {
cloud = "AZURE"
region = "centralus"
display_name = "prod-platt"
environment {
id = "env-1234nw"
}
}
output "private_link_attachment" {
value = confluent_private_link_attachment.main
}
See Terraform configuration example for creating a Private Link Attachment with ACLs using Terraform.
Create an Azure private endpoint
In Azure, create an endpoint that is associated with the Private Link Service ID of the Private Link Attachment you created in Create a Private Link Attachment.
For details on creating a private endpoint in Azure, see Create a Private Endpoint.
On the Private Endpoint page in Azure portal, click + Create.
In the Basics pane, specify the following:
Subscription: The subscription name that you selected when you created the VNet.
Resource group: The same resource group that you selected when you created the VNet.
Name: The name for the private endpoint.
Network interface name: A network interface name.
Region: The region for the private endpoint.
Click Next: Resource.
In the Resource pane, specify the following:
Connection method: Select Connect to an Azure resource by resource ID or alias.
Resource ID or alias: Paste in the Confluent Cloud Resource ID or Service Alias.
This is the alias or ID created in the previous section, Create a Private Link Attachment.
You can also use the value of the Private Link Service ID from your Network overview of the PrivateLink Attachment gateway in the Confluent Cloud Console.
Click Next: Virtual Network.
In the Virtual Network pane, specify the following:
Virtual network: Select the VNet where the private endpoint is to be created.
Subnet: Select the subnet where the private endpoint is to be created.
Network policy for private endpoints: Select the organization-approved or mandated policy. The default is Disabled.
Private IP configuration: Select Dynamically allocate IP address.
Click Next: DNS and accept the default values.
Click Next: Tags and, optionally, add tags.
Click Next: Review + create. Review the details and click Create to create the private endpoint.
Wait for the Azure deployment to complete.
Create an endpoint using the following Azure CLI:
az network private-endpoint create \
--connection-name <connection name> \
--name <endpoint name> \
--private-connection-resource-id <resource id> \
--resource-group <resource group name> \
--subnet <subnet for the endpoint>
Create a Private Link Attachment Connection
Create a Private Link Attachment Connection resource in Confluent Cloud. A Private Link Attachment Connection represents a private endpoint in your VNet.
In the Confluent Cloud Console, the Private Link Attachment Connection resources are labeled and referred to as access points.
In the Network Management tab of the desired Confluent Cloud environment, click the For serverless products tab.
Make sure the Private Link Attachment is in the correct region of the private endpoint.
Click the gateway to which you want to add the Private Link Endpoint.
Make sure the gateway is in the correct region of the VPC Private Endpoint.
In the Access points tab, click Create access point.
Using the service ID in Private Link Service ID or the service alias in Private Link Service Alias shown in Step 3 on the sliding panel, create a VPC Endpoint in Azure.
Specify the Private Endpoint ID.
The private endpoint ID is the Azure resource ID of the private endpoint that was created in Create an Azure private endpoint.
Specify the access point name.
Click Create access point to create the Private Link Endpoint.
The Private Link Attachment and Private Link Attachment Connection should now move to the
READYstate once the private endpoint connection is accepted.
Send a request to create a Private Link Attachment Connection resource:
REST request
POST https://api.confluent.cloud/networking/v1/private-link-attachment-connections
REST request body
{ "spec": { "display_name": "<PrivateLinkAttachmentEndpoint name>", "cloud": { "kind": "AzurePrivateLinkAttachmentConnection", "private_endpoint_id": "<Private Endpoint ID>", }, "environment": { "id": "<Environment ID>", }, "private_link_attachment": { "id": "<PrivateLinkAttachment>", } } }
REST response example
{ "api_version": "networking/v1", "kind": "PrivateLinkAttachmentConnection", "id": "plattc-xyzuvw", "status": { "phase": "PROVISIONING", "error_code": "", "error_message": "", } }
status.phaseisPROVISIONINGbecause a private endpoint connection has not yet been accepted.Check the status of the new Private Link Attachment Connection:
REST request
GET https://api.confluent.cloud/networking/v1/private-link-attachment-connections/<platt-id>
REST response example
{ "api_version": "networking/v1", "kind": "PrivateLinkAttachmentConnection", "id": "plattc-xyzuvw", "status": { "phase": "READY", "error_code": "", "error_message": "", "cloud": { "kind": "AzurePrivateLinkAttachmentConnectionStatus", "phase": "READY", "private_link_service_alias": "pls-plt-abcdef-az1.f5aedb5a-5830-4ca6-9285-e5c81ffca2cb.centralus.azure.privatelinkservice", "private_link_service_resource_id": "/subscriptions/12345678-9012-3456-7890-123456789012/resourceGroups/rg-abcdef/providers/Microsoft.Network/privateLinkServices/pls-plt-abcdef", "private_endpoint_id": "/subscriptions/Microsoft.Network/privateEndpoints/pe-platt-abcdef" } } }
status.phaseisREADYbecause the private endpoint connection has been accepted.status.cloudhas an object of kindAzurePrivateLinkConnectionStatus.
Use the confluent network private-link attachment connection create Confluent CLI command to create an Azure private link attachment connection:
confluent network private-link attachment connection create <connection-name> <flags>
The following command-specific flags are supported:
--cloud: Required. The cloud provider. Set toazure.--endpoint: Required. ID of an Azure private endpoint that is connected to the Azure private link service.--attachment: Required. Private link attachment ID.
You can specify additional optional CLI flags described in the Confluent CLI command reference, such as --environment.
The following is an example Confluent CLI command to create a private link attachment connection:
confluent network private-link attachment connection create azure-private-link-attachment-connection \
--cloud azure \
--endpoint /subscriptions/Microsoft.Network/privateEndpoints/pe-platt-abcdef \
--attachment platt-123456
Use the confluent_private_link_attachment_connection Confluent Terraform resource to create a Private Link Attachment Connection.
An example snippet of Terraform configuration for Private Link Attachment Connection:
resource confluent_private_link_attachment_connection "azure" {
display_name = "prod-azure-central-us-az1-connection"
environment {
id = "env-12345"
}
azure {
private_endpoint_resource_id = "/subscriptions/123aaaaa-aaaa-aaaa-aaaa-aaaaaaaaaaaa/resourceGroups/testvpc/providers/Microsoft.Network/privateEndpoints/pe-platt-abcdef-az1"
}
private_link_attachment {
id = "platt-abcdef"
}
}
output "private_link_attachment_connection" {
value = confluent_private_link_attachment_connection.azure
}
Go to the private endpoint resource in Azure Portal and verify that the private endpoint connection status is Approved.
Set up DNS records in Azure
Set up a DNS resolution and a DNS record using the Azure private DNS zone in the Azure console. This section focuses on the settings related to Confluent Cloud. For details, see Create an Azure private DNS zone.
Create a private DNS zone.
In the Confluent Cloud Console, copy the DNS Domain name in Private Link Attachment in the Network management tab, and use it as the name for the private DNS zone. It is in the form,
<region>.azure.private.confluent.cloud. For example,centralus.azure.private.confluent.cloud.In Private Zones in the Azure portal, click + Create.
In the Basics pane, enter or select the following values:
Subscription: Pre-filled with the subscription name that you selected when you created the VNet.
Resource group: Select the resource group that you selected when you created the VNet.
Name: Specify the domain name retrieved from the Confluent Cloud Console in the first step. It is in the format of
<region>.azure.private.confluent.cloud, for example,centralus.azure.private.confluent.cloud.
Click Next: Tags and, optionally, add tags.
Click Next: Review + create. Review the details and click Create a DNS zone.
Wait for the Azure deployment to complete.
To create DNS records, go to the private DNS zone resource you created in the previous step, and click + Record Set for the Confluent Cloud clusters.
Note
In Confluent Cloud with private linking, Kafka broker names you retrieve from the metadata are not static. Do not hardcode the broker names in DNS records.
Name:
*Type:
ATTL and TTL unit:
1MinuteIP address: The IP address of the private endpoint can be found under its associated network interface under Settings for the private endpoint.
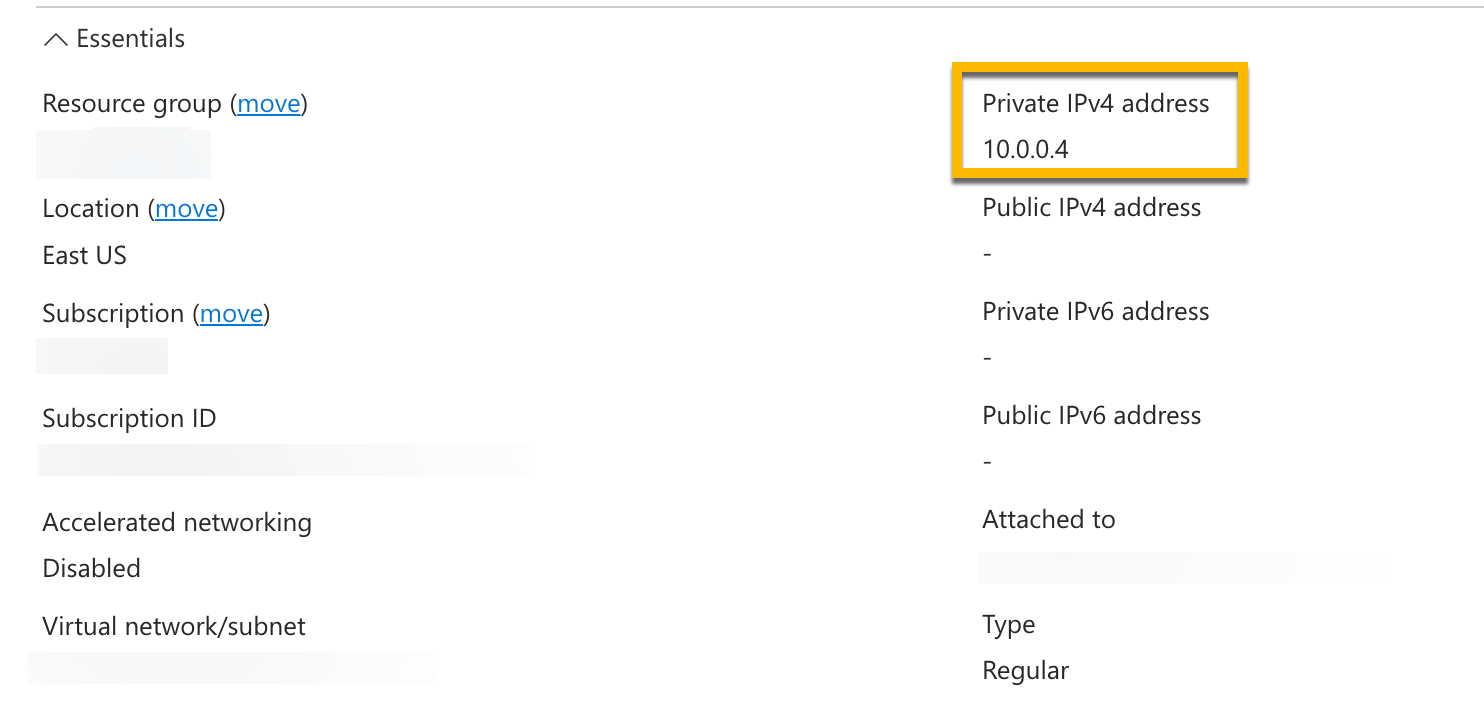
Attach the private DNS zone to the VNets where clients or applications are present.
Go to the private DNS zone resource and click Virtual network links under Settings.
Click + Add.
Specify the required values and click OK to create a virtual network link.
Connectivity scenarios
Below are examples of a few connectivity scenarios that are supported for Enterprise clusters in Confluent Cloud.
Scenario: Access one environment from one VNet
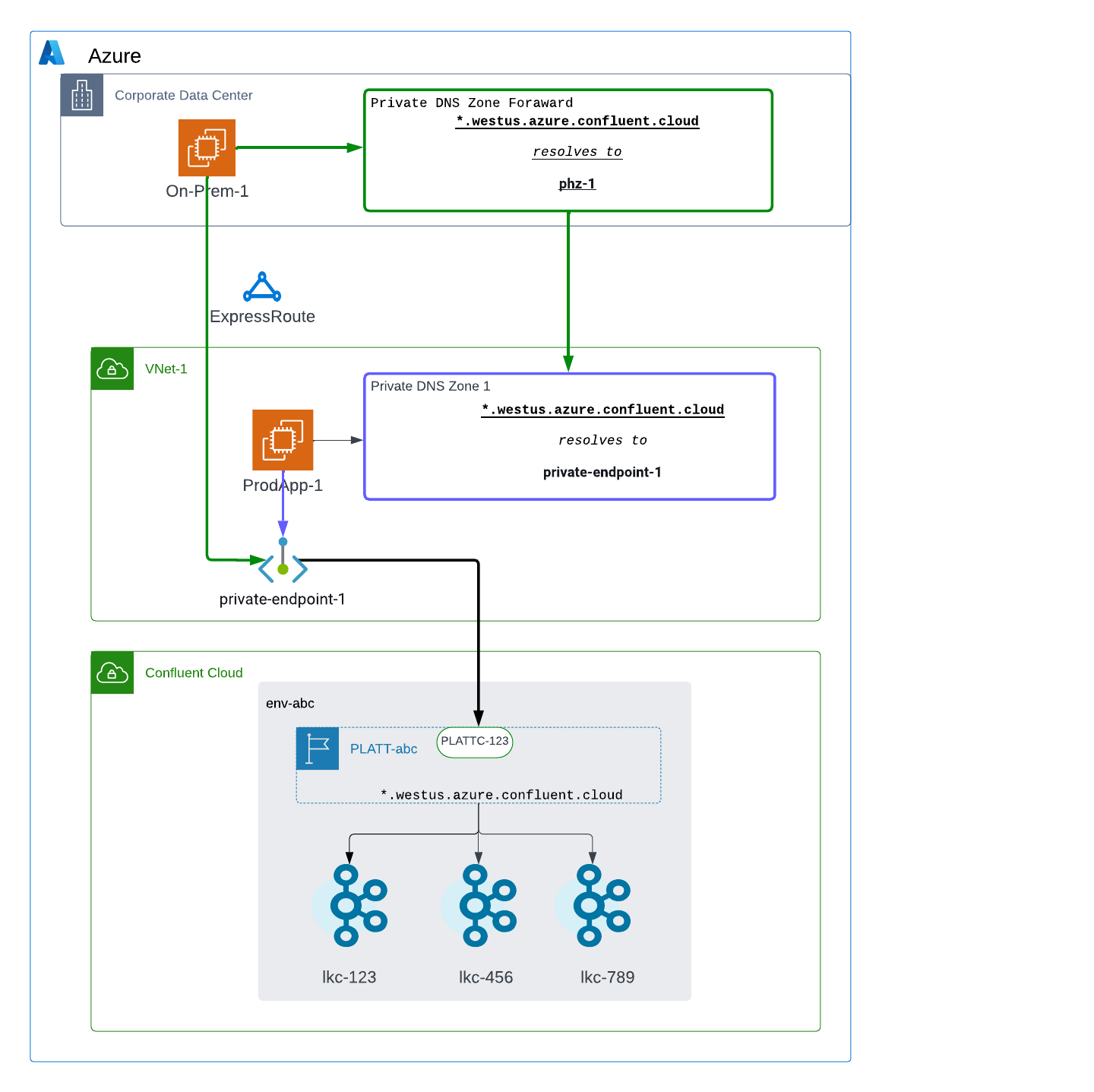
The following resources are configured:
PLATT-prodas a Private Link Attachment for accessing Kafka clusters in the env-prod environmentPLATTC-123as a Private Link Attachment Connection for theprivate-endpoint-1private endpoint inVNet-1ProdAppas a Kafka client bootstrapped withlkc-123.centralus.azure.private.confluent.cloudPrivate DNS Zone 1with the regional wildcardcentralus.azure.private.confluent.cloud
The following steps are performed:
ProdAppattempts to accesslkc-123in the env-prod environment. A DNS query forlkc-123.centralus.azure.private.confluent.cloudresolves against returnsprivate-endpoint-1.Application sends traffic to
private-endpoint-1.private-endpoint-1forwards traffic toPLATT-prod, andlkc-123can be accessed sincePLATTC-123is associated withprivate-endpoint-1.
Scenario: Access one environment from many VNet’s
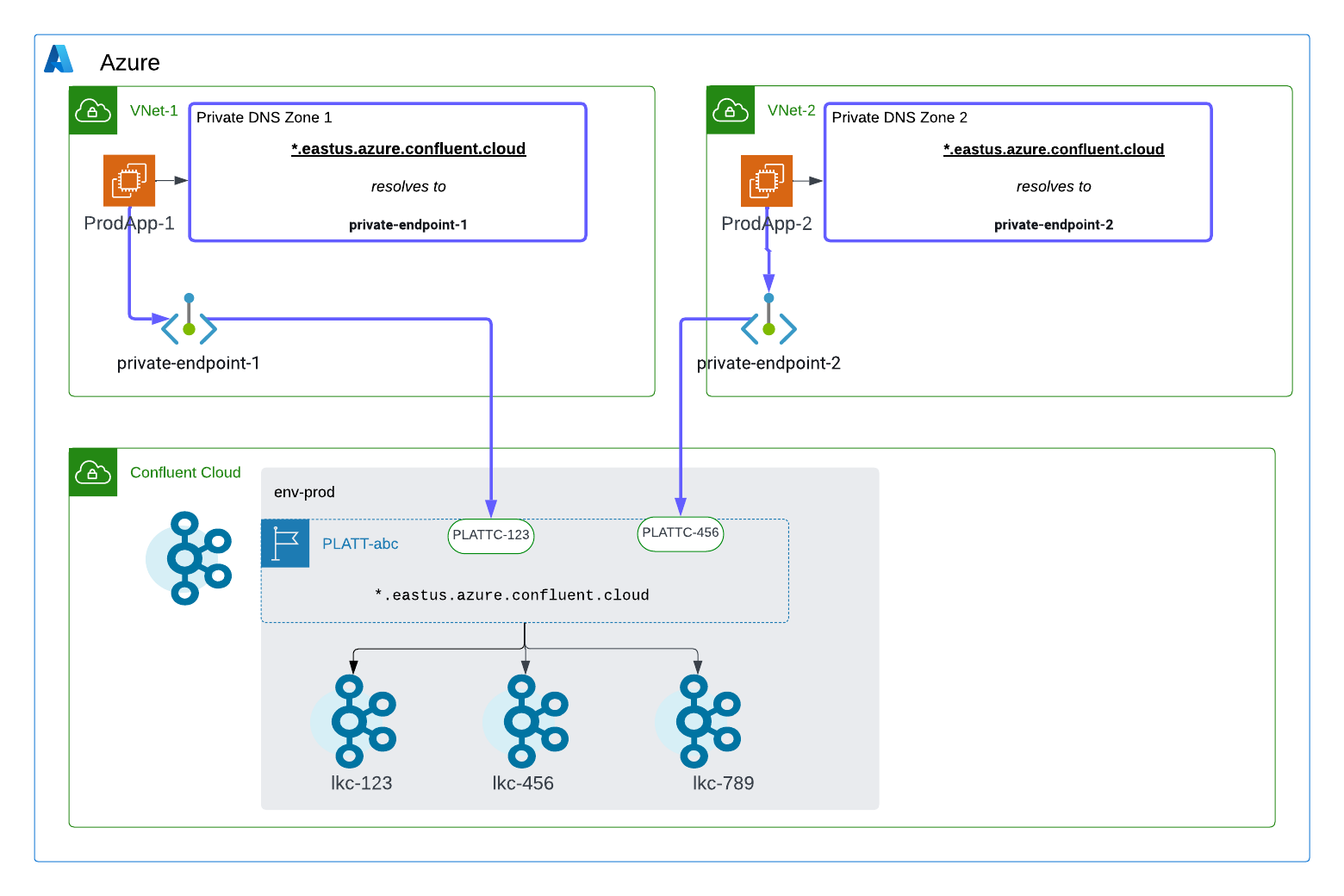
The following resources are configured:
PLATT-abcas a Private Link Attachment for accessing Kafka clusters in the env-prod environmentPLATTC-123as a Private Link Attachment Connection for theprivate-endpoint-1private endpoint inVNet-1PLATTC-456for theprivate-endpoint-2private endpoint in VNet-2ProdApp-1as a Kafka client bootstrapped withlkc-123.eastus.azure.private.confluent.cloudProdApp-2as a Kafka client bootstrapped withlkc-456.eastus.azure.private.confluent.cloudPrivate DNS Zone 1with the regional wildcard*.eastus.azure.private.confluent.cloudPrivate DNS Zone 2with the regional wildcard*.eastus.azure.private.confluent.cloud
The following steps are performed:
ProdApp-1attempts to accesslkc-123in the env-prod environment. A DNS query forlkc-123.eastus.azure.private.confluent.cloudresolves againstPrivate DNS Zone 1and returnsprivate-endpoint-1.ProdApp-1sends traffic toprivate-endpoint-1.private-endpoint-1forwards traffic toPLATT-abc, andlkc-123can be accessed sincePLATTC-123is associated withprivate-endpoint-1.ProdApp-2attempts to accesslkc-456in the env-prod environment. A DNS query forlkc-456.eastus.azure.private.confluent.cloudresolves againstPrivate DNS Zone 2and returnsprivate-endpoint-2.ProdApp-2sends traffic toprivate-endpoint-2.private-endpoint-2forwards traffic toPLATT-abc, andlkc-456can be accessed sincePLATTC-456is associated withprivate-endpoint-1.
Scenario: Access one environment from an on-premises network
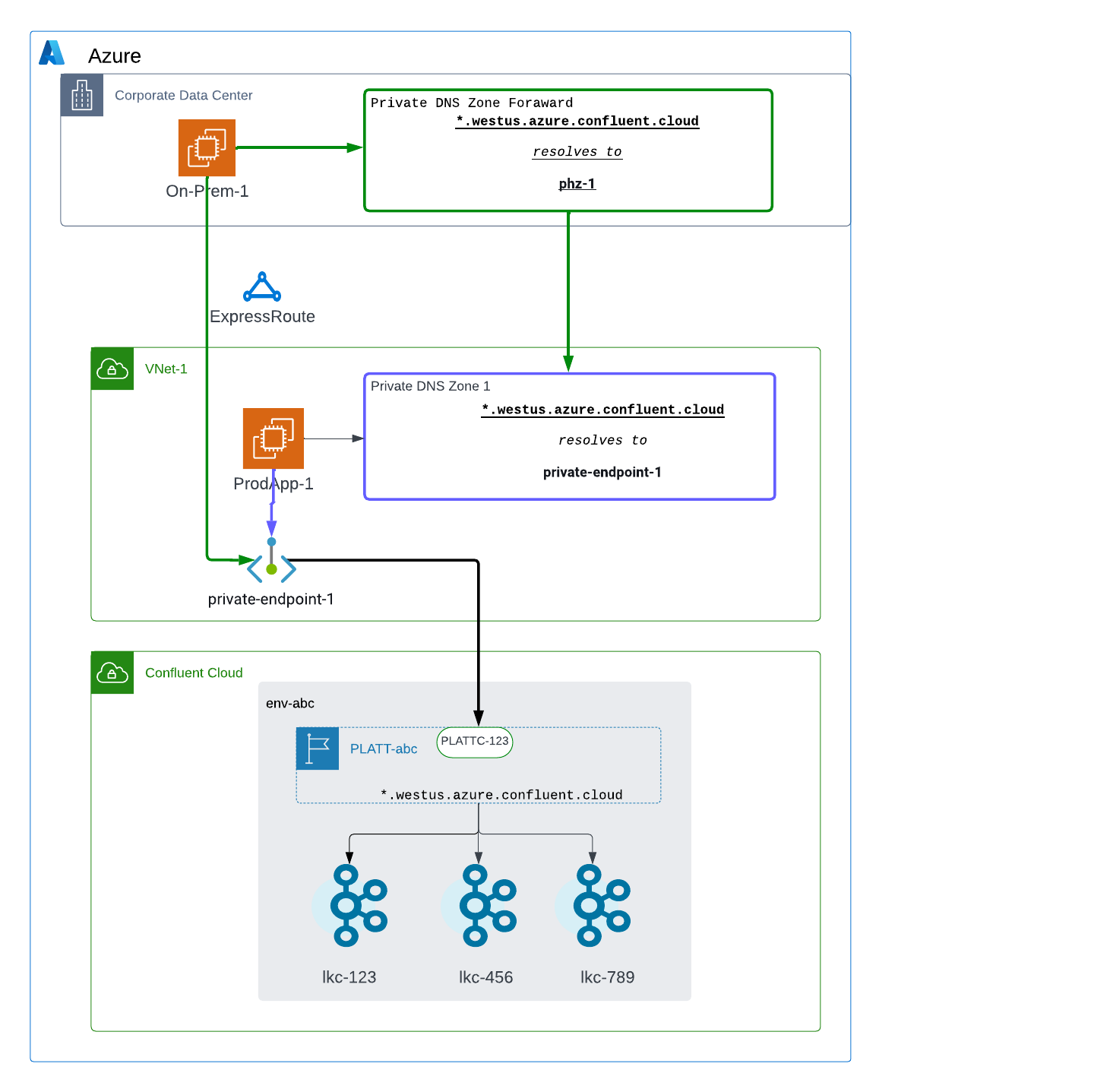
The following resources are configured:
PLATT-abcas a Private Link Attachment for accessing Kafka clusters in the env-abc environmentPLATTC-123as a Private Link Attachment Connection for theprivate-endpoint-1endpoint inVNet-1On-Prem-1as a Kafka client bootstrapped withlkc-123.westus.azure.private.confluent.cloudProdApp-1as a Kafka client bootstrapped withlkc-123.westus.azure.private.confluent.cloudPrivate DNS Zone Forwardas a DNS forwarding rule with the regional wildcard*.westus.azure.private.confluent.cloudPrivate DNS Zone 1with the regional wildcard*.westus.azure.private.confluent.cloud
The following steps are performed:
On-Prem-1attempts to accesslkc-123in the env-abc environment. A DNS query forlkc-123.westus.azure.private.confluent.cloudforwards toPrivate DNS Zone 1and returnsprivate-endpoint-1.On-Prem-1sends traffic toprivate-endpoint-1over Azure ExpressRoute.private-endpoint-1forwards traffic toPLATT-abcandlkc-123can be accessed sincePLATTC-123is associated withprivate-endpoint-1.