ServiceNow Source [Legacy] Connector for Confluent Cloud
Legacy to V2 migration
Confluent recommends upgrading to ServiceNow Source V2 to take advantage of the latest features. For more information, see Migration from V1 to V2.
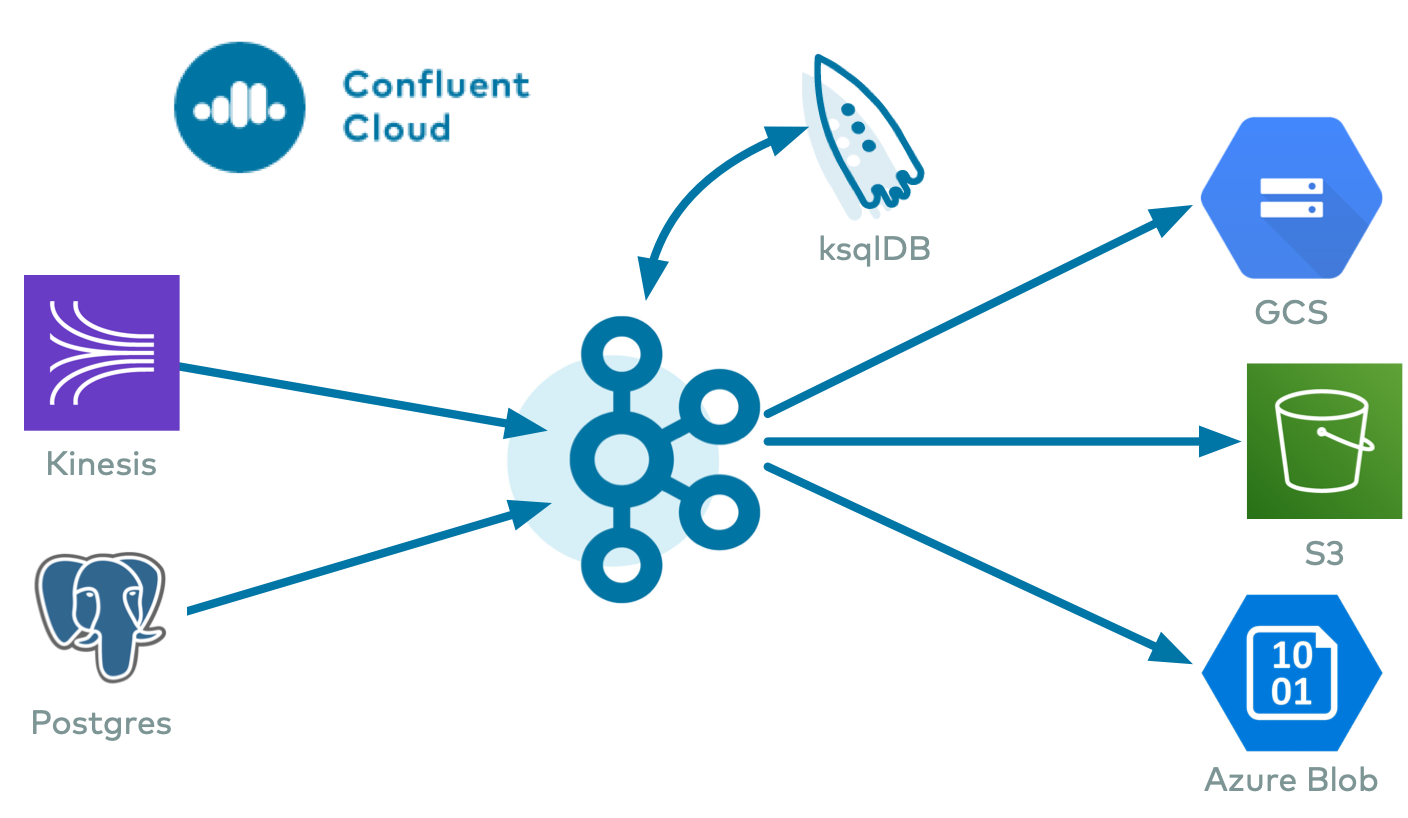
The fully-managed ServiceNow Source connector for Confluent Cloud is used to poll for additions and changes made in a ServiceNow table (see the ServiceNow documentation) and get these changes into Apache Kafka® in real time. The connector consumes data from a ServiceNow table to add and update records in a Kafka topic.
This Quick Start is for the fully-managed Confluent Cloud connector. If you are installing the connector locally for Confluent Platform, see ServiceNow Source Connector for Confluent Platform.
If you require private networking for fully-managed connectors, make sure to set up the proper networking beforehand. For more information, see Manage Networking for Confluent Cloud Connectors.
Features
The ServiceNow Source connector provides the following features:
Topics created automatically: The connector can automatically create Kafka topics.
At least once delivery: The connector guarantees that records are delivered at least once to the Kafka topic.
Automatic retries: When network failures occur, the connector automatically retries the request. The property
retry.max.timescontrols how many times retries are attempted. An exponential backoff is added to each retry interval.Elasticity: The connector allows you to configure two parameters that enforce the throughput limit:
batch.max.rowsandpoll.interval.s. The connector defaults to10000records and a30second polling interval. If a large number of updates occur within the given interval, the connector will paginate records according to configurable batch size. Note that since ServiceNow provides precision to one second, the ServiceNow Connector provides one second as the lowestpoll.interval.sconfiguration property setting.Supports one task: The connector supports running one task only. That is, one table is handled by one task.
Client-side encryption (CSFLE and CSPE) support: The connector supports CSFLE and CSPE for sensitive data. For more information about CSFLE or CSPE setup, see the connector configuration.
Supported data formats: The connector supports Avro, JSON Schema (JSON-SR), Protobuf, and JSON (schemaless) output formats. Schema Registry must be enabled to use a Schema Registry-based format (for example, Avro, JSON Schema, or Protobuf). See Schema Registry Enabled Environments for additional information.
Offset management capabilities: Supports offset management. For more information, see Manage custom offsets.
For more information and examples to use with the Confluent Cloud API for Connect, see the Confluent Cloud API for Connect Usage Examples section.
Limitations
Be sure to review the following information.
For connector limitations, see ServiceNow Source Connector limitations.
If you plan to use one or more Single Message Transforms (SMTs), see SMT Limitations.
If you plan to use Confluent Cloud Schema Registry, see Schema Registry Enabled Environments.
Manage custom offsets
You can manage the offsets for this connector. Offsets provide information on the point in the system from which the connector is accessing data. For more information, see Manage Offsets for Fully-Managed Connectors in Confluent Cloud.
To manage offsets:
Manage offsets using Confluent Cloud APIs. For more information, see Confluent Cloud API reference.
To get the current offset, make a GET request that specifies the environment, Kafka cluster, and connector name.
GET /connect/v1/environments/{environment_id}/clusters/{kafka_cluster_id}/connectors/{connector_name}/offsets
Host: https://api.confluent.cloud
Response:
Successful calls return HTTP 200 with a JSON payload that describes the offset.
{
"id": "lcc-example123",
"name": "{connector_name}",
"offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"tablename": "u_tvshows"
},
"offset": {
"offset": 108,
"schema": "eyJzY2hlbWEiOnsidHlwZSI6InN0cnVjdCIsImZpZWxkcyI6W3sidHlwZ_TRUNCATED",
"time": 1713344828000,
"url": "sys_updated_on>=2024-04-17 09:06:05"
}
}
],
"metadata": {
"observed_at": "2024-03-28T17:57:48.139635200Z"
}
}
Responses include the following information:
The position of latest offset.
The observed time of the offset in the metadata portion of the payload. The
observed_attime indicates a snapshot in time for when the API retrieved the offset. A running connector is always updating its offsets. Useobserved_atto get a sense for the gap between real time and the time at which the request was made. By default, offsets are observed every minute. CallingGETrepeatedly will fetch more recently observed offsets.Information about the connector.
To update the offset, make a POST request that specifies the environment, Kafka cluster, and connector name. Include a JSON payload that specifies new offset and a patch type.
POST /connect/v1/environments/{environment_id}/clusters/{kafka_cluster_id}/connectors/{connector_name}/offsets/request
Host: https://api.confluent.cloud
{
"type": "PATCH",
"offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"tablename": "u_tvshows"
},
"offset": {
"offset": 108,
"schema": "eyJzY2hlbWEiOnsidHlwZSI6InN0cnVjdCIsImZpZWxkcyI6W3sidHlwZ_TRUNCATED",
"time": 1713344828000,
"url": "sys_updated_on>=2024-04-17 09:06:05"
}
}
]
}
Considerations:
You can only make one offset change at a time for a given connector.
This is an asynchronous request. To check the status of this request, you must use the check offset status API. For more information, see Get the status of an offset request.
For source connectors, the connector attempts to read from the position defined by the requested offsets.
Response:
Successful calls return HTTP 202 Accepted with a JSON payload that describes the offset.
{
"id": "lcc-example123",
"name": "{connector_name}",
"offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"tablename": "u_tvshows"
},
"offset": {
"offset": 108,
"schema": "eyJzY2hlbWEiOnsidHlwZSI6InN0cnVjdCIsImZpZWxkcyI6W3sidHlwZS_TRUNCATED",
"time": 1713344828000,
"url": "sys_updated_on>=2024-04-17 09:06:05"
}
}
]
"requested_at": "2024-03-28T17:58:45.606796307Z",
"type": "PATCH"
}
Responses include the following information:
The requested position of the offsets in the source.
The time of the request to update the offset.
Information about the connector.
To delete the offset, make a POST request that specifies the environment, Kafka cluster, and connector name. Include a JSON payload that specifies the delete type.
POST /connect/v1/environments/{environment_id}/clusters/{kafka_cluster_id}/connectors/{connector_name}/offsets/request
Host: https://api.confluent.cloud
{
"type": "DELETE"
}
Considerations:
Delete requests delete the offset for the provided partition and reset to the base state. A delete request is as if you created a fresh new connector.
This is an asynchronous request. To check the status of this request, you must use the check offset status API. For more information, see Get the status of an offset request.
Do not issue delete and patch requests at the same time.
For source connectors, the connector attempts to read from the position defined in the base state.
Response:
Successful calls return HTTP 202 Accepted with a JSON payload that describes the result.
{
"id": "lcc-example123",
"name": "{connector_name}",
"offsets": [],
"requested_at": "2024-03-28T17:59:45.606796307Z",
"type": "DELETE"
}
Responses include the following information:
Empty offsets.
The time of the request to delete the offset.
Information about Kafka cluster and connector.
The type of request.
To get the status of a previous offset request, make a GET request that specifies the environment, Kafka cluster, and connector name.
GET /connect/v1/environments/{environment_id}/clusters/{kafka_cluster_id}/connectors/{connector_name}/offsets/request/status
Host: https://api.confluent.cloud
Considerations:
The status endpoint always shows the status of the most recent PATCH/DELETE operation.
Response:
Successful calls return HTTP 200 with a JSON payload that describes the result. The following is an example of an applied patch.
{
"request": {
"id": "lcc-example123",
"name": "{connector_name}",
"offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"tablename": "u_tvshows"
},
"offset": {
"offset": 108,
"schema": "eyJzY2hlbWEiOnsidHlwZSI6InN0cnVjdCIsImZpZWxkcyI6W3sidHlwZ_TRUNCATED",
"time": 1713344828000,
"url": "sys_updated_on>=2024-04-17 09:06:05"
}
}
],
"requested_at": "2024-03-28T17:58:45.606796307Z",
"type": "PATCH"
},
"status": {
"phase": "APPLIED",
"message": "The Connect framework-managed offsets for this connector have been altered successfully. However, if this connector manages offsets externally, they will need to be manually altered in the system that the connector uses."
},
"previous_offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"tablename": "u_tvshows"
},
"offset": {
"offset": 2,
"schema": "eyJzY2hlbWEiOnsidHlwZSI6InN0cnVjdCIsImZpZWxkcyI6W3sidHlwZSI6_TRUNCATED",
"time": 1713346385000,
"url": "sys_updated_on>=2024-04-17 09:33:04"
}
}
],
"applied_at": "2024-03-28T17:58:48.079141883Z"
}
Responses include the following information:
The original request, including the time it was made.
The status of the request: applied, pending, or failed.
The time you issued the status request.
The previous offsets. These are the offsets that the connector last updated prior to updating the offsets. Use these to try to restore the state of your connector if a patch update causes your connector to fail or to return a connector to its previous state after rolling back.
JSON payload
The table below offers a description of the unique fields in the JSON payload for managing offsets of the ServiceNow Source connector.
Field | Definition | Required/Optional |
|---|---|---|
| The name of the ServiceNow table. | Required |
| Timestamp is used as the offset for all records. | Required |
|
| Optional |
| Base64 encoded schema of the last record polled. | Required |
| In paginated queries, If the query is not paginated, | Optional |
Quick Start
Use this quick start to get up and running with the Confluent Cloud ServiceNow Source connector. The quick start provides the basics of selecting the connector and configuring it to stream events.
- Prerequisites
Authorized access to a Confluent Cloud cluster on Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure (Azure), or Google Cloud.
The Confluent CLI installed and configured for the cluster. See Install the Confluent CLI.
Schema Registry must be enabled to use a Schema Registry-based format (for example, Avro, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or Protobuf). See Schema Registry Enabled Environments for additional information.
You must have the ServiceNow instance URL, table name, and connector authentication details. For details, see the ServiceNow docs.
Using the Confluent Cloud Console
Step 1: Launch your Confluent Cloud cluster
To create and launch a Kafka cluster in Confluent Cloud, see Create a kafka cluster in Confluent Cloud.
Step 2: Add a connector
In the left navigation menu, click Connectors. If you already have connectors in your cluster, click + Add connector.
Step 3: Select your connector
Click the ServiceNow Source connector card.
Step 4: Enter the connector details
Note
Make sure you have all your prerequisites completed.
An asterisk ( * ) designates a required entry.
At the Add ServiceNow Source Connector screen, complete the following:
Select the topic you want to send data to from the Topics list. To create a new topic, click +Add new topic.
Select the way you want to provide Kafka Cluster credentials. You can choose one of the following options:
My account: This setting allows your connector to globally access everything that you have access to. With a user account, the connector uses an API key and secret to access the Kafka cluster. This option is not recommended for production.
Service account: This setting limits the access for your connector by using a service account. This option is recommended for production.
Use an existing API key: This setting allows you to specify an API key and a secret pair. You can use an existing pair or create a new one. This method is not recommended for production environments.
Note
Freight clusters support only service accounts for Kafka authentication.
Click Continue.
Configure the authentication properties:
ServiceNow Instance URL: The ServiceNow instance URL. For example:
https://<instancename>.service-now.com/.ServiceNow table name: The ServiceNow table name or database view name.
ServiceNow Username: The ServiceNow basic authentication username.
ServiceNow Password: The ServiceNow basic authentication password.
Click Continue.
Output messages
Select output record value format: Select the output record value format (data going to the Kafka topic). Valid values are AVRO, JSON, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or PROTOBUF. Schema Registry must be enabled to use a Schema Registry-based format (for example, Avro, JSON Schema, or Protobuf). For more information, see Schema Registry Enabled Environments.
Data encryption
Enable Client-Side Field Level Encryption for data encryption. Specify a Service Account to access the Schema Registry and associated encryption rules or keys with that schema. For more information on CSFLE or CSPE setup, see Manage encryption for connectors.
Show advanced configurations
Schema context: Select a schema context to use for this connector, if using a schema-based data format. This property defaults to the Default context, which configures the connector to use the default schema set up for Schema Registry in your Confluent Cloud environment. A schema context allows you to use separate schemas (like schema sub-registries) tied to topics in different Kafka clusters that share the same Schema Registry environment. For example, if you select a non-default context, a Source connector uses only that schema context to register a schema and a Sink connector uses only that schema context to read from. For more information about setting up a schema context, see What are schema contexts and when should you use them?.
HTTP request timeout (ms): The HTTP request timeout in milliseconds.
Maximum number of times to retry request: The maximum number of times to retry the request.
Poll interval (s): The frequency in seconds to poll for new data in each table. The minimum poll interval is 1 second and the maximum poll interval is 60 seconds.
Max rows per batch: The maximum number of rows to include in a single batch when polling for new data. This setting can be used to limit the amount of data buffered internally in the connector.
Starting time in UTC (yyyy-MM-dd): The time to start fetching all updates/creation. Default uses the time the connector launched. Note that the time is in UTC and has the required format: yyyy-MM-dd.
ServiceNow Database View Variable Prefix: The prefix to use for Service Now Database Views for timestamp and ID columns. The prefix is prepended to the columns
sys_updated_onandsys_id(for example, {servicenow.view.variable.prefix}_sys_updated_on and {servicenow.view.variable.prefix}_sys_id) to support sourcing data from views with a prefix on these columns.
Additional Configs
Value Converter Decimal Format: Specify the JSON/JSON_SR serialization format for Connect DECIMAL logical type values with two allowed literals: BASE64 to serialize DECIMAL logical types as base64 encoded binary data and NUMERIC to serialize Connect DECIMAL logical type values in JSON/JSON_SR as a number representing the decimal value.
Value Converter Replace Null With Default: Whether to replace fields that have a default value and that are null to the default value. When set to true, the default value is used, otherwise null is used. Applicable for JSON Converter.
Key Converter Schema ID Serializer: The class name of the schema ID serializer for keys. This is used to serialize schema IDs in the message headers.
Value Converter Reference Subject Name Strategy: Set the subject reference name strategy for value. Valid entries are DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy or QualifiedReferenceSubjectNameStrategy. Note that the subject reference name strategy can be selected only for PROTOBUF format with the default strategy being DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy.
Value Converter Schemas Enable: Include schemas within each of the serialized values. Input messages must contain schema and payload fields and may not contain additional fields. For plain JSON data, set this to false. Applicable for JSON Converter.
Errors Tolerance: Use this property if you would like to configure the connector’s error handling behavior. WARNING: This property should be used with CAUTION for SOURCE CONNECTORS as it may lead to dataloss. If you set this property to ‘all’, the connector will not fail on errant records, but will instead log them (and send to DLQ for Sink Connectors) and continue processing. If you set this property to ‘none’, the connector task will fail on errant records.
Value Converter Connect Meta Data: Allow the Connect converter to add its metadata to the output schema. Applicable for Avro Converters.
Value Converter Value Subject Name Strategy: Determines how to construct the subject name under which the value schema is registered with Schema Registry.
Key Converter Key Subject Name Strategy: How to construct the subject name for key schema registration.
Value Converter Ignore Default For Nullables: When set to true, this property ensures that the corresponding record in Kafka is NULL, instead of showing the default column value. Applicable for AVRO,PROTOBUF and JSON_SR Converters.
Value Converter Schema ID Serializer: The class name of the schema ID serializer for values. This is used to serialize schema IDs in the message headers.
Auto-restart policy
Enable Connector Auto-restart: Control the auto-restart behavior of the connector and its task in the event of user-actionable errors. Defaults to
true, enabling the connector to automatically restart in case of user-actionable errors. Set this property tofalseto disable auto-restart for failed connectors. In such cases, you would need to manually restart the connector.
Transforms
Single Message Transforms: To add a new SMT, see Add transforms. For more information about unsupported SMTs, see Unsupported transformations.
Processing position
Set offsets: Click Set offsets to define a specific offset for this connector to begin procession data from. For more information on managing offsets, see Manage offsets.
For all property values and definitions, see Configuration Properties .
Click Continue.
Based on the number of topic partitions you select, you will be provided with a recommended number of tasks.
To change the number of tasks, use the Range Slider to select the desired number of tasks.
Click Continue.
Step 5: Check for records
Verify that records are being produced at the Kafka topic.
For more information and examples to use with the Confluent Cloud API for Connect, see the Confluent Cloud API for Connect Usage Examples section.
Using the Confluent CLI
Complete the following steps to set up and run the connector using the Confluent CLI.
Note
Make sure you have all your prerequisites completed.
Step 1: List the available connectors
Enter the following command to list available connectors:
confluent connect plugin list
Step 2: List the connector configuration properties
Enter the following command to show the connector configuration properties:
confluent connect plugin describe <connector-plugin-name>
The command output shows the required and optional configuration properties.
Step 3: Create the connector configuration file
Create a JSON file that contains the connector configuration properties. The following example shows the required connector properties.
{
"connector.class": "ServiceNowSource",
"name": "ServiceNowSource_0",
"kafka.auth.mode": "KAFKA_API_KEY",
"kafka.api.key": "****************",
"kafka.api.secret": "************************************************",
"kafka.topic": "<topic-name>",
"output.data.format": "AVRO",
"servicenow.url": "<instance-URL>",
"servicenow.table": "<table-name>",
"servicenow.user": "<username>",
"servicenow.password": "<password>",
"tasks.max": "1",
}
Note the following property definitions:
"connector.class": Identifies the connector plugin name."name": Sets a name for your new connector.
"kafka.auth.mode": Identifies the connector authentication mode you want to use. There are two options:SERVICE_ACCOUNTorKAFKA_API_KEY(the default). To use an API key and secret, specify the configuration propertieskafka.api.keyandkafka.api.secret, as shown in the example configuration (above). To use a service account, specify the Resource ID in the propertykafka.service.account.id=<service-account-resource-ID>. To list the available service account resource IDs, use the following command:confluent iam service-account list
For example:
confluent iam service-account list Id | Resource ID | Name | Description +---------+-------------+-------------------+------------------- 123456 | sa-l1r23m | sa-1 | Service account 1 789101 | sa-l4d56p | sa-2 | Service account 2
"kafka.topic": Enter the topic name where data is sent.“
output.data.format": Enter an output data format (data going to the Kafka topic): AVRO, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), PROTOBUF, or JSON (schemaless). Schema Registry must be enabled to use a Schema Registry-based format (for example, Avro, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or Protobuf). See Schema Registry Enabled Environments for additional information."servicenow.<>": Enter the instance URL, table name (or database view name), and connector authentication details. For additional information, see the ServiceNow docs. An instance URL looks like this:https://<instancename>.service-now.com/."tasks.max": Enter the number of tasks to use with the connector. The connector supports running one task only. That is, one table is handled by one task.
Note
To enable CSFLE or CSPE for data encryption, specify the following properties:
csfle.enabled: Flag to indicate whether the connector honors CSFLE or CSPE rules.sr.service.account.id: A Service Account to access the Schema Registry and associated encryption rules or keys with that schema.
For more information on CSFLE or CSPE setup, see Manage encryption for connectors.
Single Message Transforms: See the Single Message Transforms (SMT) documentation for details about adding SMTs using the CLI.
See Configuration Properties for all property values and descriptions.
Step 4: Load the properties file and create the connector
Enter the following command to load the configuration and start the connector:
confluent connect cluster create --config-file <file-name>.json
For example:
confluent connect cluster create --config-file servicenow-source-config.json
Example output:
Created connector ServiceNowSource_0 lcc-do6vzd
Step 5: Check the connector status
Enter the following command to check the connector status:
confluent connect cluster list
Example output:
ID | Name | Status | Type | Trace
+------------+-------------------------------+---------+--------+-------+
lcc-do6vzd | ServiceNowSource_0 | RUNNING | source | |
Step 6: Check for records.
Verify that records are being produced at the Kafka topic.
For more information and examples to use with the Confluent Cloud API for Connect, see the Confluent Cloud API for Connect Usage Examples section.
Configuration Properties
Use the following configuration properties with the fully-managed connector. For self-managed connector property definitions and other details, see the connector docs in Self-managed connectors for Confluent Platform.
How should we connect to your data?
nameSets a name for your connector.
Type: string
Valid Values: A string at most 64 characters long
Importance: high
Kafka Cluster credentials
kafka.auth.modeKafka Authentication mode. It can be one of KAFKA_API_KEY or SERVICE_ACCOUNT. It defaults to KAFKA_API_KEY mode, whenever possible.
Type: string
Valid Values: SERVICE_ACCOUNT, KAFKA_API_KEY
Importance: high
kafka.api.keyKafka API Key. Required when kafka.auth.mode==KAFKA_API_KEY.
Type: password
Importance: high
kafka.service.account.idThe Service Account that will be used to generate the API keys to communicate with Kafka Cluster.
Type: string
Importance: high
kafka.api.secretSecret associated with Kafka API key. Required when kafka.auth.mode==KAFKA_API_KEY.
Type: password
Importance: high
Which topic do you want to send data to?
kafka.topicIdentifies the topic name to write the data to.
Type: string
Importance: high
Schema Config
schema.context.nameAdd a schema context name. A schema context represents an independent scope in Schema Registry. It is a separate sub-schema tied to topics in different Kafka clusters that share the same Schema Registry instance. If not used, the connector uses the default schema configured for Schema Registry in your Confluent Cloud environment.
Type: string
Default: default
Importance: medium
Output messages
output.data.formatSets the output Kafka record value format. Valid entries are AVRO, JSON_SR, PROTOBUF, or JSON. Note that you need to have Confluent Cloud Schema Registry configured if using a schema-based message format like AVRO, JSON_SR, and PROTOBUF
Type: string
Default: JSON
Importance: high
ServiceNow details
servicenow.urlServiceNow Instance URL.
Type: string
Importance: high
servicenow.tableServiceNow table name.
Type: string
Importance: high
servicenow.userServiceNow basic authentication username.
Type: string
Importance: high
servicenow.passwordServiceNow basic authentication password.
Type: password
Importance: high
connection.timeout.msHTTP request timeout in milliseconds.
Type: int
Default: 50000 (50 seconds)
Importance: low
retry.max.timesMaximum number of times to retry request.
Type: int
Default: 3
Importance: low
poll.interval.sFrequency in seconds to poll for new data in each table. The minimum poll interval is 1 second and the maximum poll interval is 60 seconds.
Type: int
Default: 30
Importance: medium
ServiceNow query details
batch.max.rowsMaximum number of rows to include in a single batch when polling for new data. This setting can be used to limit the amount of data buffered internally in the connector.
Type: int
Default: 10000
Valid Values: [1,…,10000]
Importance: low
servicenow.sinceTime to start fetching all updates/creation. Default uses the time connector launched. Note that the time is in UTC and has required format: yyyy-MM-dd.
Type: string
Importance: medium
servicenow.view.variable.prefixPrefix to be used for Service Now Database Views for timestamp and id columns. The prefix will be pre-appended to the columns sys_updated_on and sys_id i.e. {servicenow.view.variable.prefix}_sys_updated_on and {servicenow.view.variable.prefix}_sys_id to support sourcing data from views with prefix on these columns.
Type: string
Importance: medium
Number of tasks for this connector
tasks.maxMaximum number of tasks for the connector.
Type: int
Valid Values: [1,…,1]
Importance: high
Additional Configs
value.converter.connect.meta.dataAllow the Connect converter to add its metadata to the output schema. Applicable for Avro Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
errors.toleranceUse this property if you would like to configure the connector’s error handling behavior. WARNING: This property should be used with CAUTION for SOURCE CONNECTORS as it may lead to dataloss. If you set this property to ‘all’, the connector will not fail on errant records, but will instead log them (and send to DLQ for Sink Connectors) and continue processing. If you set this property to ‘none’, the connector task will fail on errant records.
Type: string
Default: none
Importance: low
key.converter.key.schema.id.serializerThe class name of the schema ID serializer for keys. This is used to serialize schema IDs in the message headers.
Type: string
Default: io.confluent.kafka.serializers.schema.id.PrefixSchemaIdSerializer
Importance: low
key.converter.key.subject.name.strategyHow to construct the subject name for key schema registration.
Type: string
Default: TopicNameStrategy
Importance: low
value.converter.decimal.formatSpecify the JSON/JSON_SR serialization format for Connect DECIMAL logical type values with two allowed literals:
BASE64 to serialize DECIMAL logical types as base64 encoded binary data and
NUMERIC to serialize Connect DECIMAL logical type values in JSON/JSON_SR as a number representing the decimal value.
Type: string
Default: BASE64
Importance: low
value.converter.ignore.default.for.nullablesWhen set to true, this property ensures that the corresponding record in Kafka is NULL, instead of showing the default column value. Applicable for AVRO,PROTOBUF and JSON_SR Converters.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
value.converter.reference.subject.name.strategySet the subject reference name strategy for value. Valid entries are DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy or QualifiedReferenceSubjectNameStrategy. Note that the subject reference name strategy can be selected only for PROTOBUF format with the default strategy being DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy.
Type: string
Default: DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy
Importance: low
value.converter.replace.null.with.defaultWhether to replace fields that have a default value and that are null to the default value. When set to true, the default value is used, otherwise null is used. Applicable for JSON Converter.
Type: boolean
Default: true
Importance: low
value.converter.schemas.enableInclude schemas within each of the serialized values. Input messages must contain schema and payload fields and may not contain additional fields. For plain JSON data, set this to false. Applicable for JSON Converter.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
value.converter.value.schema.id.serializerThe class name of the schema ID serializer for values. This is used to serialize schema IDs in the message headers.
Type: string
Default: io.confluent.kafka.serializers.schema.id.PrefixSchemaIdSerializer
Importance: low
value.converter.value.subject.name.strategyDetermines how to construct the subject name under which the value schema is registered with Schema Registry.
Type: string
Default: TopicNameStrategy
Importance: low
Auto-restart policy
auto.restart.on.user.errorEnable connector to automatically restart on user-actionable errors.
Type: boolean
Default: true
Importance: medium
Next Steps
For an example that shows fully-managed Confluent Cloud connectors in action with Confluent Cloud for Apache Flink, see the Cloud ETL Demo. This example also shows how to use Confluent CLI to manage your resources in Confluent Cloud.