Egress Private Link Endpoint Setup: MongoDB Atlas on Azure for Confluent Cloud
This topic presents the steps for configuring the MongoDB Atlas Sink connector in Confluent Cloud with Azure Private Link and Egress Private Link Endpoint.
Prerequisites
The following is a list of prerequisites for configuring the MongoDB Altas connector with an Egress Private Link Endpoint:
In Confluent Cloud, one of the following cluster types was set up with the specified network resource:
A Dedicated cluster with a Confluent Cloud network
For the steps to create a Confluent Cloud network, see Create a Confluent Cloud network. The Connection type of the network needs to be “Private Link Access”.
A Enterprise cluster with a network gateway
For the steps to create a gateway, see Create a gateway for outbound connectivity in Confluent Cloud.
A Dedicated MongoDB Atlas database was created to sink data into and is running within the same region and cloud as the Confluent Cloud cluster.
A source topic was created to sink data into MongoDB Atlas.
Step 1. Create a MongoDB private endpoint
In MongoDB, create a private endpoint for your Dedicated MongoDB Atlas database:
Go to Network Access → Private Endpoint → Dedicated Cluster.
Click Add Private Endpoint.
Select the applicable cloud provider and region of your Dedicated MongoDB Atlas database.
Make a note of the Atlas Endpoint Service value which is required for creating a Confluent Cloud Egress Private Link Endpoint.
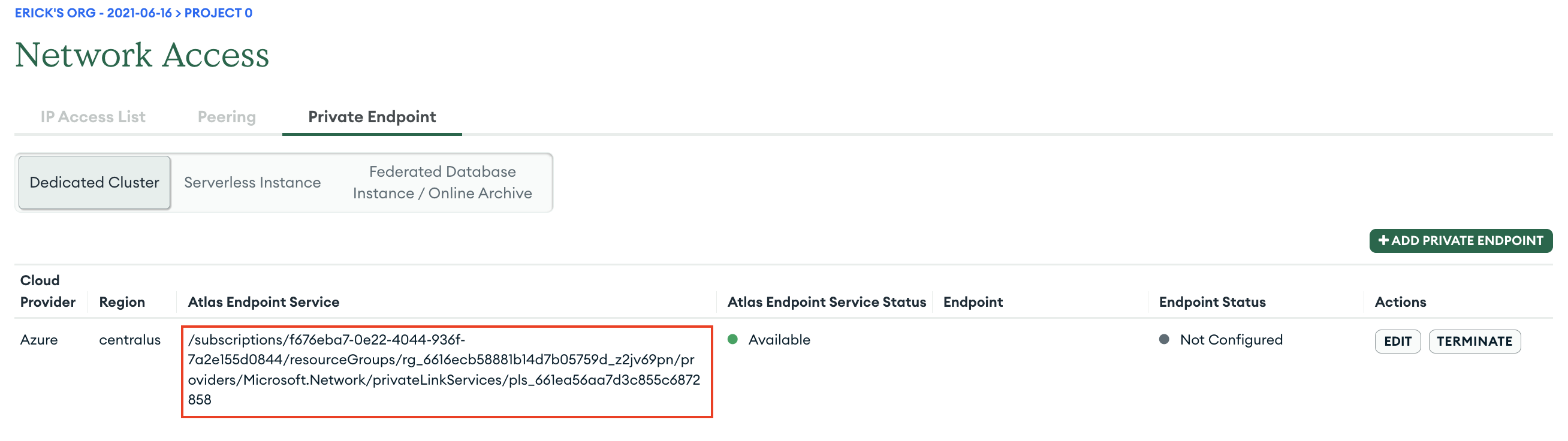
You can close the workflow for now. You will edit the rest of the configuration after you create a VPC endpoint ID in Confluent Cloud.
Step 2. Create an Egress Private Link Endpoint
Confluent Cloud Egress Private Link Endpoints are Azure Private Endpoints used to connect to Azure Private Link Services.
In the Network management page or tab of the desired Confluent Cloud environment, click the Confluent Cloud network you want to add the Private Link Endpoint to. The Connection Type of the network needs to be “Private Link Access”.
Click Create endpoint in the Egress connections tab.
Click the service you want to connect to, specifically, MongoDB.
Follow the guided steps to specify the field values, including:
Name: The name of the Private Link Endpoint.
Resource ID: The resource ID/Endpoint Service value of the Private Link service you retrieved in Step 1.
Note that the resource alias is not supported.
Sub-resource name: Leave blank.
Click Create to create the Private Link Endpoint.
If there are additional steps for the specific target service, follow the prompt to complete the tasks, and then click Finish.
Once the status of the Egress Private Link Endpoint changes from “Provisioning” to “Pending”, make a note of the Resource ID and IP Address values. The values are required to finish setting up a private endpoint for MongoDB Atlas.

In the Network management page or tab of the desired Confluent Cloud environment, click the For serverless products tab.
Click the gateway to which you want to add the Private Link Endpoint.
In the Access points tab, click Add access point.
Click the service you want to connect to, specifically, MongoDB.
Follow the guided steps to specify the field values, including:
Access point name: The name of the Private Link Endpoint.
Resource ID: The resource ID/Endpoint Service value of the Private Link service you retrieved in Step 1.
Note that the resource alias is not supported.
Sub-resource name: Leave blank.
Click Create access point to create the Private Link Endpoint.
If there are additional steps for the specific target service, follow the prompt to complete the tasks, and then click Finish.
Step 3. Configure the MongoDB private endpoint
In the MongoDB console, click Edit for the previously created MongoDB private endpoint.
Click Next.
Specify the Endpoint Resource ID and Private Endpoint IP Address associated with your Confluent Cloud Egress Private Link Endpoint. Click Create.
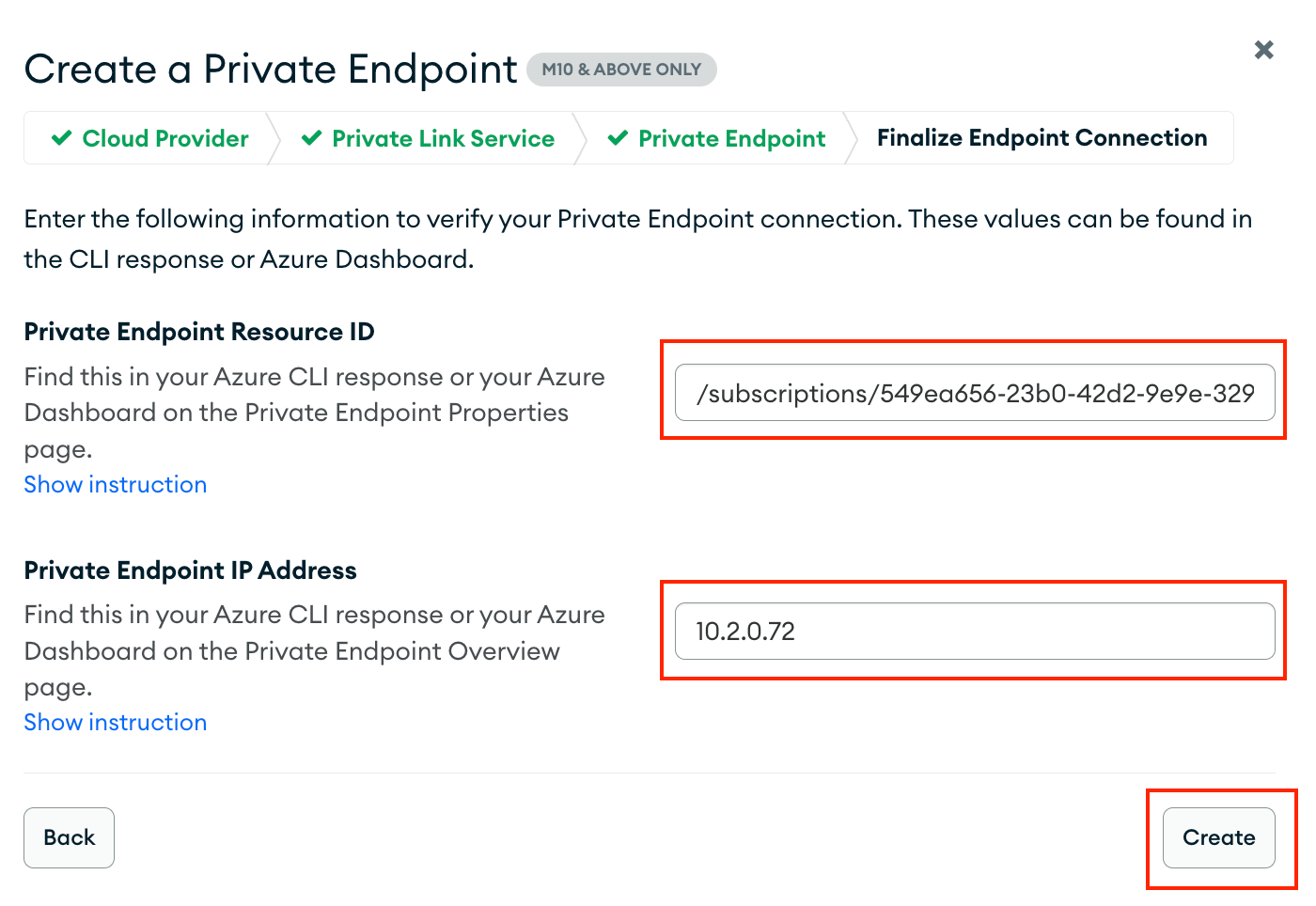
Once Endpoint Status changes to “Available”, you are ready to create the Confluent Cloud MongoDB Sink connector.
Step 4. Create the MongoDB Atlas Sink connector
Specify the authentication details for MongoDB.
In the MongoDB Atlas console, click Database under Deployment.
Click Connect for the associated database.
Select the Private Endpoint connection type, and select the endpoint you created in Step 3.
Click Choose a connection method.
Select Shell in the Access your data through tools section.
Get the endpoint as shown.
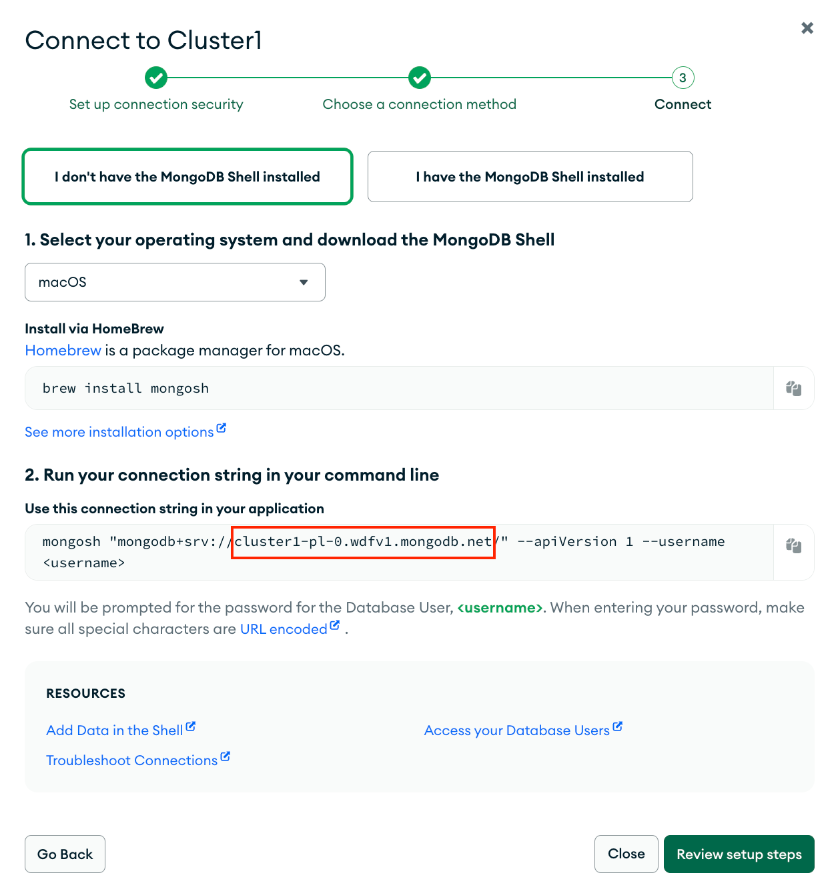
In Confluent Cloud, specify the MongoDB credentials during the connector creation steps.
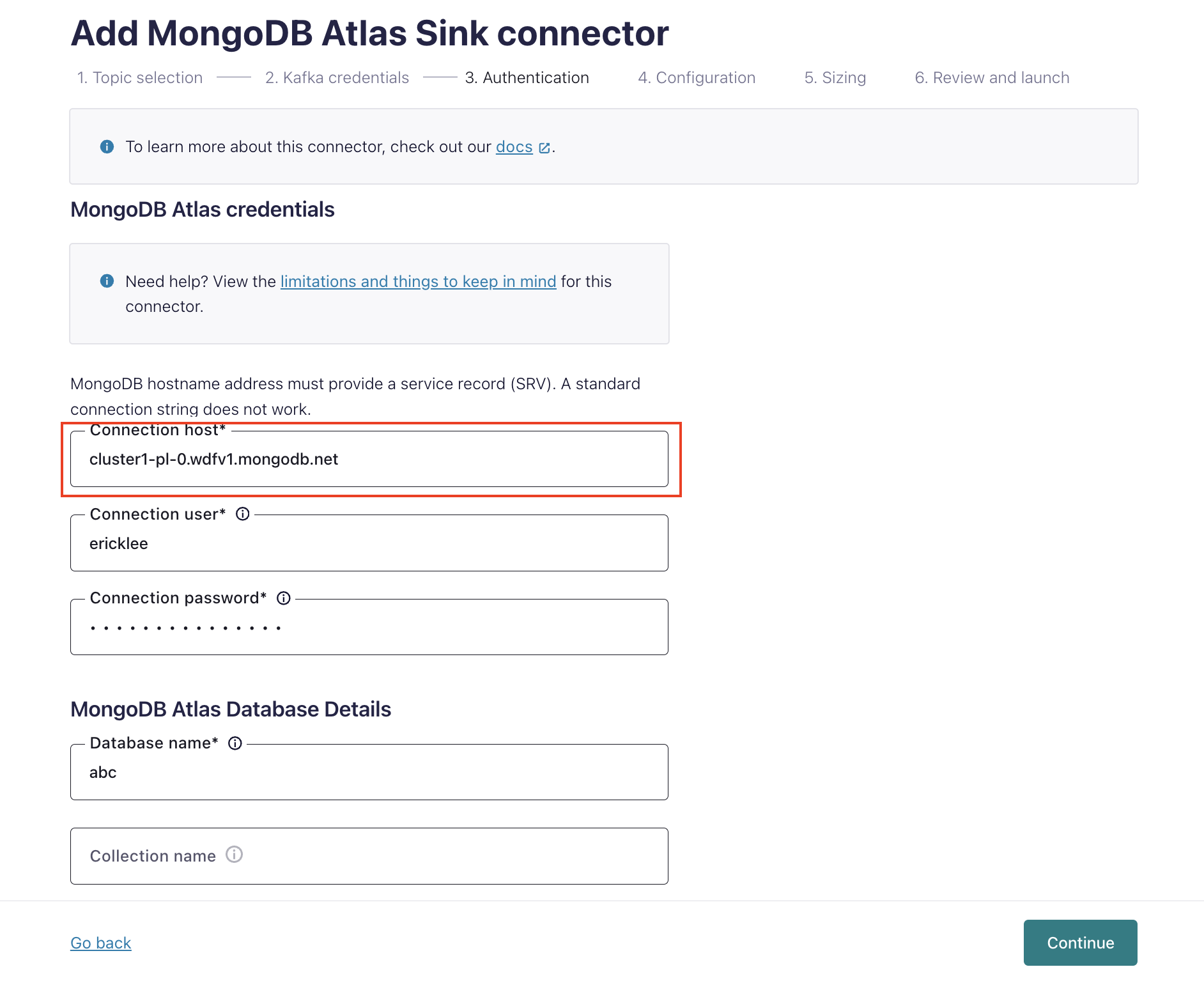
In the Connection host field, specify the endpoint you retrieved in the previous step.
Note
When you configure a private endpoint, ensure that the standard hostname matches the correct private link endpoint, for example “-pl-0” as shown in the screen below.
Follow the steps to create the source connector or the sink connector in Confluent Cloud.