Manage Networking for Confluent Cloud Connectors
This topic provides an overview of the networking features supported for fully managed connectors in Confluent Cloud.
The following diagram summarizes networking features supported for fully managed connectors. You can use it as the starting point when you determine the public or private networking for fully managed connectors.
For Confluent Cloud networking details, see the Cloud Networking docs.
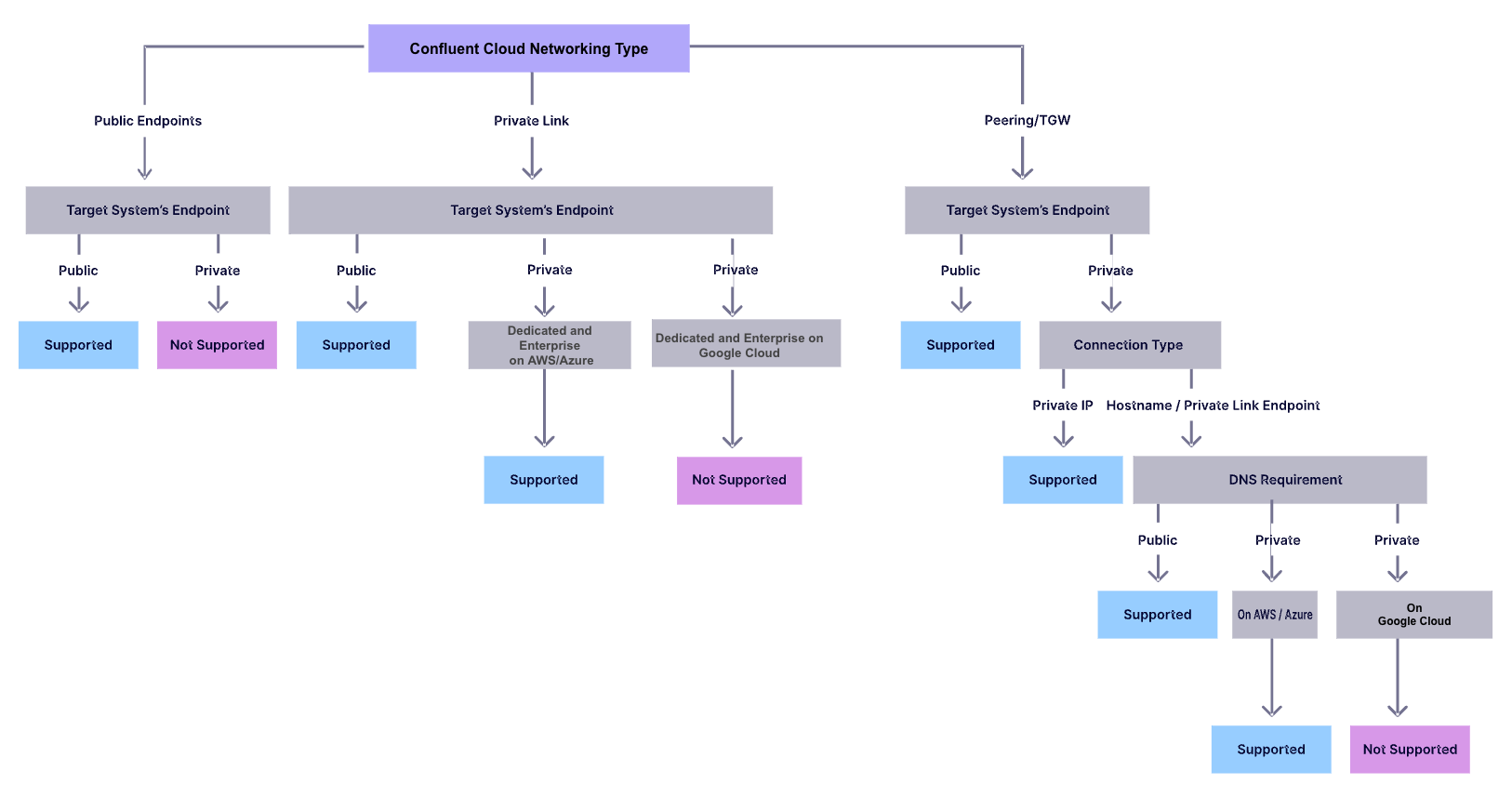
Target service networking supportability
The following table lists the networking supportability of the connectors with links to associated setup guides.
External Target Service | Confluent Cloud Private Link (AWS Dedicated & Enterprise) | Confluent Cloud Private Link (Azure Dedicated & Enterprise) | Confluent Cloud Private Link (Google Cloud Dedicated) | Confluent Cloud Peering / Transit Gateway | Confluent Cloud Public |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Self-managed services | Yes | Yes with DNS Forwarding: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud | Yes only if the endpoint is public | ||
AWS first-party services
| Yes only if the endpoint is public | Yes only if the endpoint is public | Yes | Yes only if the endpoint is public | |
RDS | Yes only if the endpoint is public | Yes only if the endpoint is public | Yes | Yes only if the endpoint is public | |
DocumentDB | Yes only if the endpoint is public | Yes only if the endpoint is public | Yes | Yes only if the endpoint is public | |
OpenSearch | If private connectivity is required, use OpenSearch Ingestion. | Yes only if the endpoint is public | Yes only if the endpoint is public | Yes | Yes only if the endpoint is public |
Azure first-party services
| Yes only if the endpoint is public | Yes only if the endpoint is public | Yes with Azure DNS Forwarding | Yes only if the endpoint is public | |
Google Cloud first-party services
| Yes only if the endpoint is public | Yes only if the endpoint is public | Yes only if the endpoint is public | Yes only if the endpoint is public | |
Snowflake | Yes | Yes only if the endpoint is public | |||
MongoDB Atlas | Yes | Yes only if the endpoint is public | |||
Neo4j | Yes only for self-managed Neo4j instances on Azure | Yes only for self-managed Neo4j instances on Google Cloud | Yes | Yes only if the endpoint is public | |
ElasticSearch | Yes | Yes only if the endpoint is public. Resource Alias is not currently supported by Confluent Cloud. | Yes | Yes | Yes only if the endpoint is public |
Salesforce | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes only if the endpoint is public |
Splunk | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes only if the endpoint is public |
Couchbase | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes only if the endpoint is public |
The following pages describe how to configure Egress Private Link Endpoints / Egress Private Service Connect Endpoints for connectors:
Egress IP address ranges
The following tabs provide network connectivity IP address details. Note that a Connect node runs in the same VPC/VNet as the cluster the Connect node was provisioned with. This is true for all cluster types (Basic, Standard, Enterprise, Dedicated, and Freight). For Confluent Cloud networking details, see the Cloud Networking docs.
Public egress IP addresses are available on all the major cloud platforms. For details, see Public Egress IP Addresses for Confluent Cloud Connectors.
Public egress IP addresses are not supported with Custom Connectors.
The following information applies to a fully managed Sink or Source connector connecting to an external system using a public IP address.
Cluster network type | Public IP address connectivity | IP range used by the connector |
|---|---|---|
Public Endpoint | Yes | A set of public egress IP addresses (see Public Egress IP Addresses for Confluent Cloud Connectors) |
VPC Peering and Transit Gateway | Yes | Dynamic public IP/CIDR range from the cloud provider region where the Confluent Cloud cluster is located |
Private Link | Yes | Dynamic public IP/CIDR range from the cloud provider region where the Confluent Cloud cluster is located |
The following information applies to a fully managed Sink or Source connector connecting to an external system using a private IP address.
Cluster network type | Private IP address connectivity | IP range used by the connector |
|---|---|---|
VPC Peering and Transit Gateway | Yes. DNS Forwarding is required when a private DNS is in use. | The source IP address used is from the /16 CIDR range configured by the customer for the Confluent Cloud cluster |
Private Link | AWS: Yes using Egress PrivateLink Endpoint on AWS [*] Azure: Yes using Egress Private Link Endpoint on Azure [*] GCP: Yes using Egress Private Link Endpoint on Google Cloud [*] | The IP address of the load balancer which hosts the private link service |
Public Endpoint | No | N/A |
[*] The price premium will be $0.03/task/hour for Egress Private Link Endpoints. For more information about Confluent Cloud connector pricing, see Confluent Pricinng.
See the following cloud provider documentation for additional information:
DNS zones
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the system used to translate URLs/Hostnames to IP addresses, for example, www.confluent.io to 54.177.145.149.
A public DNS server contains DNS records that can be resolved using the public internet. A private DNS server contains DNS records that can only be resolved in a private network, such as a VPC or an on-prem environment.
One way to check if a given hostname uses public DNS is running the dig command with a public DNS resolver:
dig [DNS-server] <hostname>
DNS-server can be any public DNS server, such as Google DNS server (8.8.8.8) and Cloudflare DNS server (1.1.1.1).
For example:
dig 8.8.8.8 www.confluent.io
Fully managed connectors in Confluent Cloud support the following types of DNS zones/servers for resolving and accessing required endpoints.
AWS | Azure | Google Cloud | |
|---|---|---|---|
Public DNS | Supported | Supported | Supported |
Private DNS | Supported with DNS Forwarding | Supported with DNS Forwarding | Supported with DNS Forwarding |
Troubleshoot networking issues for fully managed connectors
This page describes common networking-related errors you may encounter when creating connectors, and it provides checklists that can help you to troubleshoot the issues.
Issues with Peering or Transit Gateway
Errors trying to connect via FQDN (fully qualified domain name) with publicly resolvable DNS
If able to directly connect to the private IP address, there is an issue when resolving DNS.
If not able to connect to the private IP address:
Check the peering/Transit Gateway setup, routes, associated firewalls, security groups, and network access control lists.
Check ports and protocol settings.
Errors trying to connect via FQDN with DNS that is not publicly resolvable
Check if DNS forwarding is correctly set up with the right IP address for the DNS server and is forwarding the needed domain name. For details, see DNS Forwarding for AWS or DNS Forwarding for Azure.
Check your DNS setup, peering/Transit Gateway setup, routes, associated firewalls, security groups, and network access control lists.
Check ports and protocol settings.
Issues with Private Link
Errors related to a private endpoint when directly connecting to a private IP address
Ensure that the Egress PrivateLink Endpoint is correctly set up. For details, see Use AWS Egress PrivateLink Endpoints for Dedicated Clusters on Confluent Cloud.
Check the associated firewalls, security groups, and network access control lists.
Check ports and protocol settings.
Errors related to a private endpoint when directly connecting to an FQDN
If the FQDN is publicly resolvable:
Ensure that the Egress PrivateLink Endpoint is correctly set up. For details, see Use AWS Egress PrivateLink Endpoints for Dedicated Clusters on Confluent Cloud.
Check the associated firewalls, security groups, and network access control lists.
Check ports and protocol settings.
If the FQDN is not publicly resolvable:
Ensure that the DNS record is set up for the Egress PrivateLink Endpoint. For details, see Create a private DNS record in Confluent Cloud.
Check the associated firewalls, security groups, and network access control lists.
Check ports and protocol settings.