Get Started with the MongoDB Atlas Source Connector for Confluent Cloud
The fully-managed MongoDB Atlas Source connector for Confluent Cloud moves data from a MongoDB replica set into an Apache Kafka® cluster. The connector configures and consumes change stream event documents and publishes them to a Kafka topic.
Note
Sign up for a Confluent Cloud trial and get $400 of free credit.
If you require private networking for fully-managed connectors, make sure to set up the proper networking beforehand. For more information, see Manage Networking for Confluent Cloud Connectors.
Features
The MongoDB Atlas Source connector supports both MongoDB Atlas and self-managed MongoDB databases.
The connector offers the following features:
At least once delivery: The connector guarantees that records are delivered at least once to the Kafka topic.
Topics created automatically: The connector automatically creates Kafka topics using the naming convention:
<prefix>.<database-name>.<collection-name>. The topics are created with the properties:topic.creation.default.partitions=1andtopic.creation.default.replication.factor=3. You add the prefix when setting up the connection in the Quick Start steps. For more information, see Maximum message size. Note that if you want to create topics with specific settings, create the topics before running this connector.Database authentication: The connector supports both username/password-based and X.509 certificate-based authentication. For more information on MONGODB-X.509-based authentication setup, see connector authentication.
Output data formats: The connector supports Avro, Byte, JSON (schemaless), JSON Schema, Protobuf or String output data. Schema Registry must be enabled to use a Schema Registry-based format (for example, Avro, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or Protobuf). See Schema Registry Enabled Environments for additional information.
Large size records: The connector supports MongoDb documents up to 20 MB in size on Dedicated Kafka clusters and 8 MB on other clusters.
Select configuration properties:
poll.await.time.ms: The amount of time to wait before checking for new results in the change stream.poll.max.batch.size: The maximum number of change stream documents to include in a single batch when polling for new data. This setting can be used to limit the amount of data buffered internally in the connector.
Offset management capabilities: The connector supports offset management. For more information, see Manage custom offsets.
For more information and examples to use with the Confluent Cloud API for Connect, see the Confluent Cloud API for Connect Usage Examples section.
Limitations
Be sure to review the following information.
For connector limitations, see MongoDB Atlas Source Connector limitations.
If you plan to use one or more Single Message Transforms (SMTs), see SMT Limitations.
If you plan to use Confluent Cloud Schema Registry, see Schema Registry Enabled Environments.
Maximum message size
This connector creates topics automatically. When it creates topics, the internal connector configuration property max.message.bytes is set to the following:
Basic cluster:
8 MBStandard cluster:
8 MBEnterprise cluster:
8 MBDedicated cluster:
20 MB
For more information about Confluent Cloud clusters, see Kafka Cluster Types in Confluent Cloud.
Manage custom offsets
You can manage the offsets for this connector. Offsets provide information on the point in the system from which the connector is accessing data. For more information, see Manage Offsets for Fully-Managed Connectors in Confluent Cloud.
To manage offsets:
Manage offsets using Confluent Cloud APIs. For more information, see Confluent Cloud API reference.
To get the current offset, make a GET request that specifies the environment, Kafka cluster, and connector name.
GET /connect/v1/environments/{environment_id}/clusters/{kafka_cluster_id}/connectors/{connector_name}/offsets
Host: https://api.confluent.cloud
Response:
Successful calls return HTTP 200 with a JSON payload that describes the offset.
{
"id": "lcc-example123",
"name": "{connector_name}",
"offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"ns": "mongodb+srv://cluster0.2a5tnof.mongodb.net/"
},
"offset": {
"_id": "{\"_data\": \"82661F7DDE000000012B042C0100296E5A1004737030_TRUNCATED\"}"
}
}
],
"metadata": {
"observed_at": "2024-03-28T17:57:48.139635200Z"
}
}
Responses include the following information:
The position of latest offset.
The observed time of the offset in the metadata portion of the payload. The
observed_attime indicates a snapshot in time for when the API retrieved the offset. A running connector is always updating its offsets. Useobserved_atto get a sense for the gap between real time and the time at which the request was made. By default, offsets are observed every minute. CallingGETrepeatedly will fetch more recently observed offsets.Information about the connector.
To update the offset, make a POST request that specifies the environment, Kafka cluster, and connector name. Include a JSON payload that specifies new offset and a patch type.
POST /connect/v1/environments/{environment_id}/clusters/{kafka_cluster_id}/connectors/{connector_name}/offsets/request
Host: https://api.confluent.cloud
{
"type": "PATCH",
"offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"ns": "mongodb+srv://cluster0.2a5tnof.mongodb.net/"
},
"offset": {
"_id": "{\"_data\": \"82661F7DDE000000012B042C0100296E5A100473703049_TRUNCATED\"}"
}
}
]
}
Considerations:
You can only make one offset change at a time for a given connector.
This is an asynchronous request. To check the status of this request, you must use the check offset status API. For more information, see Get the status of an offset request.
For source connectors, the connector attempts to read from the position defined by the requested offsets.
Response:
Successful calls return HTTP 202 Accepted with a JSON payload that describes the offset.
{
"id": "lcc-example123",
"name": "{connector_name}",
"offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"ns": "mongodb+srv://cluster0.2a5tnof.mongodb.net/"
},
"offset": {
"_id": "{\"_data\": \"82661F7DDE000000012B042C0100296E5A1004737030_TRUNCATED\"}"
}
}
],
"requested_at": "2024-03-28T17:58:45.606796307Z",
"type": "PATCH"
}
Responses include the following information:
The requested position of the offsets in the source.
The time of the request to update the offset.
Information about the connector.
To delete the offset, make a POST request that specifies the environment, Kafka cluster, and connector name. Include a JSON payload that specifies the delete type.
POST /connect/v1/environments/{environment_id}/clusters/{kafka_cluster_id}/connectors/{connector_name}/offsets/request
Host: https://api.confluent.cloud
{
"type": "DELETE"
}
Considerations:
Delete requests delete the offset for the provided partition and reset to the base state. A delete request is as if you created a fresh new connector.
This is an asynchronous request. To check the status of this request, you must use the check offset status API. For more information, see Get the status of an offset request.
Do not issue delete and patch requests at the same time.
For source connectors, the connector attempts to read from the position defined in the base state.
Response:
Successful calls return HTTP 202 Accepted with a JSON payload that describes the result.
{
"id": "lcc-example123",
"name": "{connector_name}",
"offsets": [],
"requested_at": "2024-03-28T17:59:45.606796307Z",
"type": "DELETE"
}
Responses include the following information:
Empty offsets.
The time of the request to delete the offset.
Information about the Kafka cluster and connector.
The type of request.
To get the status of a previous offset request, make a GET request that specifies the environment, Kafka cluster, and connector name.
GET /connect/v1/environments/{environment_id}/clusters/{kafka_cluster_id}/connectors/{connector_name}/offsets/request/status
Host: https://api.confluent.cloud
Considerations:
The status endpoint always shows the status of the most recent PATCH/DELETE operation.
Response:
Successful calls return HTTP 200 with a JSON payload that describes the result. The following is an example of an applied patch.
{
"request": {
"id": "lcc-example123",
"name": "{connector_name}",
"offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"ns": "mongodb+srv://cluster0.2a5tnof.mongodb.net/"
},
"offset": {
"_id": "{\"_data\": \"82661F7DDE000000012B042C0100296E5A100473703_TRUNCATED\"}"
}
}
],
"requested_at": "2024-03-28T17:58:45.606796307Z",
"type": "PATCH"
},
"status": {
"phase": "APPLIED",
"message": "The Connect framework-managed offsets for this connector have been altered successfully. However, if this connector manages offsets externally, they will need to be manually altered in the system that the connector uses."
},
"previous_offsets": [
{
"partition": {
"ns": "mongodb+srv://cluster0.2a5tnof.mongodb.net/"
},
"offset": {
"_id": "{\"_data\": \"82661FF4CF000000042B042C0100296E5A100473703049_TRUNCATED\"}"
}
}
],
"applied_at": "2024-03-28T17:58:48.079141883Z"
}
Responses include the following information:
The original request, including the time it was made.
The status of the request: applied, pending, or failed.
The time you issued the status request.
The previous offsets. These are the offsets that the connector last updated prior to updating the offsets. Use these to try to restore the state of your connector if a patch update causes your connector to fail or to return a connector to its previous state after rolling back.
JSON payload
The table below offers a description of the unique fields in the JSON payload for managing offsets of the MongoDB Atlas Source connector.
Field | Definition | Required/Optional |
|---|---|---|
|
| Required |
|
| Required |
Quick Start
Use this quick start to get up and running with the Confluent Cloud MongoDB Atlas Source connector. The quick start provides the basics of selecting the connector and configuring it to consume data from MongoDB and persist the data to Kafka.
- Prerequisites
Authorized access to a Confluent Cloud cluster on Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure (Azure), or Google Cloud.
The Confluent CLI installed and configured for the cluster. See Install the Confluent CLI.
Schema Registry must be enabled to use a Schema Registry-based format (for example, Avro, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or Protobuf). See Schema Registry Enabled Environments for additional information.
Access to a MongoDB database. Note that the connection user must have privileged action “find” to query the MongoDB database. For more information, see Query and Write Actions.
The MongoDB hostname address must provide a service record (SRV) when connecting to MONGODB_ATLAS. For MONGODB_SELF_MANAGED, a standard connection string is required.
The connector automatically creates Kafka topics using the naming convention:
<prefix>.<database-name>.<collection-name>. The topics are created with the properties:topic.creation.default.partitions=1andtopic.creation.default.replication.factor=3. If you want to create topics with specific settings, create the topics before running this connector.Important
If you are configuring granular access using a service account, and you leave the optional Topic prefix (
prefix) configuration property empty, the connector uses the Database name (database-name) entered as the prefix. You must grant ACLCREATEandWRITEaccess to the database name prefix (see ACL access). If both theprefixanddatabase-nameconfiguration properties are not used, you must do one of the following:If you know the databases to capture, create individual ACLs for each topic. The topic name will have the database name as the prefix.
Create ACLs for all Kafka topics, using the (*) wildcard in the ACL entries as shown below:
confluent kafka acl create --allow --service-account "<service-account-id>" --operation create --topic "*" .. code-block:: bash confluent kafka acl create --allow --service-account "<service-account-id>" --operation write --topic "*"
Create create RBAC role bindings.
If you have a VPC-peered cluster in Confluent Cloud, consider configuring a PrivateLink Connection between MongoDB Atlas and the VPC. For additional networking considerations, see Networking and DNS. To use a set of public egress IP addresses, see Public Egress IP Addresses for Confluent Cloud Connectors.
Kafka cluster credentials. The following lists the different ways you can provide credentials.
Enter an existing service account resource ID.
Create a Confluent Cloud service account for the connector. Make sure to review the ACL entries required in the service account documentation. Some connectors have specific ACL requirements.
Create a Confluent Cloud API key and secret. To create a key and secret, you can use confluent api-key create or you can autogenerate the API key and secret directly in the Cloud Console when setting up the connector.
Using the Confluent Cloud Console
Step 1: Launch your Confluent Cloud cluster
To create and launch a Kafka cluster in Confluent Cloud, see Create a kafka cluster in Confluent Cloud.
Step 2: Add a connector
In the left navigation menu, click Connectors. If you already have connectors in your cluster, click + Add connector.
Step 3: Select your connector
Click the MongoDB Atlas Source connector card.
Step 4: Enter the connector details
Note
Make sure you have all your prerequisites completed.
An asterisk ( * ) designates a required entry.
You can specify connection string options in the connection host. For example:
cluster4-r5q3r7.gcp.mongodb.net/?readPreference=secondary&readConcernLevel=local. For more information about connection string options, see MongoDB Connection String Options.
Note
The connector does not support following connection string options in
connection.hostconfig:tlsCertificateKeyFile,tlsCertificateKeyFilePassword,tlsCAFile,tlsAllowInvalidCertificates,tlsInsecure,tlsAllowInvalidHostnames,authMechanism,authMechanismProperties,gssapiServiceName.Other options like
readPreference,readConcernLevel, orwdefined in MongoDB Connection String Options can be configured inconnection.hostconfiguration. For example,cluster4-r5q3r7.gcp.mongodb.net/?readPreference=secondary&readConcernLevel=local&appName=test&w=majority.- The connector supports connecting to self-managed MongoDB database.
Use
mongodb.instance.typeas MONGODB_SELF_MANAGED and specify theconnection.hostaccordingly to connect to self-managed instance. For example,54.190.171.123:27017/?authSource=admin.
At the MongoDB Atlas Source Connector screen, complete the following:
In the Topic prefix field, define a topic prefix your connector will use to publish to Kafka topics. The connector will Kafka topics using the following naming convention: <prefix>.<database-name>.<collection-name>. If you want to create topics with specific settings, create the topics before running this connector.
Important
If you are configuring granular access using a service account, and you leave the optional Topic prefix (prefix) configuration property empty, the connector uses the Database name (database-name) entered as the prefix. You must grant ACL CREATE and WRITE access to the database name prefix (see ACL access). If both the prefix and database-name configuration properties are not used, you must do one of the following:
If you know the databases to capture, create individual ACLs for each topic. The topic name will have the database name as the prefix.
Create ACLs for all Kafka topics, using the (*) wildcard in the ACL entries as shown below:
confluent kafka acl create --allow --service-account "<service-account-id>" --operation create --topic "*" .. code-block:: bash confluent kafka acl create --allow --service-account "<service-account-id>" --operation write --topic "*"
Create create RBAC role bindings.
Select the way you want to provide Kafka Cluster credentials. You can choose one of the following options:
My account: This setting allows your connector to globally access everything that you have access to. With a user account, the connector uses an API key and secret to access the Kafka cluster. This option is not recommended for production.
Service account: This setting limits the access for your connector by using a service account. This option is recommended for production.
Use an existing API key: This setting allows you to specify an API key and a secret pair. You can use an existing pair or create a new one. This method is not recommended for production environments.
Note
Freight clusters support only service accounts for Kafka authentication.
Click Continue.
Configure the authentication properties:
MongoDB instance type
MongoDB instance type: Specify the MongoDB deployment type. Use MONGODB_ATLAS for cloud hosted Atlas clusters or MONGODB_SELF_MANAGED for self hosted MongoDB instances.
MongoDB authentication mechanism
Authentication mechanism: Choose an authentication mechanism for MongoDB. Use SCRAM-SHA-256 for username/password authentication. Use MONGODB-X509 for certificate-based authentication. For MONGODB-X509, you must configure the SSL keystore properties.
MongoDB credentials
Connection host: The MongoDB host with connection string options. Use a hostname address and not a full URL. For example, use
cluster4-r5q3r7.gcp.mongodb.net/?readPreference=secondaryfor MONGODB_ATLAS and54.190.171.123:27017/?authSource=adminfor MONGODB_SELF_MANAGED.Note
You don’t need to manually add the connection string parameters
authMechanism=MONGODB-X509&authSource=$externalas part of the host. The connector automatically includes the parameter when you selectMONGODB-X.509as the authentication mechanism.Connection user: The MongoDB Atlas connection user.
Connection password: The MongoDB Atlas connection password. When entering the password, make sure that any special characters are URL encoded.
MongoDB Database Details
Database name: The MongoDB Atlas database name. If not set, all databases in the cluster are watched.
Collection name: Single MongoDB collection to watch. If not set, all collections databases in the cluster are watched.
SSL Configuration
SSL keystore file: Upload the SSL keystore file containing the server certificate and enter the SSL keystore password used to access the keystore.
SSL keystore password: Password used to access the keystore.
SSL truststore file: Upload the SSL truststore file containing a server CA certificate and enter the truststore SSL truststore password used to access the truststore.
SSL truststore password: Password used to access the truststore.
Click Continue.
Output Kafka record value format: Sets the output Kafka record value format. Valid entries are AVRO, JSON_SR, PROTOBUF, JSON, STRING or BSON. Note that you need to have Confluent Cloud Schema Registry configured if using a schema-based message format like AVRO, JSON_SR, and PROTOBUF.
Output Kafka record key format: Sets the output Kafka record key format. Valid entries are AVRO, JSON_SR, PROTOBUF, STRING or JSON. Note that you need to have Confluent Cloud Schema Registry configured if using a schema-based message format like AVRO, JSON_SR, and PROTOBUF.
Show advanced configurations
Schema context: Select a schema context to use for this connector, if using a schema-based data format. This property defaults to the Default context, which configures the connector to use the default schema set up for Schema Registry in your Confluent Cloud environment. A schema context allows you to use separate schemas (like schema sub-registries) tied to topics in different Kafka clusters that share the same Schema Registry environment. For example, if you select a non-default context, a Source connector uses only that schema context to register a schema and a Sink connector uses only that schema context to read from. For more information about setting up a schema context, see What are schema contexts and when should you use them?.
Publish full document only: Set whether to return only the
fullDocumentfield from the change stream event document produced by any update event. ThefullDocumentfield contains the most current version of the updated document. Sets thechange.stream.full.document=updateLookupsetting so updated documents will be included.Publish tombstone events on documents deletion: When set to
true, the connector returns the tombstone events when documents are deleted. Tombstone events contain the keys of deleted documents with null values. This setting applies only whenpublish.full.document.onlyistrue.Change stream full document: Determines what to return for update operations when using a Change Stream. The
defaultsetting returns the differences between the original document and the updated document. TheupdateLookupsetting returns the differences between the original document and updated document as well as a copy of the entire updated document at a point in time after the update. ThewhenAvailablesetting returns the updated document, if available. Therequiredsetting returns the updated document and raises an error if it is not available.Change stream full document before change: Configures the document pre-image your change stream returns on update operations. The
defaultsetting suppresses the document pre-image. When set towhenAvailablesetting returns the document pre-image if it’s available, before it was replaced, updated, or deleted. Therequiredsetting returns the document pre-image and raises an error if it is not available.Use the ``documentKey`` for the source record key: Use the document key as the source record key.
Show expanded events: Determines if change streams notifies for DDL events, such as
createIndexesanddropIndexesevents. This functionality is new in version 6.0. See MongoDB documentation for more details onshowExpandedEvents. This setting is required to showupdateDescription.disambiguatedPathsin update events, helping clarify changes that involve ambiguous fields. This specific feature is new in version 6.1. See MongoDB documentation for more details ondisambiguatedPaths.The collation options: The JSON representation of the collation options to use for the change stream. Use the
Collation.asDocument().toJson()to create the specific json representation.Output json formatter: The output format of json strings can be configured to be either: DefaultJson: The legacy strict json formatter. ExtendedJson: The fully type safe extended json formatter. SimplifiedJson: Simplified Json, with ObjectId, Decimals, Dates and Binary values represented as strings. Users can provide their own implementation of the com.mongodb.kafka.connect.source.json.formatter.
Topic separator: A separator to use when the connector joins prefix, database, collection, and suffix values. These joined values form the Kafka topic name where data is published. Defaults to
..Topic suffix: A suffix to append to database and collection names to generate the name of the Kafka topic the connector creates.
Output schema infer value: Whether the connector should infer the schema of the
SourceRecord. The connector processes each document in isolation and may generate many schemas. This setting only works with AVRO, JSON, JSON_SR, or PROTOBUF data formats.Topic namespace map: Add a JSON object that maps change stream document namespaces to topics. For additional information, see Topic Namespace Map. Multiple collections with records having varying schema are mapped to a single topic for AVRO, JSON_SR, or PROTOBUF data formats. These are registered to a single subject name. If the schemas are not backward compatible, the connector fails until you change the schema compatibility in Confluent Cloud Schema Registry.
Additional Configs
Value Converter Replace Null With Default: Whether to replace fields that have a default value and that are null to the default value. When set to true, the default value is used, otherwise null is used. Applicable for JSON Converter.
Value Converter Reference Subject Name Strategy: Set the subject reference name strategy for value. Valid entries are DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy or QualifiedReferenceSubjectNameStrategy. Note that the subject reference name strategy can be selected only for PROTOBUF format with the default strategy being DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy.
Value Converter Schemas Enable: Include schemas within each of the serialized values. Input messages must contain schema and payload fields and may not contain additional fields. For plain JSON data, set this to false. Applicable for JSON Converter.
Errors Tolerance: Use this property if you would like to configure the connector’s error handling behavior. WARNING: This property should be used with CAUTION for SOURCE CONNECTORS as it may lead to dataloss. If you set this property to ‘all’, the connector will not fail on errant records, but will instead log them (and send to DLQ for Sink Connectors) and continue processing. If you set this property to ‘none’, the connector task will fail on errant records.
Value Converter Ignore Default For Nullables: When set to true, this property ensures that the corresponding record in Kafka is NULL, instead of showing the default column value. Applicable for AVRO,PROTOBUF and JSON_SR Converters.
Value Converter Decimal Format: Specify the JSON/JSON_SR serialization format for Connect DECIMAL logical type values with two allowed literals: BASE64 to serialize DECIMAL logical types as base64 encoded binary data and NUMERIC to serialize Connect DECIMAL logical type values in JSON/JSON_SR as a number representing the decimal value.
Key Converter Schema ID Serializer: The class name of the schema ID serializer for keys. This is used to serialize schema IDs in the message headers.
Value Converter Connect Meta Data: Allow the Connect converter to add its metadata to the output schema. Applicable for Avro Converters.
Value Converter Value Subject Name Strategy: Determines how to construct the subject name under which the value schema is registered with Schema Registry.
Key Converter Key Subject Name Strategy: How to construct the subject name for key schema registration.
Value Converter Schema ID Serializer: The class name of the schema ID serializer for values. This is used to serialize schema IDs in the message headers.
Auto-restart policy
Enable Connector Auto-restart: Control the auto-restart behavior of the connector and its task in the event of user-actionable errors. Defaults to
true, enabling the connector to automatically restart in case of user-actionable errors. Set this property tofalseto disable auto-restart for failed connectors. In such cases, you would need to manually restart the connector.
Connection details
Poll wait time (ms): The amount of time to wait before checking for new results on the change stream.
Maximum documents to include in a batch: The maximum number of change stream documents to include in a single batch when polling for new data.
Pipeline: An array of JSON objects describing the pipeline operations to filter or modify the change events output.
Startup mode: Specifies how the connector starts up when there is no source offset available. If no source offset is available, the connector may either ignore all or some of the existing source data, or it may first copy all existing source data and then continue processing new data. When set to
latest(the default), the connector ignores all existing source data. If set totimestamp, the connector actuates startup.mode.timestamp.* properties. If no properties are configured,timestampis equivalent tolatest. If set tocopy_existing, the connector copies all existing source data to Change Stream events. This setting is equivalent to the deprecated settingcopy.existing=true.Copy existing namespace regex: Regular expression that matches the namespaces (
databaseName.collectionName) from which to copy data.Copy existing pipeline: An array of JSON objects describing the pipeline operations to run when copying existing data. It will only be applied for existing documents which are being copied.
Start timestamp: Actuated only if
startup.mode=timestamp. Specifies the starting point for the change stream. Accepted values can be an integer number of seconds since the Epoch in decimal format (for example,30), or an instant in the ISO-8601 format with one second precision (for example,1970-01-01T00:00:30Z), or a BSON Timestamp in the canonical extended JSON (v2) format (for example,{"$timestamp": {"t": 30,"i": 0}}).Cursor batch size: The number of documents to return in a batch. The value defaults to
0. The maximum cursor batch size is50.Output Schema Key: The Avro schema definition for the key value of the SourceRecord.
Output Schema Value: The Avro schema definition for the value of the SourceRecord.
Error handling
Heartbeat interval: The number of milliseconds the connector waits between sending heartbeat messages.
Heartbeat topic name: The name of the topic on which the connector should publish heartbeat messages. You must provide a positive value in the
heartbeat.interval.mssetting to enable this feature.Remove field on schema mismatch: If true, remove fields from the document that are not present in the schema. Otherwise, throw an error or send the documents to the DLQ depending on the value of errors.tolerance being set to ALL or NONE respectively.
Offset partition name: The custom offset partition name to use. Use this option to instruct the connector to start a new change stream when an existing offset contains an invalid resume token. If you leave this setting blank, the connector uses the default partition name from the connection details.
Error handling Mongo
Error tolerance: Allows you to customize how the connector handles errors. By default, this is set to
NONEand the connector handles errors using the error handling tolerance configured for the Connect framework.Output errors: Whether or not the connector sends output conversion errors to the dead letter queue (DLQ). When using a schema, this prevents unprocessable (poison) messages from causing the connector task to fail. The connector outputs messages to the DLQ as extended JSON for the specified topic. Enabling this property requires that the Error tolerance property be set to
all. By default, the connector does not output messages to the DLQ.
Server API
Server API version: The MongoDB server API version to use. This property is disabled by default.
Deprecation errors: Whether or not to require the connector to report the use of deprecated server APIs as errors. This property is disabled by default.
Strict: Sets whether the application requires strict server API version enforcement.
Producer configuration
Producer linger(ms): Artificial delay for records to be sent together.
Producer batch size(bytes): Record batch size in bytes.
Transforms
Single Message Transforms: To add a new SMT, see Add transforms. For more information about unsupported SMTs, see Unsupported transformations.
Processing position
Set offsets: Click Set offsets to define a specific offset for this connector to begin procession data from. For more information on managing offsets, see Manage offsets.
For all property values and definitions, see Configuration Properties.
Click Continue.
The connector supports running a single task.
Click Continue.
Verify the connection details by previewing the running configuration.
Tip
For information about previewing your connector output, see Data Previews for Confluent Cloud Connectors.
After you’ve validated that the properties are configured to your satisfaction, click Launch.
The status for the connector should go from Provisioning to Running.
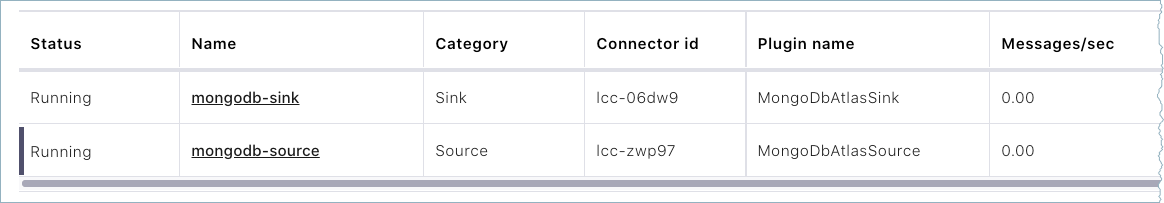
Step 5: Check the Kafka topic
After the connector is running, verify that MongoDB documents are populating the Kafka topic. If the config startup.mode=copy_existing and the connector restarts due to any reason, you may see duplicate records in the topic.
For more information and examples to use with the Confluent Cloud API for Connect, see the Confluent Cloud API for Connect Usage Examples section.
Using the Confluent CLI
Complete the following steps to set up and run the connector using the Confluent CLI.
Note
Make sure you have all your prerequisites completed.
Step 1: List the available connectors
Enter the following command to list available connectors:
confluent connect plugin list
Step 2: List the connector configuration properties
Enter the following command to show the connector configuration properties:
confluent connect plugin describe <connector-plugin-name>
The command output shows the required and optional configuration properties.
Step 3: Create the connector configuration file
Create a JSON file that contains the connector configuration properties. The following example shows the required connector properties.
{
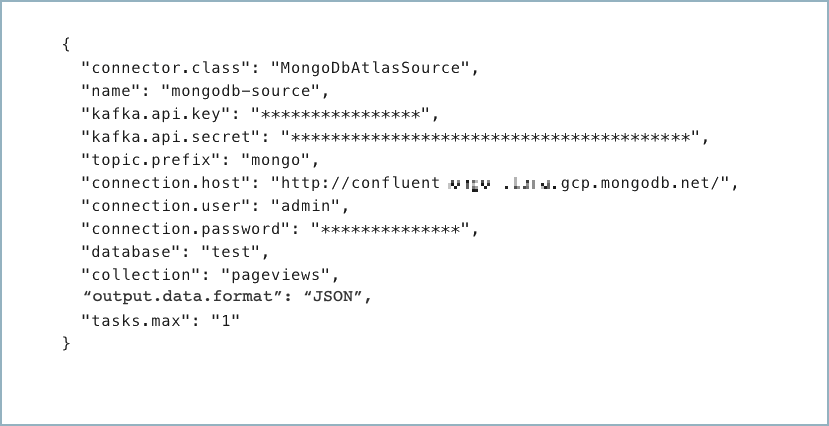
"connector.class": "MongoDbAtlasSource",
"name": "<my-connector-name>",
"kafka.auth.mode": "KAFKA_API_KEY",
"kafka.api.key": "<my-kafka-api-key>",
"kafka.api.secret": "<my-kafka-api-secret>",
"topic.prefix": "<topic-prefix>",
"connection.host": "<database-host-address>",
"connection.user": "<database-username>",
"connection.password": "<database-password>",
"database": "<database-name>",
"collection": "<database-collection-name>",
"poll.await.time.ms": "5000",
"poll.max.batch.size": "1000",
"startup.mode": "copy_existing",
"output.data.format": "JSON",
"tasks.max": "1"
}
Note the following property definitions:
"connector.class": Identifies the connector plugin name."name": Sets a name for your new connector.
"kafka.auth.mode": Identifies the connector authentication mode you want to use. There are two options:SERVICE_ACCOUNTorKAFKA_API_KEY(the default). To use an API key and secret, specify the configuration propertieskafka.api.keyandkafka.api.secret, as shown in the example configuration (above). To use a service account, specify the Resource ID in the propertykafka.service.account.id=<service-account-resource-ID>. To list the available service account resource IDs, use the following command:confluent iam service-account list
For example:
confluent iam service-account list Id | Resource ID | Name | Description +---------+-------------+-------------------+------------------- 123456 | sa-l1r23m | sa-1 | Service account 1 789101 | sa-l4d56p | sa-2 | Service account 2
(Optional)
"topic.prefix": Enter a topic prefix. The connector automatically creates Kafka topics using the naming convention:<prefix>.<database-name>.<collection-name>. The tables are created with the properties:topic.creation.default.partitions=1andtopic.creation.default.replication.factor=3. If you want to create topics with specific settings, create the topics before running this connector. Note the following:If you are configuring granular access using a service account, you must set up ACLs for the topic prefix.
If you are using a dedicated cluster and have a MongoDb document greater than 2MB in size, create the topic beforehand with property
max.message.bytesset to match the largest document size or greater than the largest document size (8388608 bytes maximum).
Important
If you are configuring granular access using a service account, and you leave the optional Topic prefix (
topic.prefix) configuration property empty, you must grant ACLCREATEandWRITEaccess to all the Kafka topics or create RBAC role bindings. To add ACLs, you use the (*) wildcard in the ACL entries as shown in the following examples.confluent kafka acl create --allow --service-account "<service-account-id>" --operation create --topic "*"
confluent kafka acl create --allow --service-account "<service-account-id>" --operation write --topic "*"
(Optional)
"topic.namespace.map": A JSON map that maps change stream document namespaces to topics. For example:{\"db\": \"dbTopic\", \"db.coll\": \"dbCollTopic\"}will map all change stream documents from thedbdatabase todbTopic.<collectionName>apart from any documents from thedb.collnamespace which map to thedbCollTopictopic. If you want to map all messages to a single topic use*. For example:{\"*\": \"everyThingTopic\", \"db.coll\": \"exceptionToTheRuleTopic\"}will map all change stream documents to theeveryThingTopicapart from thedb.collmessages. Note that any prefix configuration will still apply. If multiple collections with records having varying schema are mapped to a single topic with AVRO, JSON_SR, and PROTOBUF, then multiple schemas will be registered under a single subject name. If these schemas are not backward compatible to each other, the connector will fail until you change the schema compatibility in Confluent Cloud Schema Registry."connection.host": The MongoDB host with connection string options. Use a hostname address and not a full URL. For example, usecluster4-r5q3r7.gcp.mongodb.net/?readPreference=secondaryfor MONGODB_ATLAS and54.190.171.123:27017/?authSource=adminfor MONGODB_SELF_MANAGED.
Note
The connector does not support following connection string options in
connection.hostconfig:tlsCertificateKeyFile,tlsCertificateKeyFilePassword,tlsCAFile,tlsAllowInvalidCertificates,tlsInsecure,tlsAllowInvalidHostnames,authMechanism,authMechanismProperties,gssapiServiceName.Other options like
readPreference,readConcernLevel, orwdefined in MongoDB Connection String Options can be configured inconnection.hostconfiguration. For example,cluster4-r5q3r7.gcp.mongodb.net/?readPreference=secondary&readConcernLevel=local&appName=test&w=majority.- The connector supports connecting to self-managed MongoDB database.
Use
mongodb.instance.typeas MONGODB_SELF_MANAGED and specify theconnection.hostaccordingly to connect to self-managed instance. For example,54.190.171.123:27017/?authSource=admin.
(Optional)
"collection": The collection name. If the property is not used, all collections are watched in the supplied database.(Optional)
"poll.await.time.ms": The amount of time to wait before checking for new results in the change stream. If not used, this property defaults to 5000 ms (5 seconds).(Optional)
"poll.max.batch.size": The maximum number of change stream documents to include in a single batch when polling for new data. This setting can be used to limit the amount of data buffered internally in the connector. If not used, this property defaults to 100 records.(Optional)
"pipeline": An array of JSON objects that represents the pipeline operations to filter or modify the change stream output. For example:[{"$match": {"ns.coll": {"$regex": /^(collection1|collection2)$/}}}]sets the connector to listen to thecollection1andcollection2collections only. If not used, this property defaults to an empty array.(Optional)
"startup.mode": Specifies how the connector should start up when there is no source offset available. Resuming a change stream requires a resume token, which the connector gets from the source offset. If no source offset is available, the connector may either ignore all or some of the existing source data, or may at first copy all existing source data and then continue with processing new data. When set tolatest(default), the connector ignores all existing source data. If set totimestamp, the connector actuates startup.mode.timestamp.* properties. If no properties are configured,timestampis equivalent tolatest. Ifstartup.mode=copy_existing, the connector copies all existing source data to Change Stream events. This setting is equivalent to the deprecated settingcopy.existing=true.(Optional)
"startup.mode.timestamp.start.at.operation.time": Actuated only ifstartup.mode=timestamp. Specifies the starting point for the change stream. Accepted values can be an integer number of seconds since the Epoch in decimal format (for example,30), or an instant in the ISO-8601 format with one second precision (for example,1970-01-01T00:00:30Z), or a BSON Timestamp in the canonical extended JSON (v2) format (for example,{"$timestamp": {"t": 30, "i": 0}})(Optional)
"startup.mode.copy.existing.namespace.regex": Regex that matches the namespaces from which the existing documents are copied. A namespace is represented asdatabaseName.collectionName. For example,stats\.page.*matches all collections that start withpagein thestatsdatabase.(Optional)
"startup.mode.copy.existing.pipeline": An array of JSON objects that describes the pipeline operations to run when copying existing data. It is applied to existing documents that are being copied. If not used, this property defaults to an empty array.(Optional)
"publish.full.document.only": Set whether to return only thefullDocumentfield from the change stream event document produced by any update event. ThefullDocumentfield contains the most current version of the updated document. Sets thechange.stream.full.document=updateLookupsetting so updated documents will be included.Note
This automatic configuration only occurs at the time of connector creation. Changing this setting while the connector is already running will not retroactively apply or update the
change.stream.full.documentbehavior.(Optional)
"publish.full.document.only.tombstone.on.delete": When set totrue, the connector returns the tombstone events when documents are deleted. Tombstone events contain the keys of deleted documents with null values. This setting applies only whenpublish.full.document.onlyistrue.(Optional)
"change.stream.full.document": Determines what to return for update operations when using a Change Stream. Thedefaultsetting returns the differences between the original document and the updated document. When set toupdateLookupsetting returns the differences between the original document and updated document as well as a copy of the entire updated document at a point in time after the update. ThewhenAvailablesetting returns the updated document, if available. Therequiredsetting returns the updated document and raises an error if it is not available.(Optional)
"change.stream.full.document.before.change": Configures the document pre-image your change stream returns on update operations. Thedefaultsetting suppresses the document pre-image. When set towhenAvailablesetting returns the document pre-image if it’s available, before it was replaced, updated, or deleted. When set torequiredsetting returns the document pre-image and raises an error if it is not available."output.data.format": Sets the output Kafka record value format (data coming from the connector). Valid entries areAVRO,JSON_SR,PROTOBUF,JSON,STRINGorBSON. You must have Confluent Cloud Schema Registry configured if using a schema-based message format (for example, Avro, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or Protobuf).It chooses the appropriate converter and populates the derived settings
output.format.keyandoutput.format.valueaccording to the table shown below.output.data.formatConverter
output.format.keyoutput.format.valueAVROAvroConverter
schema
schema
JSON_SRJsonSchemaConverter
schema
schema
PROTOBUFProtobufConverter
schema
schema
JSONJsonConverter
schema
schema
STRINGStringConverter
json
json
BSONByteArrayConverter
bson
bson
If you select AVRO, be sure to set Compatibility mode (
schema.compatibility.level) toNONEin Schema Registry. Note that schemas are generated per document in isolation. If not set to NONE, there is a chance that the new schema generated for the new document will not be backward compatible with previous versions of the schema.(Optional)
"heartbeat.interval.ms": The number of milliseconds the connector waits between sending heartbeat messages. If not used, this property defaults to 0. Thus, no heartbeat message is sent by default. If set to a positive number, the connector sends heartbeat messages when source records are not published in the specified interval. This mechanism improves resumability of the connector for low volume namespaces. See the Invalid Resume Token page in MongoDb documentation for more information on this feature. When using SMTs, use predicates to prevent SMTs from processing the heartbeat messages. For example, if the heartbeat topic name is__mongodb_heartbeatsand the connector is writing the actual database records into topics that do not share common prefix with the heartbeat topic; use the following configuration to prevent heartbeat messages from being processed by the transform with an alias say,mongoTransform:"predicates": "isHeartbeatTopicPrefix","predicates.isHeartbeatTopicPrefix.type": "org.apache.kafka.connect.transforms.predicates.TopicNameMatches","predicates.isHeartbeatTopicPrefix.pattern": "__mongodb.*","transforms.mongoTransform.predicate": "isHeartbeatTopicPrefix","transforms.mongoTransform.negate": "true".(Optional)
"heartbeat.topic.name": The name of the topic on which the connector should publish heartbeat messages. You must provide a positive value in theheartbeat.interval.mssetting to enable this feature. If setting the heartbeat messages for multiple connectors, you must ensure that the heartbeat topic names for the connectors are unique. If not set, this defaults to__mongodb_heartbeats."tasks.max": The connector supports running a single task.
Single Message Transforms: See the Single Message Transforms (SMT) documentation for details about adding SMTs using the CLI.
See Configuration Properties for all property values and definitions.
Step 4: Load the properties file and create the connector
Enter the following command to load the configuration and start the connector:
confluent connect cluster create --config-file <file-name>.json
For example:
confluent connect cluster create --config-file mongo-db-source.json
Example output:
Created connector confluent-mongodb-source lcc-ix4dl
Step 5: Check the connector status
Enter the following command to check the connector status:
confluent connect cluster list
Example output:
ID | Name | Status | Type
+-----------+---------------------------+---------+-------+
lcc-ix4dl | confluent-mongodb-source | RUNNING | source
Step 6: Check the Kafka topic.
After the connector is running, verify that MongoDB documents are populating the Kafka topic. If the config startup.mode=copy_existing and the connector restarts due to any reason, you may see duplicate records in the topic.
For more information and examples to use with the Confluent Cloud API for Connect, see the Confluent Cloud API for Connect Usage Examples section.
Configuration Properties
Use the following configuration properties with the fully-managed connector. For self-managed connector property definitions and other details, see the connector docs in Self-managed connectors for Confluent Platform.
How should we connect to your data?
nameSets a name for your connector.
Type: string
Valid Values: A string at most 64 characters long
Importance: high
Kafka Cluster credentials
kafka.auth.modeKafka Authentication mode. It can be one of KAFKA_API_KEY or SERVICE_ACCOUNT. It defaults to KAFKA_API_KEY mode, whenever possible.
Type: string
Valid Values: SERVICE_ACCOUNT, KAFKA_API_KEY
Importance: high
kafka.api.keyKafka API Key. Required when kafka.auth.mode==KAFKA_API_KEY.
Type: password
Importance: high
kafka.service.account.idThe Service Account that will be used to generate the API keys to communicate with Kafka Cluster.
Type: string
Importance: high
kafka.api.secretSecret associated with Kafka API key. Required when kafka.auth.mode==KAFKA_API_KEY.
Type: password
Importance: high
Schema Config
schema.context.nameAdd a schema context name. A schema context represents an independent scope in Schema Registry. It is a separate sub-schema tied to topics in different Kafka clusters that share the same Schema Registry instance. If not used, the connector uses the default schema configured for Schema Registry in your Confluent Cloud environment.
Type: string
Default: default
Importance: medium
How do you want to name your topic(s)?
topic.prefixPrefix to prepend to table names to generate the name of the Apache Kafka® topic to publish data to.
Type: string
Importance: high
topic.namespace.mapJSON object that maps change stream document namespaces to topics. Any prefix configuration will still apply. In case multiple collections with records having varying schema are mapped to single topic with AVRO, JSON_SR, and PROTOBUF, then multiple schemas will be registered under single subject name. If these schemas are not backward compatible to each other, the connector will fail until you change the schema compatibility in Confluent Cloud Schema Registry.
Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: low
How should we connect to your MongoDB database?
mongodb.instance.typeSpecifies the type of MongoDB instance the connector will connect to.
Type: string
Default: MONGODB_ATLAS
Valid Values: MONGODB_ATLAS, MONGODB_SELF_MANAGED
Importance: high
mongodb.auth.mechanismChoose an authentication mechanism for MongoDB. Use SCRAM-SHA-256 for username/password authentication. Use MONGODB-X509 for certificate-based authentication. For MONGODB-X509, you must configure the SSL keystore properties.
Type: string
Default: SCRAM-SHA-256
Valid Values: MONGODB-X509, SCRAM-SHA-256
Importance: high
connection.hostFor MongoDB Atlas, provide the SRV connection host (e.g., mycluster.abc123.mongodb.net). For Self Managed MongoDB, provide the host and port in MongoDB URI format, e.g., host1:27017 or host1:27017/?replicaSet=myReplicaSet.
Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: high
connection.userMongoDB connection user.
Type: string
Importance: high
connection.passwordMongoDB connection password.
Type: password
Importance: high
connection.ssl.truststore.fileThe trust store file containing trusted certificates. Supported formats include JKS and PKCS12. If not set, the default Java trust store is used.
Type: password
Default: [hidden]
Importance: medium
connection.ssl.truststorePasswordThe password for the trust store file.
Type: password
Default: [hidden]
Importance: medium
connection.ssl.keystore.fileThe key store file containing the client certificate and private key for MONGODB-X509 authentication. Supported formats include JKS and PKCS12.
Type: password
Default: [hidden]
Importance: medium
connection.ssl.keystorePasswordThe password for the key store file. This is optional for the client and only needed if
connection.ssl.keystore.fileis configured.Type: password
Default: [hidden]
Importance: medium
databaseMongoDB database name.
Type: string
Importance: high
Database details
collectionMongoDB collection name.
Type: string
Importance: medium
Connection details
poll.await.time.msThe amount of time to wait before checking for new results on the change stream.
Type: int
Default: 5000 (5 seconds)
Valid Values: [1,…]
Importance: low
poll.max.batch.sizeMaximum number of change stream documents to include in a single batch when polling for new data. This setting can be used to limit the amount of data buffered internally in the connector.
Type: int
Default: 100
Valid Values: [1,…,1000]
Importance: low
pipelineAn array of JSON objects describing the pipeline operations to filter or modify the change events output. For example, [{“$match”: {“ns.coll”: {“$regex”: /^(collection1|collection2)$/}}}] will set your source connector to listen to the “collection1” and “collection2” collections only.
Type: string
Default: []
Importance: medium
startup.modeSpecifies how the connector should start up when there is no source offset available. If set to ‘latest’, the connector ignores all existing source data. If set to ‘timestamp’, the connector actuates startup.mode.timestamp.* properties. If no properties are configured, timestamp is equivalent to latest. If startup.mode=copy_existing, the connector copies all existing source data to Change Stream events.
Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: high
startup.mode.copy.existing.namespace.regexRegular expression that matches the namespaces (databaseName.collectionName) from which to copy data. For example, stats.page.* matches all collections that starts with “page” in “stats” database.
Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: medium
startup.mode.copy.existing.pipelineAn array of JSON objects describing the pipeline operations to run when copying existing data. It will only be applied for existing documents which are being copied.
Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: medium
startup.mode.timestamp.start.at.operation.timeActuated only if startup.mode=timestamp. Specifies the starting point for the change stream.
Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: medium
batch.sizeThe number of documents to return in a batch.
Type: int
Default: 0
Valid Values: […,50]
Importance: low
output.schema.keyThe Avro schema definition for the key value of the SourceRecord.
Type: string
Default: { “type”: “record”, “name”: “keySchema”, “fields”: [{ “name”: “_id”, “type”: “string”}]}
Valid Values: A string at most 100000 characters long
Importance: medium
output.schema.valueThe Avro schema definition for the value of the SourceRecord.
Type: string
Default: {“name”: “ChangeStream”, “type”: “record”, “fields”: [{“name”: “_id”, “type”: “string”}, {“name”: “operationType”, “type”: [“string”, “null”]}, {“name”: “fullDocumentBeforeChange”, “type”: [“string”, “null”]}, {“name”: “fullDocument”, “type”: [“string”, “null”]}, {“name”: “ns”, “type”: [{“name”: “ns”, “type”: “record”, “fields”: [{“name”: “db”, “type”: “string”}, {“name”: “coll”, “type”: [“string”, “null”]}]}, “null”]}, {“name”: “to”, “type”: [{“name”: “to”, “type”: “record”, “fields”: [{“name”: “db”, “type”: “string”}, {“name”: “coll”, “type”: [“string”, “null”]}]}, “null”]}, {“name”: “documentKey”, “type”: [“string”, “null”]}, {“name”: “updateDescription”, “type”: [{“name”: “updateDescription”, “type”: “record”, “fields”: [{“name”: “updatedFields”, “type”: [“string”, “null”]}, {“name”: “removedFields”, “type”: [{“type”: “array”, “items”: “string”}, “null”]}]}, “null”]}, {“name”: “clusterTime”, “type”: [“string”, “null”]}, {“name”: “txnNumber”, “type”: [“long”, “null”]}, {“name”: “lsid”, “type”: [{“name”: “lsid”, “type”: “record”, “fields”: [{“name”: “id”, “type”: “string”}, {“name”: “uid”, “type”: “string”}]}, “null”]}]}
Valid Values: A string at most 100000 characters long
Importance: medium
Producer configuration
linger.msArtificial delay for records to be sent together.
Type: long
Default: 0
Valid Values: [0,…,20000]
Importance: medium
producer.batch.sizeRecord batch size in bytes.
Type: int
Default: 16384
Valid Values: [0,…,491520]
Importance: medium
Output messages
output.data.formatSets the output Kafka record value format. Valid entries are AVRO, JSON_SR, PROTOBUF, JSON, STRING or BSON. Note that you need to have Confluent Cloud Schema Registry configured if using a schema-based message format like AVRO, JSON_SR, and PROTOBUF
Type: string
Default: STRING
Importance: high
output.key.formatSets the output Kafka record key format. Valid entries are AVRO, JSON_SR, PROTOBUF, STRING or JSON. Note that you need to have Confluent Cloud Schema Registry configured if using a schema-based message format like AVRO, JSON_SR, and PROTOBUF
Type: string
Default: STRING
Valid Values: AVRO, JSON, JSON_SR, PROTOBUF, STRING
Importance: high
publish.full.document.onlyOnly publish the changed document instead of the full change stream document. Sets the change.stream.full.document=updateLookup automatically so updated documents will be included.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: high
publish.full.document.only.tombstone.on.deleteReturn the tombstone events when documents are deleted. Tombstone events contain the keys of deleted documents with null values. This setting applies only when publish.full.document.only is true
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: high
change.stream.full.documentDetermines what to return for update operations when using a Change Stream. When set to ‘updateLookup’ setting returns the differences between the original document and updated document as well as a copy of the entire updated document at a point in time after the update. The ‘whenAvailable’ setting returns the updated document, if available. The ‘required’ setting returns the updated document and raises an error if it is not available.
Type: string
Default: default
Importance: high
change.stream.full.document.before.changeConfigures the document pre-image your change stream returns on update operations. When set to ‘whenAvailable’ setting returns the document pre-image if it’s available, before it was replaced, updated, or deleted. When set to ‘required’ setting returns the document pre-image and raises an error if it is not available.
Type: string
Default: default
Importance: high
change.stream.document.key.as.keyUse the document key as the source record key.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: medium
change.stream.show.expanded.eventsDetermines if change streams notifies for DDL events, such as
createIndexesanddropIndexesevents. This functionality is new in version 6.0. See MongoDB documentation for more details onshowExpandedEvents. This setting is required to showupdateDescription.disambiguatedPathsin update events, helping clarify changes that involve ambiguous fields. This specific feature is new in version 6.1. See MongoDB documentation for more details ondisambiguatedPaths.Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: medium
collationThe JSON representation of the collation options to use for the change stream. Use the
Collation.asDocument().toJson()to create the specific json representation.Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: high
output.json.formatThe output format of json strings can be configured to be either: DefaultJson: The legacy strict json formatter. ExtendedJson: The fully type safe extended json formatter. SimplifiedJson: Simplified Json, with ObjectId, Decimals, Dates and Binary values represented as strings. Users can provide their own implementation of the com.mongodb.kafka.connect.source.json.formatter.
Type: string
Default: DefaultJson
Importance: high
topic.separatorSeparator to use when joining prefix, database, collection, and suffix values. This generates the name of the Kafka topic to publish data to. Used by the ‘DefaultTopicMapper’.
Type: string
Default: .
Importance: low
topic.suffixSuffix to append to database and collection names to generate the name of the Kafka topic to publish data to.
Type: string
Importance: low
output.schema.infer.valueWhether the connector should infer the schema for the value document of the Source Record. Since the connector processes each document in isolation, the connector may generate many schemas. The connector only reads this setting when you set your ‘Output Kafka record value format’ setting to AVRO, JSON, JSON_SR and PROTOBUF.
Type: boolean
Default: true
Importance: low
Error handling
heartbeat.interval.msThe number of milliseconds the connector waits between sending heartbeat messages. The connector sends heartbeat messages when source records are not published in the specified interval. This mechanism improves resumability of the connector for low volume namespaces. When using SMTs, use predicates to prevent SMTs from processing the heartbeat messages. See connector documentation for more details.
Type: int
Default: 0
Importance: medium
heartbeat.topic.nameThe name of the topic on which the connector should publish heartbeat messages. You must provide a positive value in the “heartbeat.interval.ms” setting to enable this feature.
Type: string
Default: __mongodb_heartbeats
Importance: medium
remove.field.on.schema.mismatchIf true, remove fields from the document that are not present in the schema. Otherwise, throw an error or send the documents to the DLQ depending on the value of errors.tolerance being set to ALL or NONE respectively.
Type: boolean
Default: true
Importance: medium
mongo.errors.toleranceUse this property if you would like to configure the connector’s error handling behavior differently from the Connect framework’s.
Type: string
Default: NONE
Importance: medium
mongo.errors.deadletterqueue.topic.nameWhether to output conversion errors to the dead letter queue. Stops poison messages when using schemas, any message will be outputted as extended json on the specified topic. By default messages are not outputted to the dead letter queue. Also requires errors.tolerance=all.
Type: string
Importance: medium
offset.partition.nameThe custom offset partition name to use. You can use this option to instruct the connector to start a new change stream when an existing offset contains an invalid resume token. If you leave this setting blank, the connector uses the default partition name based on the connection details.
Type: string
Default: “”
Importance: medium
Server API
server.api.versionThe server API version to use. Disabled by default.
Type: string
Importance: low
server.api.deprecation.errorsSets whether the connector requires use of deprecated server APIs to be reported as errors.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
server.api.strictSets whether the application requires strict server API version enforcement.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
Number of tasks for this connector
tasks.maxMaximum number of tasks for the connector.
Type: int
Valid Values: [1,…,1]
Importance: high
Additional Configs
header.converterThe converter class for the headers. This is used to serialize and deserialize the headers of the messages.
Type: string
Importance: low
producer.override.compression.typeThe compression type for all data generated by the producer. Valid values are none, gzip, snappy, lz4, and zstd.
Type: string
Importance: low
producer.override.linger.msThe producer groups together any records that arrive in between request transmissions into a single batched request. More details can be found in the documentation: https://docs.confluent.io/platform/current/installation/configuration/producer-configs.html#linger-ms.
Type: long
Valid Values: [100,…,1000]
Importance: low
value.converter.allow.optional.map.keysAllow optional string map key when converting from Connect Schema to Avro Schema. Applicable for Avro Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.auto.register.schemasSpecify if the Serializer should attempt to register the Schema.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.connect.meta.dataAllow the Connect converter to add its metadata to the output schema. Applicable for Avro Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.enhanced.avro.schema.supportEnable enhanced schema support to preserve package information and Enums. Applicable for Avro Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.enhanced.protobuf.schema.supportEnable enhanced schema support to preserve package information. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.flatten.unionsWhether to flatten unions (oneofs). Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.generate.index.for.unionsWhether to generate an index suffix for unions. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.generate.struct.for.nullsWhether to generate a struct variable for null values. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.int.for.enumsWhether to represent enums as integers. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.latest.compatibility.strictVerify latest subject version is backward compatible when use.latest.version is true.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.object.additional.propertiesWhether to allow additional properties for object schemas. Applicable for JSON_SR Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.optional.for.nullablesWhether nullable fields should be specified with an optional label. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.optional.for.proto2Whether proto2 optionals are supported. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.scrub.invalid.namesWhether to scrub invalid names by replacing invalid characters with valid characters. Applicable for Avro and Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.use.latest.versionUse latest version of schema in subject for serialization when auto.register.schemas is false.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.use.optional.for.nonrequiredWhether to set non-required properties to be optional. Applicable for JSON_SR Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.wrapper.for.nullablesWhether nullable fields should use primitive wrapper messages. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
value.converter.wrapper.for.raw.primitivesWhether a wrapper message should be interpreted as a raw primitive at root level. Applicable for Protobuf Converters.
Type: boolean
Importance: low
errors.toleranceUse this property if you would like to configure the connector’s error handling behavior. WARNING: This property should be used with CAUTION for SOURCE CONNECTORS as it may lead to dataloss. If you set this property to ‘all’, the connector will not fail on errant records, but will instead log them (and send to DLQ for Sink Connectors) and continue processing. If you set this property to ‘none’, the connector task will fail on errant records.
Type: string
Default: none
Importance: low
key.converter.key.schema.id.serializerThe class name of the schema ID serializer for keys. This is used to serialize schema IDs in the message headers.
Type: string
Default: io.confluent.kafka.serializers.schema.id.PrefixSchemaIdSerializer
Importance: low
key.converter.key.subject.name.strategyHow to construct the subject name for key schema registration.
Type: string
Default: TopicNameStrategy
Importance: low
key.converter.replace.null.with.defaultWhether to replace fields that have a default value and that are null to the default value. When set to true, the default value is used, otherwise null is used. Applicable for JSON Key Converter.
Type: boolean
Default: true
Importance: low
key.converter.schemas.enableInclude schemas within each of the serialized keys. Input message keys must contain schema and payload fields and may not contain additional fields. For plain JSON data, set this to false. Applicable for JSON Key Converter.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
value.converter.decimal.formatSpecify the JSON/JSON_SR serialization format for Connect DECIMAL logical type values with two allowed literals:
BASE64 to serialize DECIMAL logical types as base64 encoded binary data and
NUMERIC to serialize Connect DECIMAL logical type values in JSON/JSON_SR as a number representing the decimal value.
Type: string
Default: BASE64
Importance: low
value.converter.flatten.singleton.unionsWhether to flatten singleton unions. Applicable for Avro and JSON_SR Converters.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
value.converter.ignore.default.for.nullablesWhen set to true, this property ensures that the corresponding record in Kafka is NULL, instead of showing the default column value. Applicable for AVRO,PROTOBUF and JSON_SR Converters.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
value.converter.reference.subject.name.strategySet the subject reference name strategy for value. Valid entries are DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy or QualifiedReferenceSubjectNameStrategy. Note that the subject reference name strategy can be selected only for PROTOBUF format with the default strategy being DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy.
Type: string
Default: DefaultReferenceSubjectNameStrategy
Importance: low
value.converter.replace.null.with.defaultWhether to replace fields that have a default value and that are null to the default value. When set to true, the default value is used, otherwise null is used. Applicable for JSON Converter.
Type: boolean
Default: true
Importance: low
value.converter.schemas.enableInclude schemas within each of the serialized values. Input messages must contain schema and payload fields and may not contain additional fields. For plain JSON data, set this to false. Applicable for JSON Converter.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Importance: low
value.converter.value.schema.id.serializerThe class name of the schema ID serializer for values. This is used to serialize schema IDs in the message headers.
Type: string
Default: io.confluent.kafka.serializers.schema.id.PrefixSchemaIdSerializer
Importance: low
value.converter.value.subject.name.strategyDetermines how to construct the subject name under which the value schema is registered with Schema Registry.
Type: string
Default: TopicNameStrategy
Importance: low
Auto-restart policy
auto.restart.on.user.errorEnable connector to automatically restart on user-actionable errors.
Type: boolean
Default: true
Importance: medium
Suggested Reading
Blog post: Using the Fully Managed MongoDB Atlas Connector in a Secure Environment
Blog post: Announcing the MongoDB Atlas Sink and Source connectors in Confluent Cloud
Next Steps
For an example that shows fully-managed Confluent Cloud connectors in action with Confluent Cloud for Apache Flink, see the Cloud ETL Demo. This example also shows how to use Confluent CLI to manage your resources in Confluent Cloud.